|
Blanco Fracture Zone
The Blanco Fracture Zone or Blanco Transform Fault Zone (BTFZ) is a right lateral transform fault zone, which runs northwest off the coast of Oregon in the Pacific Northwest of the United States, extending from the Gorda Ridge in the south to the Juan de Fuca Ridge in the north. Morphology The Blanco Transform Fault Zone is an approximately 350 km long zone that varies in width between 20 and 75 km. The Blanco Fracture Zone starts about 150 km off Cape Blanco, and extends northwest to about 500 km off of Newport. It consists of a series of deep basins interrupted by transform faults. The western part of the fracture zone, from the Cascadia Depression to the Juan de Fuca Ridge, moves at 1.4 cm/a; the eastern segment, from the Cascadia Depression to the Gorda Ridge moves at 3.9 cm/a. The whole zone averages a slip rate of 2.0 cm/a. Through it, Cascadia Channel passes. Eastern segment The principal feature of the eastern portion of the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
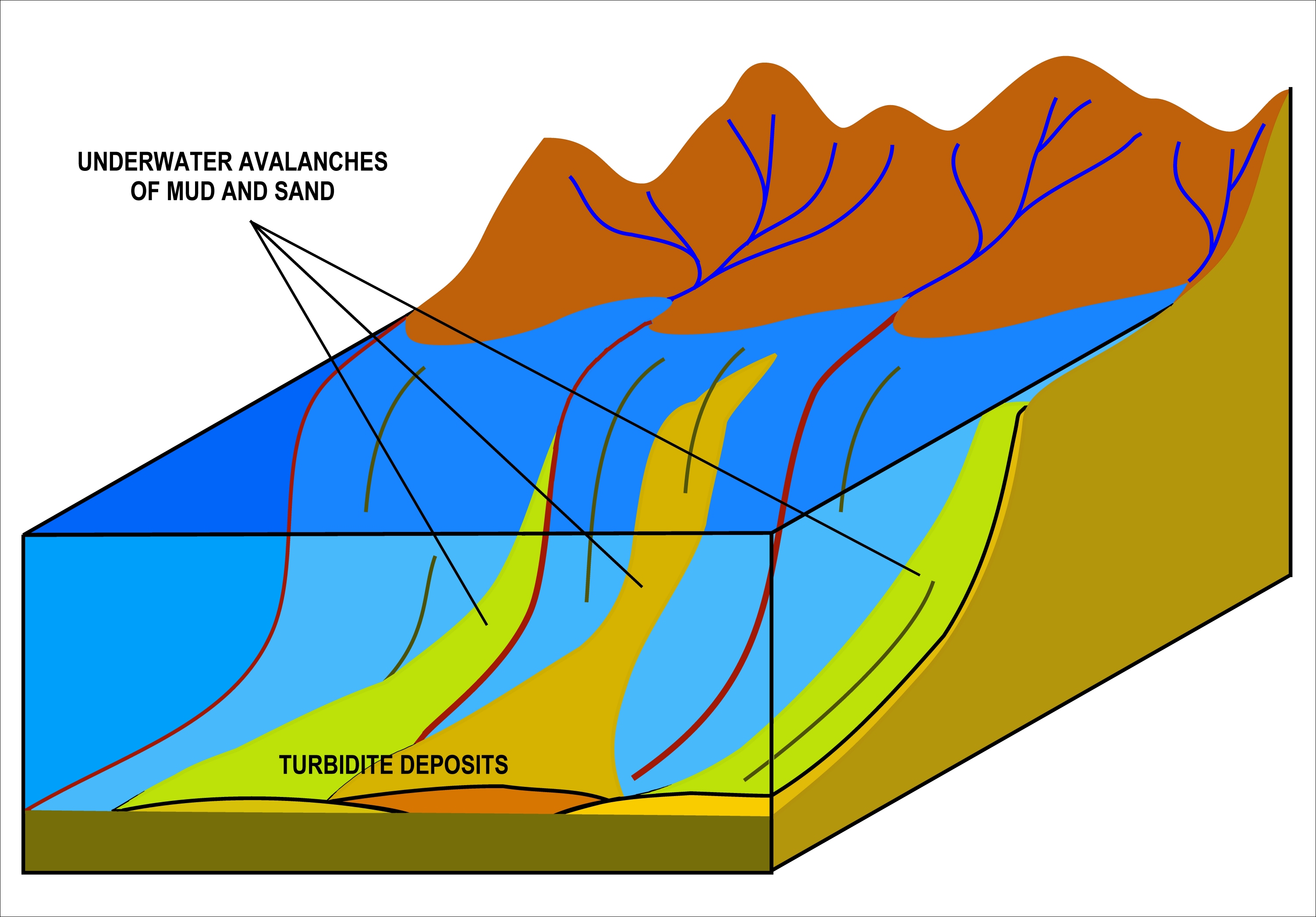
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendocino Fracture Zone
The Mendocino Fracture Zone is a fracture zone and transform boundary over 4000 km (2500 miles) long, starting off the coast of Cape Mendocino in far northern California. It runs westward from a triple junction with the San Andreas Fault and the Cascadia subduction zone to the southern end of the Gorda Ridge. It continues on west of its junction with the Gorda Ridge, as an inactive remnant section which extends for several hundred miles. Technically, a fracture zone is not a transform fault, but in the case of the Mendocino, the term has been loosely applied to the active fault segment east of the Gorda Ridge as well as to the true fracture zone segment west of it. Many seismologists refer to the active segment as the Mendocino Fault or Mendocino fault zone. The fault section demarcates the boundary between the northwestward-moving Pacific Plate and the eastward-moving Gorda Plate. The Gorda Plate is subducting beneath the North American Plate just offshore of Cape Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Pacific Northwest
The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition (including rock, minerals, and soils), structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides. The geology of the Pacific Northwest is vast and complex. Most of the region began forming about 200 million years ago as the North American Plate started to drift westward during the rifting of Pangaea. Since that date, the western edge of North America has grown westward as a succession of island arcs and assorted ocean-floor rocks have been added along the continental margin. There are at least five geologic provinces in the area: the Cascade Volcanoes, the Columbia Plateau, the North Cascades, the Coast Mountains, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astoria Fan
The Astoria Fan is a submarine fan. It has sediment, radiating asymmetrically southward from the mouth of the Astoria Canyon. From Astoria Canyon's mouth, the fan extends about to its western end, which is the Cascadia Channel. The fan proper ends south of the canyon mouth, although its depositional basin extends southward another to the Blanco Fracture Zone. Astoria Fan is generally asymmetrical. It extends roughly west of the mouth of Astoria Canyon, and about north, to Willapa Channel. Others trace different dimensions. Headed west, the fan crosses the continental shelf, trending sinuously down to the base of the continental slope. Near Astoria Canyon, it is at a depth of . The fan is approximately long. It varies in width from to . It has numerous tributaries. The fan extends about to its western boundary, which is the Cascadia Channel. Ash from the eruption of Mount Mazama has been found, in Astoria Fan. It may have been cut in the Pleistocene. It appears the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richter Magnitude Scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper, where he called it the "magnitude scale". This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale, denoted as ML or . Because of various shortcomings of the original scale, most seismological authorities now use other similar scales such as the moment magnitude scale () to report earthquake magnitudes, but much of the news media still erroneously refers to these as "Richter" magnitudes. All magnitude scales retain the logarithmic character of the original and are scaled to have roughly comparable numeric values (typically in the middle of the scale). Due to the variance in earthquakes, it is essential to understand the Richter scale uses logarithms simply to make the measurements manageable (i.e., a magnitude 3 quake factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Swarm
In seismology, an earthquake swarm is a sequence of seismic events occurring in a local area within a relatively short period. The time span used to define a swarm varies, but may be days, months, or years. Such an energy release is different from the situation when a major earthquake (main shock) is followed by a series of aftershocks: in earthquake swarms, no single earthquake in the sequence is obviously the main shock. In particular, a cluster of aftershocks occurring after a mainshock ''is not'' a swarm. History and generalities In the Ore Mountains (Erzgebirge), which form the border between the Czech Republic and Germany, western Bohemia and the Vogtland region, have been known since the 16th century as prone to frequent earthquake swarms, which typically last a few weeks to a few months. Austrian geologist Josef Knett, while studying in 1899 a swarm of about a hundred events felt in western Bohemia/Vogtland in January-February 1824, coined the noun ''Schwarmbeben'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Tectonics
Strike-slip tectonics or wrench tectonics is the type of tectonics that is dominated by lateral (horizontal) movements within the Earth's crust (and lithosphere). Where a zone of strike-slip tectonics forms the boundary between two tectonic plates, this is known as a transform or conservative plate boundary. Areas of strike-slip tectonics are characterised by particular deformation styles including: ''stepovers'', ''Riedel shears'', ''flower structures'' and ''strike-slip duplexes''. Where the displacement along a zone of strike-slip deviates from parallelism with the zone itself, the style becomes either transpressional or transtensional depending on the sense of deviation. Strike-slip tectonics is characteristic of several geological environments, including oceanic and continental transform faults, zones of oblique collision and the deforming foreland of zones of continental collision. Deformation styles Stepovers When strike-slip fault zones develop, they typically form as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
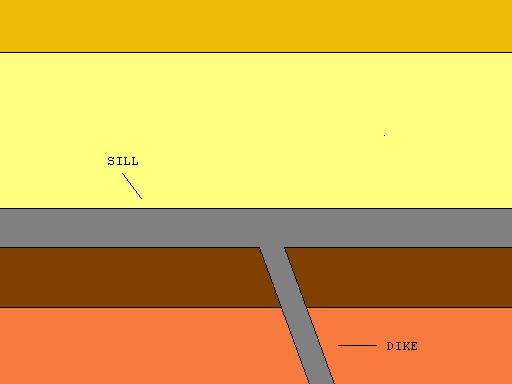
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A ''sill'' is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that a sill does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex . and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existing bedding pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |