|
Blood In Stool
Blood in stool looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically originating from upper gastrointestinal bleeding; or to hematochezia, with a red color, typically originating from lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Evaluation of the blood found in stool depends on its characteristics, in terms of color, quantity and other features, which can point to its source, however, more serious conditions can present with a mixed picture, or with the form of bleeding that is found in another section of the tract. The term "blood in stool" is usually only used to describe visible blood, and not fecal occult blood, which is found only after physical examination and chemical laboratory testing. In infants, the Apt test can be used to distinguish fetal hemoglobin from maternal blood based on the differences in composition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''oesophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, “I carry”) + ἔφαγον (éphagon, “I ate”). The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epithel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation, also known as ruptured bowel, is a hole in the wall of part of the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain and tenderness. When the hole is in the stomach or early part of the small intestine, the onset of pain is typically sudden while with a hole in the large intestine onset may be more gradual. The pain is usually constant in nature. Sepsis, with an increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, fever, and confusion may occur. The cause can include trauma such as from a knife wound, eating a sharp object, or a medical procedure such as colonoscopy, bowel obstruction such as from a volvulus, colon cancer, or diverticulitis, stomach ulcers, ischemic bowel, and a number of infections including '' C. difficile''. A hole allows intestinal contents to enter the abdominal cavity. The entry of bacteria results in a condition kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is the condition of having multiple pouches (diverticulum, diverticula) in the colon (anatomy), colon that are not inflamed. These are outpockets of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through weaknesses of muscle layers in the colon wall. Diverticula do not cause symptoms in most people. Diverticular disease occurs when diverticula become clinically inflamed, a condition known as diverticulitis. Diverticula typically occur in the sigmoid colon, which is commonplace for increased pressure. The left side of the colon is more commonly affected in the United States while the right side is more commonly affected in Asia. Diagnosis is often during routine colonoscopy or as an incidental finding during CT scan. It is common in Western countries with about half of those over the age of 60 affected in Canada and the United States. Diverticula are uncommon before the age of 40, and increase in incidence beyond that age. Rates are lower in Africa; the reasons for this rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdominal pain of sudden onset, but the onset may also occur over a few days. There may also be nausea; and diarrhea or constipation. Fever or blood in the stool suggests a complication. Repeated attacks may occur. The causes of diverticulitis are unclear. Risk factors may include obesity, lack of exercise, smoking, a family history of the disease, and use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The role of a low fiber diet as a risk factor is unclear. Having pouches in the large intestine that are not inflamed is known as diverticulosis. Inflammation occurs in between 10% and 25% at some point in time, and is due to a bacterial infection. Diagnosis is typically by CT scan, though blood tests, colonoscopy, or a lower gastrointestinal se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their initial introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, which are involved in blood clotting. There are two general types of NSAIDs available: non-selective, and COX-2 selective. Most N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
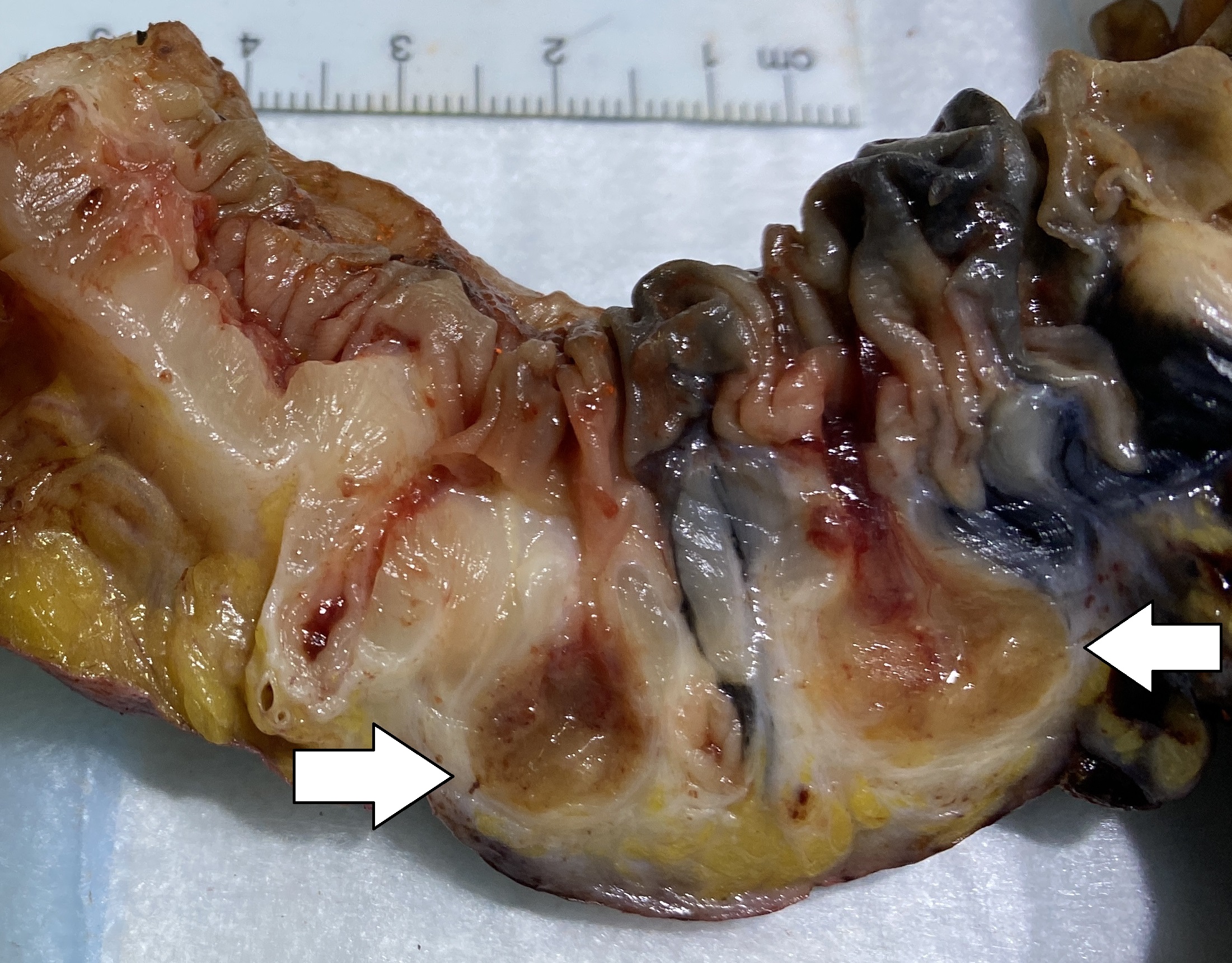
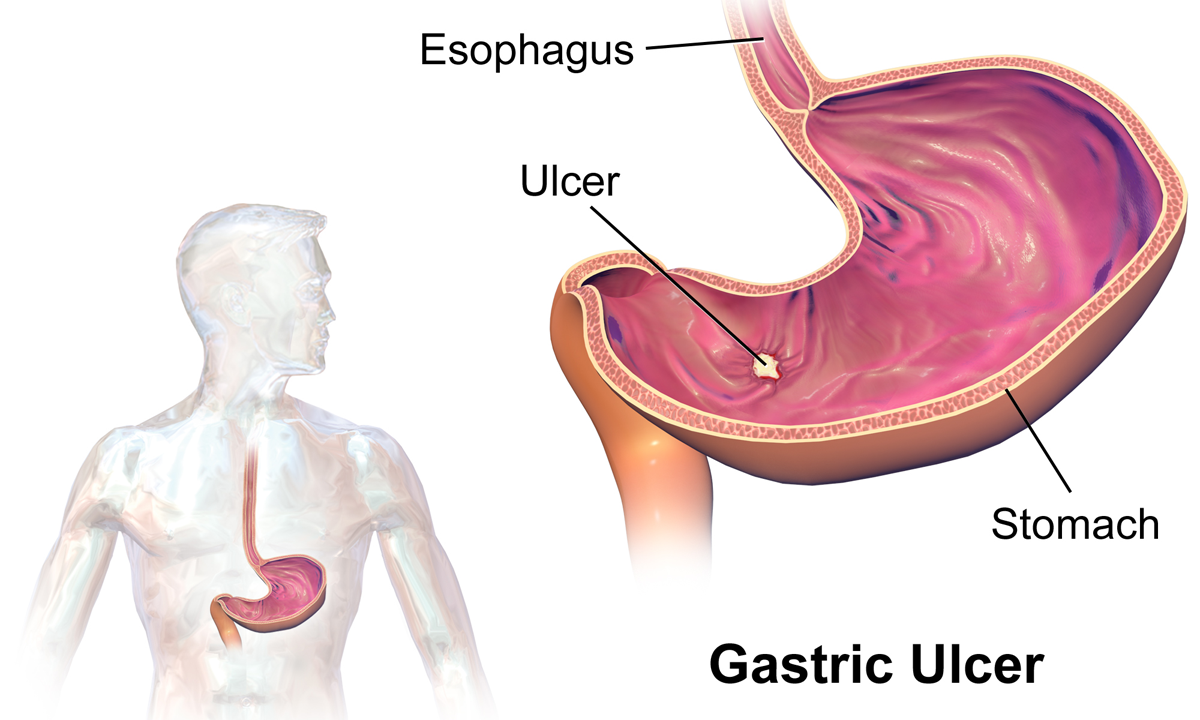
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement. Complications from constipation may include hemorrhoids, anal fissure or fecal impaction. The normal frequency of bowel movements in adults is between three per day and three per week. Babies often have three to four bowel movements per day while young children typically have two to three per day. Constipation has many causes. Common causes include slow movement of stool within the colon, irritable bowel syndrome, and pelvic floor disorders. Underlying associated diseases include hypothyroidism, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, colon cancer, diverticulitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Medications associated with constipation include opioids, certain antacids, calcium channel blockers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring (the level of the puborectalis sling) or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin ''Wikt:rectum, rectum Wikt:intestinum, intestinum'', meaning ''straight intestine''. Structure The rectum is a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The most common cause is infection by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |