|
Black–Derman–Toy Model
In mathematical finance, the Black–Derman–Toy model (BDT) is a popular short-rate model used in the pricing of bond options, swaptions and other interest rate derivatives; see . It is a one-factor model; that is, a single stochastic factor—the short rate—determines the future evolution of all interest rates. It was the first model to combine the mean-reverting behaviour of the short rate with the log-normal distribution, and is still widely used. History The model was introduced by Fischer Black, Emanuel Derman, and Bill Toy. It was first developed for in-house use by Goldman Sachs in the 1980s and was published in the ''Financial Analysts Journal'' in 1990. A personal account of the development of the model is provided in Emanuel Derman's memoir '' My Life as a Quant''. Formulae Under BDT, using a binomial lattice, one calibrates the model parameters to fit both the current term structure of interest rates (yield curve), and the volatility structure for interest rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-neutral Probability
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure (also called an equilibrium measure, or ''equivalent martingale measure'') is a probability measure such that each share price is exactly equal to the discounted expectation of the share price under this measure. This is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market, a derivative's price is the discounted expected value of the future payoff under the unique risk-neutral measure. Such a measure exists if and only if the market is arbitrage-free. The easiest way to remember what the risk-neutral measure is, or to explain it to a probability generalist who might not know much about finance, is to realize that it is: # The probability measure of a transformed random variable. Typically this transformation is the utility function of the payoff. The risk-neutral measure would be the measure corresponding to an expectation of the payoff with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Analysts Journal
The ''Financial Analysts Journal'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering investment management, published by Routledge on behalf of the CFA Institute. It was established in 1945 and , the editor-in-chief is William N. Goetzmann. History In 1945, the New York Society of Security Analysts established ''The Analysts Journal'', which in 1960 was renamed the ''Financial Analysts Journal'' when the society was merged into the CFA Institute. From 1960 to 2016, the journal appeared bimonthly; from 2017 onwards it has been published quarterly. Since 1960, the journal has been published by Routledge. Starting in 1960, the journal has awarded the annual "Graham and Dodd Awards of Excellence" to "recognize excellence in research and financial writing in the ''Financial Analysts Journal''". As of August 2022, the editor-in-chief is William N. Goetzmann. Reception In a 2011 study of academic business and financial journals, the School of Management of Cranfield University gav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential (mathematics)
In mathematics, differential refers to several related notions derived from the early days of calculus, put on a rigorous footing, such as infinitesimal differences and the derivatives of functions. The term is used in various branches of mathematics such as calculus, differential geometry, algebraic geometry and algebraic topology. Introduction The term differential is used nonrigorously in calculus to refer to an infinitesimal ("infinitely small") change in some varying quantity. For example, if ''x'' is a variable, then a change in the value of ''x'' is often denoted Δ''x'' (pronounced ''delta x''). The differential ''dx'' represents an infinitely small change in the variable ''x''. The idea of an infinitely small or infinitely slow change is, intuitively, extremely useful, and there are a number of ways to make the notion mathematically precise. Using calculus, it is possible to relate the infinitely small changes of various variables to each other mathematically using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-neutral Measure
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure (also called an equilibrium measure, or ''equivalent martingale measure'') is a probability measure such that each share price is exactly equal to the discounted expectation of the share price under this measure. This is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market, a derivative's price is the discounted expected value of the future payoff under the unique risk-neutral measure. Such a measure exists if and only if the market is arbitrage-free. The easiest way to remember what the risk-neutral measure is, or to explain it to a probability generalist who might not know much about finance, is to realize that it is: # The probability measure of a transformed random variable. Typically this transformation is the utility function of the payoff. The risk-neutral measure would be the measure corresponding to an expectation of the payoff with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brownian Motion
Brownian motion, or pedesis (from grc, πήδησις "leaping"), is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas). This pattern of motion typically consists of random fluctuations in a particle's position inside a fluid sub-domain, followed by a relocation to another sub-domain. Each relocation is followed by more fluctuations within the new closed volume. This pattern describes a fluid at thermal equilibrium, defined by a given temperature. Within such a fluid, there exists no preferential direction of flow (as in transport phenomena). More specifically, the fluid's overall linear and angular momenta remain null over time. The kinetic energies of the molecular Brownian motions, together with those of molecular rotations and vibrations, sum up to the caloric component of a fluid's internal energy (the equipartition theorem). This motion is named after the botanist Robert Brown, who first described the phenomenon in 1827, while looking throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Differential Equation
A stochastic differential equation (SDE) is a differential equation in which one or more of the terms is a stochastic process, resulting in a solution which is also a stochastic process. SDEs are used to model various phenomena such as stock prices or physical systems subject to thermal fluctuations. Typically, SDEs contain a variable which represents random white noise calculated as the derivative of Brownian motion or the Wiener process. However, other types of random behaviour are possible, such as jump processes. Random differential equations are conjugate to stochastic differential equations. Background Stochastic differential equations originated in the theory of Brownian motion, in the work of Albert Einstein and Smoluchowski. These early examples were linear stochastic differential equations, also called 'Langevin' equations after French physicist Langevin, describing the motion of a harmonic oscillator subject to a random force. The mathematical theory of stochasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-76
The Black model (sometimes known as the Black-76 model) is a variant of the Black–Scholes option pricing model. Its primary applications are for pricing options on future contracts, bond options, interest rate cap and floors, and swaptions. It was first presented in a paper written by Fischer Black in 1976. Black's model can be generalized into a class of models known as log-normal forward models, also referred to as LIBOR market model. The Black formula The Black formula is similar to the Black–Scholes formula for valuing stock options except that the spot price of the underlying is replaced by a discounted futures price F. Suppose there is constant risk-free interest rate ''r'' and the futures price ''F(t)'' of a particular underlying is log-normal with constant volatility ''σ''. Then the Black formula states the price for a European call option of maturity ''T'' on a futures contract with strike price ''K'' and delivery date ''T (with T' \geq T) is : c = e^ N(d_1) - K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate Cap
An interest rate cap is a type of interest rate derivative in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate exceeds the agreed strike price. An example of a cap would be an agreement to receive a payment for each month the LIBOR rate exceeds 2.5%. Similarly an interest rate floor is a derivative contract in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate is below the agreed strike price. Caps and floors can be used to hedge against interest rate fluctuations. For example, a borrower who is paying the LIBOR rate on a loan can protect himself against a rise in rates by buying a cap at 2.5%. If the interest rate exceeds 2.5% in a given period the payment received from the derivative can be used to help make the interest payment for that period, thus the interest payments are effectively "capped" at 2.5% from the borrowers' point of view. Interest rate cap An interest rate cap is a derivative in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate Cap
An interest rate cap is a type of interest rate derivative in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate exceeds the agreed strike price. An example of a cap would be an agreement to receive a payment for each month the LIBOR rate exceeds 2.5%. Similarly an interest rate floor is a derivative contract in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate is below the agreed strike price. Caps and floors can be used to hedge against interest rate fluctuations. For example, a borrower who is paying the LIBOR rate on a loan can protect himself against a rise in rates by buying a cap at 2.5%. If the interest rate exceeds 2.5% in a given period the payment received from the derivative can be used to help make the interest payment for that period, thus the interest payments are effectively "capped" at 2.5% from the borrowers' point of view. Interest rate cap An interest rate cap is a derivative in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
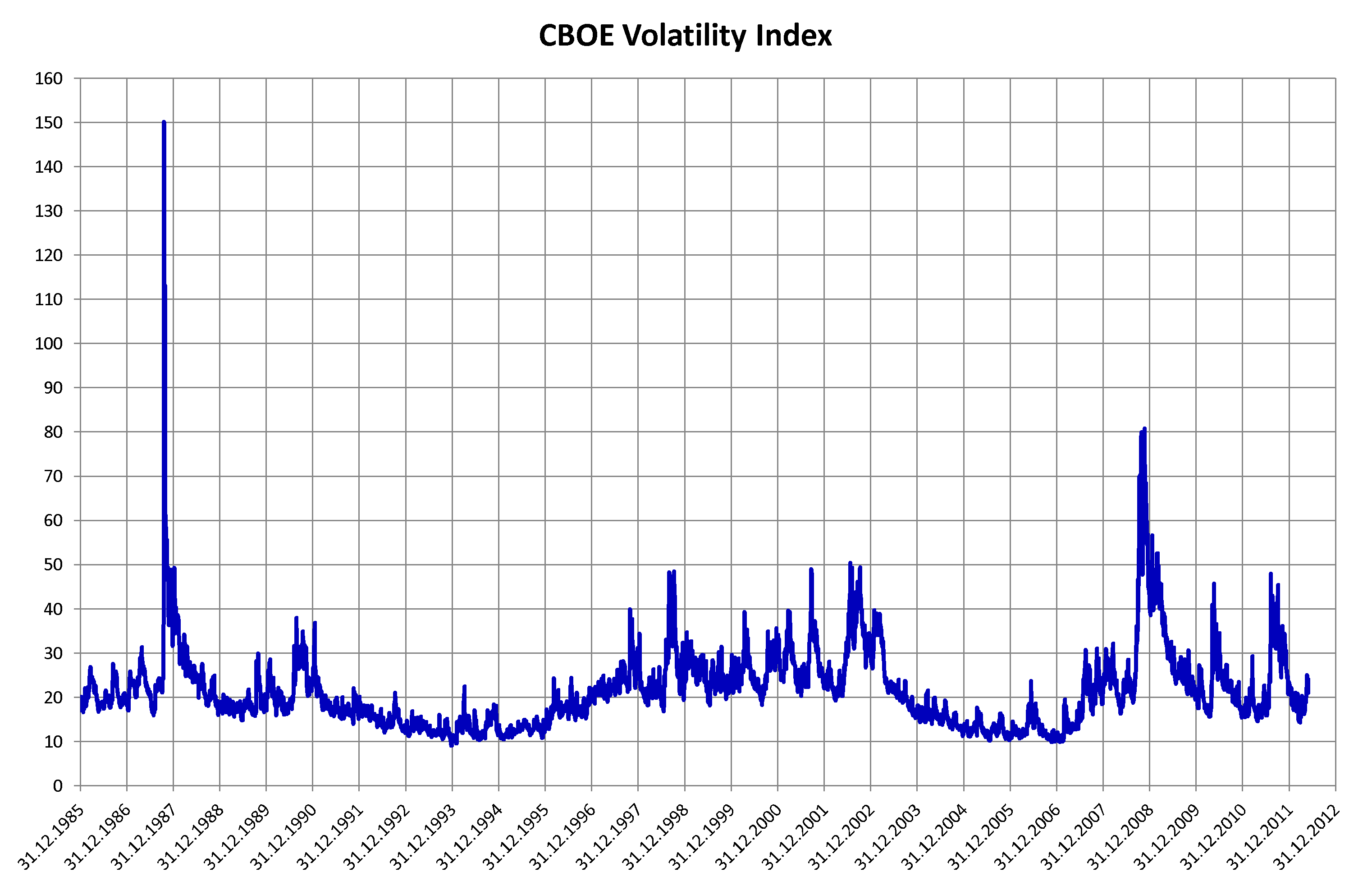
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn calculated using the sum of squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield Curve
In finance, the yield curve is a graph which depicts how the yields on debt instruments - such as bonds - vary as a function of their years remaining to maturity. Typically, the graph's horizontal or x-axis is a time line of months or years remaining to maturity, with the shortest maturity on the left and progressively longer time periods on the right. The vertical or y-axis depicts the annualized yield to maturity. Those who issue and trade in forms of debt, such as loans and bonds, use yield curves to determine their value. Shifts in the shape and slope of the yield curve are thought to be related to investor expectations for the economy and interest rates. Ronald Melicher and Merle Welshans have identified several characteristics of a properly constructed yield curve. It should be based on a set of securities which have differing lengths of time to maturity, and all yields should be calculated as of the same point in time. All securities measured in the yield curve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Finding
In mathematics and computing, a root-finding algorithm is an algorithm for finding zeros, also called "roots", of continuous functions. A zero of a function , from the real numbers to real numbers or from the complex numbers to the complex numbers, is a number such that . As, generally, the zeros of a function cannot be computed exactly nor expressed in closed form, root-finding algorithms provide approximations to zeros, expressed either as floating-point numbers or as small isolating intervals, or disks for complex roots (an interval or disk output being equivalent to an approximate output together with an error bound). Solving an equation is the same as finding the roots of the function . Thus root-finding algorithms allow solving any equation defined by continuous functions. However, most root-finding algorithms do not guarantee that they will find all the roots; in particular, if such an algorithm does not find any root, that does not mean that no root exists. Most nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |