|
Bliss Alley
BLISS is a system programming language developed at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) by W. A. Wulf, D. B. Russell, and A. N. Habermann around 1970. It was perhaps the best known system language until C debuted a few years later. Since then, C became popular and common, and BLISS faded into obscurity. When C was in its infancy, a few projects within Bell Labs debated the merits of BLISS vs. C. BLISS is a typeless block-structured programming language based on expressions rather than statements, and includes constructs for exception handling, coroutines, and macros. It does not include a goto statement. The name is variously said to be short for ''Basic Language for Implementation of System Software'' or ''System Software Implementation Language, Backwards''. It was sometimes called "Bill's Language for Implementing System Software", after Bill Wulf. The original Carnegie Mellon compiler was notable for its extensive use of optimizations, and formed the basis of the classic bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
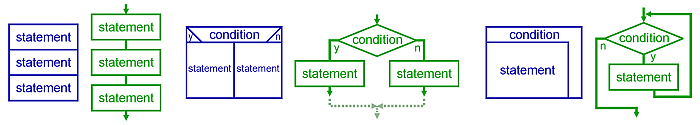
Structured Programming
Structured programming is a programming paradigm aimed at improving the clarity, quality, and development time of a computer program by making extensive use of the structured control flow constructs of selection ( if/then/else) and repetition ( while and for), block structures, and subroutines. It emerged in the late 1950s with the appearance of the ALGOL 58 and ALGOL 60 programming languages, with the latter including support for block structures. Contributing factors to its popularity and widespread acceptance, at first in academia and later among practitioners, include the discovery of what is now known as the structured program theorem in 1966, and the publication of the influential "Go To Statement Considered Harmful" open letter in 1968 by Dutch computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra, who coined the term "structured programming". Structured programming is most frequently used with deviations that allow for clearer programs in some particular cases, such as when exceptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALGOL
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in textbooks and academic sources for more than thirty years. In the sense that the syntax of most modern languages is "Algol-like", it was arguably more influential than three other high-level programming languages among which it was roughly contemporary: FORTRAN, Lisp, and COBOL. It was designed to avoid some of the perceived problems with FORTRAN and eventually gave rise to many other programming languages, including PL/I, Simula, BCPL, B, Pascal, and C. ALGOL introduced code blocks and the begin...end pairs for delimiting them. It was also the first language implementing nested function definitions with lexical scope. Moreover, it was the first programming language which gave detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Design Of An Optimizing Compiler
''The Design of an Optimizing Compiler'' (Elsevier Science Ltd, 1980, ), by William Wulf, Richard K. Johnson, Charles B. Weinstock, Steven O. Hobbs, and Charles Geschke, Charles M. Geschke, was published in 1975 by Elsevier. It describes the BLISS optimizing compiler for the PDP-11, written at Carnegie Mellon University in the early 1970s. The compiler ran on a PDP-10 and was one of the first to produce well-optimized code for a minicomputer. Because of its elegant design and the quality of the generated code, the compiler and book remain classics in the compiler field. Although the original book has been out of print for many years, a print on demand version remains available from University Microfilms International. Reception ''Software: Practice and Experience'' said compiling experts would benefit the most with ''The Design of an Optimizing Compiler''. References External links''The Design of an Optimizing Compiler'' - Online version at CMU Computer programming books C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |