|
Block (telecommunications)
In telecommunications a block is one of: * A group of bits or digits that is transmitted as a unit and that may be encoded for error-control purposes. * A string of records, words, or characters, that for technical or logical purposes are treated as a unit. Blocks (a) are separated by interblock gaps, (b) are delimited by an end-of-block signal, and (c) may contain one or more records. A block is usually subjected to some type of block processing, such as multidimensional parity checking, associated with it. A block transfer attempt is a coordinated sequence of user and telecommunication system activities undertaken to effect transfer of an individual block from a source user to a destination user. A block transfer attempt begins when the first bit of the block crosses the functional interface between the source user and the telecommunication system. A block transfer attempt ends either in ''successful block transfer'' or in ''block transfer failure''. Successful block transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error
An error (from the Latin ''error'', meaning "wandering") is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect. In some usages, an error is synonymous with a mistake. The etymology derives from the Latin term 'errare', meaning 'to stray'. In statistics, "error" refers to the difference between the value which has been computed and the correct value. An error could result in failure or in a deviation from the intended performance or behavior. Human behavior One reference differentiates between "error" and "mistake" as follows: In human behavior the norms or expectations for behavior or its consequences can be derived from the intention of the actor or from the expectations of other individuals or from a social grouping or from social norms. (See deviance.) Gaffes and faux pas can be labels for certain instances of this kind of error. More serious departures from social norms carry labels such as misbehavior and labels from the legal system, such as misdemeanor and crime. Departures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
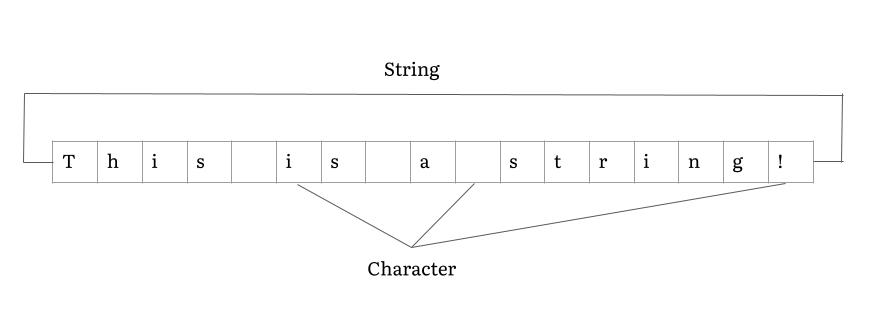
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parity Bit
A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code. Parity bits are a simple form of error detecting code. Parity bits are generally applied to the smallest units of a communication protocol, typically 8-bit octets (bytes), although they can also be applied separately to an entire message string of bits. The parity bit ensures that the total number of 1-bits in the string is even or odd. Accordingly, there are two variants of parity bits: even parity bit and odd parity bit. In the case of even parity, for a given set of bits, the bits whose value is 1 are counted. If that count is odd, the parity bit value is set to 1, making the total count of occurrences of 1s in the whole set (including the parity bit) an even number. If the count of 1s in a given set of bits is already even, the parity bit's value is 0. In the case of odd parity, the coding is reversed. For a given set of bits, if the count of bits with a value of 1 is even, the parity bit value is se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User (telecommunications)
In telecommunications, a user is a person, organization, or other entity that employs the services provided by a telecommunication system, or by an information processing system, for transfer of information. A user functions as a source or final destination of user information, or both. A user ''may'' also be the subscriber, i.e. the customer paying for the service. User is also a person or process accessing an AIS by direct connections (e.g., via terminals) or indirect connections. "Indirect connection" relates to persons who prepare input data or receive output that is not reviewed for content or classification by a responsible individual. Sources * {{FS1037C MS188 * National Information Systems Security Glossary See also * User (computing) A user is a person who utilizes a computer or network service. A user often has a user account and is identified to the system by a username (or user name). Other terms for username include login name, screenname (or screen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Standard 1037C
Federal Standard 1037C, titled Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunication Terms, is a United States Federal Standard issued by the General Services Administration pursuant to the Federal Property and Administrative Services Act of 1949, as amended. This document provides federal departments and agencies a comprehensive source of definitions of terms used in telecommunications and directly related fields by international and U.S. government telecommunications specialists. As a publication of the U.S. government, prepared by an agency of the U.S. government, it appears to be mostly available as a public domain resource, but a few items are derived from copyrighted sources: where this is the case, there is an attribution to the source. This standard was superseded in 2001 by American National Standard T1.523-2001, Telecom Glossary 2000, which is published by ATIS. The old standard is still frequently used, because the new standard is protected by copyright, as usual for A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIL-STD-188
MIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications. Purpose Faced with "past technical deficiencies in telecommunications systems and equipment and software…that were traced to basic inadequacies in the application of telecommunication standards and to the lack of a well defined…program for their review, control and implementation", the U.S. Department of Defense looked to develop a series of standards that would alleviate the problem. By 1988, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) issued Instruction 4630.8 (reissued in 1992, 2002, 2004) stating its policy that "all forces for joint and combined operations be supported through compatible, interoperable, and integrated Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence systems. … nd that all suchsystems developed for use by U.S. forces are considered to be for joint use." To achieve this the director of the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) is charged with "developing information techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block (data Storage)
In computing (specifically data transmission and data storage), a block, sometimes called a physical record, is a sequence of bytes or bits, usually containing some whole number of records, having a maximum length; a ''block size''. Data thus structured are said to be ''blocked''. The process of putting data into blocks is called ''blocking'', while ''deblocking'' is the process of extracting data from blocks. Blocked data is normally stored in a data buffer, and read or written a whole block at a time. Blocking reduces the overhead and speeds up the handling of the data stream. For some devices, such as magnetic tape and CKD disk devices, blocking reduces the amount of external storage required for the data. Blocking is almost universally employed when storing data to 9-track magnetic tape, NAND flash memory, and rotating media such as floppy disks, hard disks, and optical discs. Most file systems are based on a block device, which is a level of abstraction for the hardwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |