|
Black Tar Heroin
Black tar heroin is a form of heroin that is sticky like tar or hard like coal. Its dark color is the result of crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Despite its name, black tar heroin can also be dark orange or dark brown in appearance. Black tar heroin is impure diamorphine. Other forms of heroin require additional steps of purification post acetylation. With black tar, the product's processing stops immediately after acetylation. Its unique consistency however is due to acetylation without a reflux apparatus. As in homebake heroin in Australia and New Zealand the crude acetylation results in a gooey mass. Black tar as a type holds a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is another result of crude acetylation. The lack of proper reflux during acetylation fails to remove much of the moisture retained in the acetylating agent, glacial acetic acid. Black tar heroin is often produced in Latin America, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heroin Black Tar
Black tar heroin is a form of heroin that is sticky like tar or hard like coal. Its dark color is the result of crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Despite its name, black tar heroin can also be dark orange or dark brown in appearance. Black tar heroin is impure diamorphine. Other forms of heroin require additional steps of purification post acetylation. With black tar, the product's processing stops immediately after acetylation. Its unique consistency however is due to acetylation without a reflux apparatus. As in Homebake_(slang), homebake heroin in Australia and New Zealand the crude acetylation results in a gooey mass. Black tar as a type holds a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is another result of crude acetylation. The lack of proper reflux during acetylation fails to remove much of the moisture retained in the acetylating agent, glacial acetic acid. Black tar heroin is often produced in La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brown powders sold illegally around the world as heroin have variable "cuts". Black tar heroin is a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation during clandestine production of street heroin. Heroin is used medically in several countries to relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy. It is typically injected, usually into a vein, but it can also be smoked, snorted, or inhaled. In a clinical context, the route of administration is most commonly intravenous injection; it may also be given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, as well as orally in the form of tablets. The onset of effects is usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Drug Intelligence Center
The United States National Drug Intelligence Center (NDIC), established in 1993, was a component of the U.S. Department of Justice and a member of the United States Intelligence Community, Intelligence Community. ThGeneral Counterdrug Intelligence Plan implemented in February 2000, designated NDIC as the nation's principal center for strategic domestic counterdrug intelligence. The NDIC ceased to exist on June 16, 2012. Its former DOMEX and strategic analysis functions transferred over to the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). Creation On September 5, 1989 George H. W. Bush, President George H.W. Bush with his Director of the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) William Bennett, unveiled hiNational Drug Control Strategywhich outlined the President's strategy for coordinating the combined efforts of various federal programs to reduce drug use and drug trafficking in the United States. The inaugural strategy was to announce that ONDCP would develop an intelligence c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Cocaine
Black cocaine ( es, italic=no, coca negra) is a mixture of regular cocaine Freebase (chemistry), base or cocaine hydrochloride with various other substances. These other substances are added * to camouflage the typical appearance (pigments and dyes, e.g. charcoal), * to interfere with color-based drug tests (mixing thiocyanates and iron(III) chloride, iron salts or cobalt salts forms deep red complexes in solution), * to make the mixture undetectable by detection dog, drug sniffing dogs (activated carbon may sufficiently absorb trace odors). Since the result is usually black, it is generally smuggled as toner, fingerprint powder, fertilizer, pigment, metal moldings, or charcoal. The pure cocaine base can be recovered from the mixture by extraction (chemistry), extraction (freebase) or acid-base extraction (hydrochloride) using common solvent, organic solvents such as methylene chloride or acetone. A second process is required to convert cocaine base into powdered cocaine hydrochlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
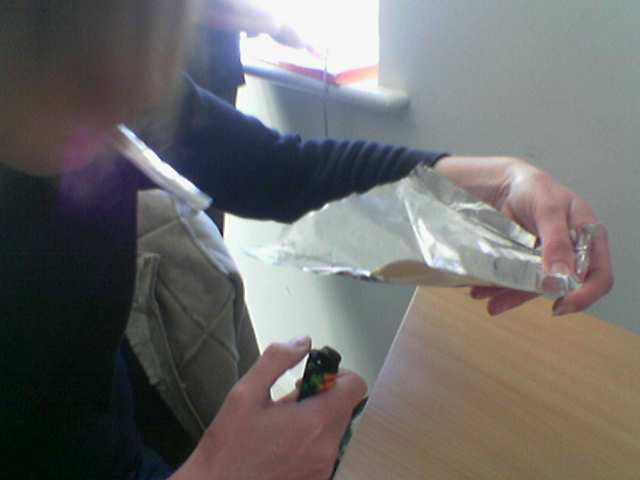
Chasing The Dragon
"Chasing the dragon" (CTD) (), or "foily" in Australian English, refers to inhaling the vapor from a heated solution of a powdered psychoactive drug on a sheet of aluminum foil. The moving vapor is chased after with a tube (often rolled foil) through which the user inhales. The "chasing" occurs as the user gingerly keeps the liquid moving in order to keep it from overheating and burning up too quickly, on a heat conducting material such as aluminium foil. Another use of the term "chasing the dragon" refers to the elusive pursuit of a high equal to the user’s first in the use of a drug, which after acclimation is no longer achievable. Used in this way, “chasing the dragon” can refer to any recreational drug administered by any means. Etymology Chasing the dragon is a slang phrase of Cantonese origin from Hong Kong. The Hong Kong film Chasing the Dragon is named from the origin of the etymology. Cultural aspects Aluminum foil is considered to be low-quality drug paraphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
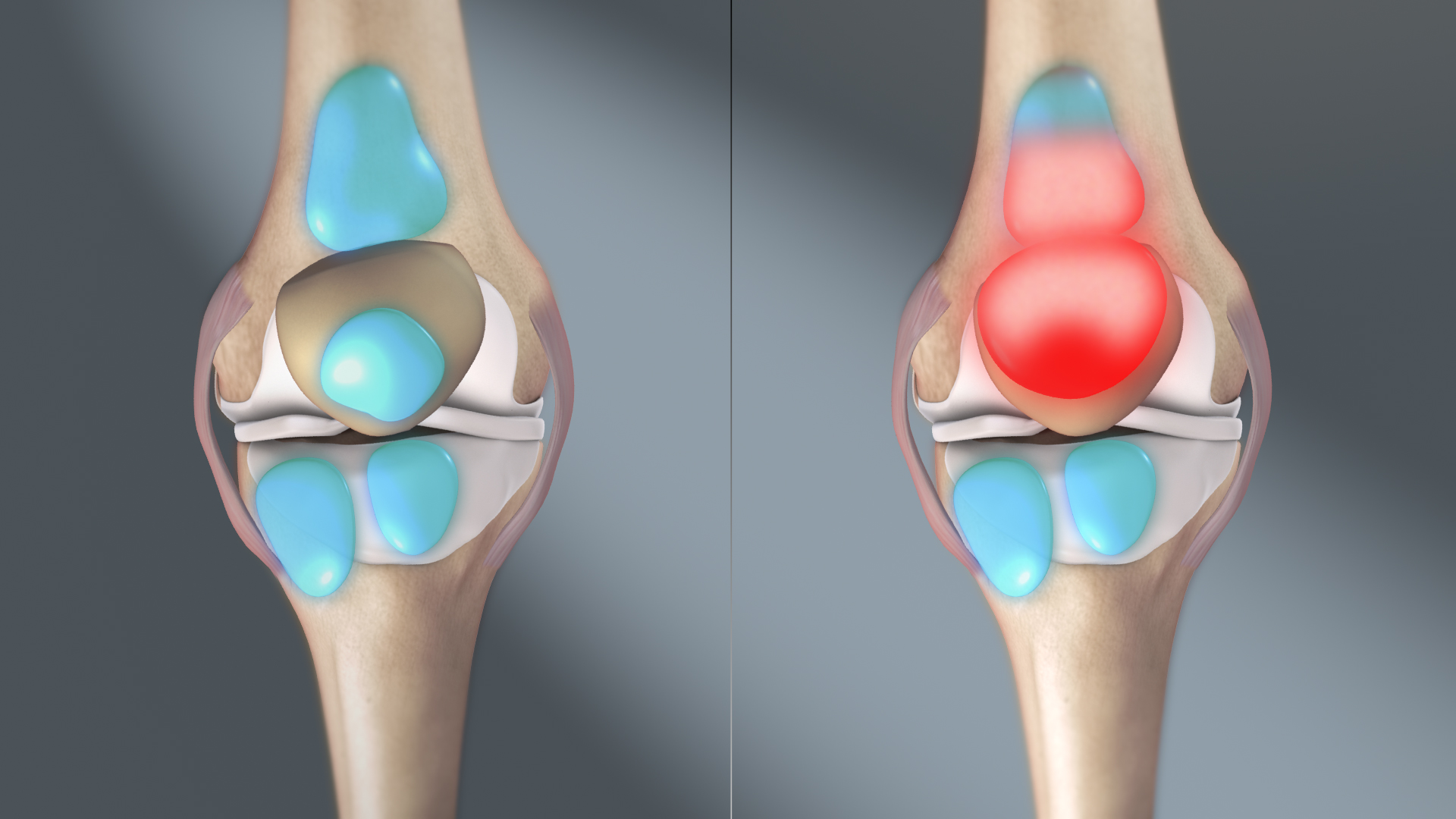
Septic Arthritis
Acute septic arthritis, infectious arthritis, suppurative arthritis, osteomyelitis, or joint infection is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Generally speaking, symptoms typically include redness, heat and pain in a single joint associated with a decreased ability to move the joint. Onset is usually rapid. Other symptoms may include fever, weakness and headache. Occasionally, more than one joint may be involved, especially in neonates and younger children. In neonates, infants during the first year of life, and toddlers, the signs and symptoms of septic arthritis can be deceptive and mimic other infectious and non-infectious disorders. In children, septic arthritis is usually caused by non-specific bacterial infection and commonly hematogenous, i.e., spread through the bloodstream. Septic arthritis and/or acute hematogenous osteomyelitis usually occurs in children with no co-occurring health problems. Other routes of infection include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults. The cause is usually a bacterial infection, but rarely can be a fungal infection. It may occur by spread from the blood or from surrounding tissue. Risks for developing osteomyelitis include diabetes, intravenous drug use, prior removal of the spleen, and trauma to the area. Diagnosis is typically suspected based on symptoms and basic laboratory tests as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).This is because plain radiographs are unremarkable in the first few days following acute infection. Diagnosis is further confirmed by blood tests, medical imaging, or bone biopsy. Treatment of bacterial osteomyelitis often involves both antimicrobials and sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath (called the synovium) that surrounds a tendon, typically leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Tenosynovitis can be either infectious or noninfectious. Common clinical manifestations of noninfectious tenosynovitis include de Quervain tendinopathy and stenosing tenosynovitis (more commonly known as trigger finger) Signs and symptoms Infectious tenosynovitis occurs between 2.5% and 9.4% of all hand infections. Kanavel's cardinal signs is used to diagnose infectious tenosynovitis. They are: tenderness to touch along the flexor aspect of the finger, fusiform enlargement of the affected finger, the finger being held in slight flexion at rest, and severe pain with passive extension. Fever may also be present but is uncommon. Pathogenesis Infectious tenosynovitis is the infection of closed synovial sheaths in the flexor tendons of the fingers. It is usually caused by trauma, but bacteria can spread from other site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae (fluid filled sacs) of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursae rest at the points where internal functionaries, such as muscles and tendons, slide across bone. Healthy bursae create a smooth, almost frictionless functional gliding surface making normal movement painless. When bursitis occurs, however, movement relying on the inflamed bursa becomes difficult and painful. Moreover, movement of tendons and muscles over the inflamed bursa aggravates its inflammation, perpetuating the problem. Muscle can also be stiffened. Signs and symptoms Bursitis commonly affects superficial bursae. These include the subacromial, prepatellar, retrocalcaneal, and ''pes anserinus'' bursae of the shoulder, knee, heel and shin, etc. (see below). Symptoms vary from localized warmth and erythema to joint pain and sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloodstream Infections
Bloodstream infections (BSIs), which include bacteremias when the infections are bacterial and fungemias when the infections are fungal, are infections present in the blood. Blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of microbes in the blood (most commonly accomplished by blood cultures) is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, which is the host response to bacteria. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream as a severe complication of infections (like pneumonia or meningitis), during surgery (especially when involving mucous membranes such as the gastrointestinal tract), or due to catheters and other foreign bodies entering the arteries or veins (including during intravenous drug abuse). Transient bacteremia can result after dental procedures or brushing of teeth. Bacteremia can have several important health consequences. The immune response to the bacteria can cause sepsis and septic shock, which has a high mortality rate. Bacteria can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium Botulinum
''Clostridium botulinum'' is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming, motile bacterium with the ability to produce the neurotoxin botulinum. The botulinum toxin can cause botulism, a severe flaccid paralytic disease in humans and other animals, and is the most potent toxin known to mankind, natural or synthetic, with a lethal dose of 1.3–2.1 ng/kg in humans.(2010). Chapter 19. ''Clostridium'', ''Peptostreptococcus'', ''Bacteroides'', and Other Anaerobes. In Ryan K.J., Ray C (Eds), ''Sherris Medical Microbiology'', 5th ed. ''C. botulinum'' is a diverse group of pathogenic bacteria initially grouped together by their ability to produce botulinum toxin and now known as four distinct groups, ''C. botulinum'' groups I–IV, as well as some strains of ''Clostridium butyricum'' and ''Clostridium baratii'', are the bacteria responsible for producing botulinum toxin. ''C. botulinum'' is responsible for foodborne botulism (ingestion of preformed toxin), infant bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |