|
Black Lipid Membranes
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. They are used to study the fundamental properties of biological membranes in a simplified and well-controlled environment, and increasingly in bottom-up synthetic biology for the construction of artificial cells. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids. There are many different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages and disadvantages. The first system developed was the black lipid membrane or “painted” bilayer, which allows simple electrical characterization of bilayers but is short-lived and can be difficult to work with. Supported bilayers are anchored to a solid substrate, incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilayer
A bilayer is a double layer of closely packed atoms or molecules. The properties of bilayers are often studied in condensed matter physics, particularly in the context of semiconductor devices, where two distinct materials are united to form junctions (such as p–n junctions, Schottky junctions, etc.). Layered materials, such as graphene, boron nitride, or transition metal dichalchogenides, have unique electronic properties as a bilayer system and are an active area of current research. In biology a common example is the Lipid bilayer, which describes the structure of multiple organic structures, such as the membrane of a cell. See also * Monolayer * Non-carbon nanotube * Semiconductor * Thin film A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer ( monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many ... References Phases of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
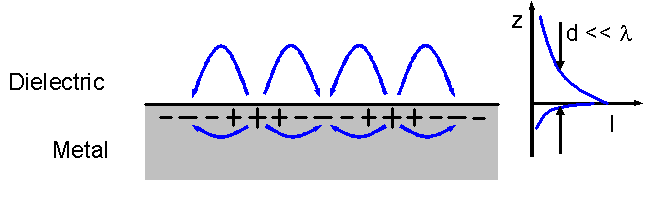
Surface Plasmon Resonance
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measuring adsorption of material onto planar metal (typically gold or silver) surfaces or onto the surface of metal nanoparticles. It is the fundamental principle behind many color-based biosensor applications and lab-on-a-chip sensors. It should be stressed that SPR is not a resonance on the planar surface and it is a polariton or surface-wave like phenomenon. Explanation The surface plasmon polariton is a non-radiative electromagnetic surface wave that propagates in a direction parallel to the negative permittivity/dielectric material interface. Since the wave is on the boundary of the conductor and the external medium (air, water or vacuum for example), these oscillations are very sensitive to any change of this boundary, such as the adso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy
A total internal reflection fluorescence microscope (TIRFM) is a type of microscope with which a thin region of a specimen, usually less than 200 nanometers can be observed. TIRFM is an imaging modality which uses the excitation of fluorescent cells in a thin optical specimen section that is supported on a glass slide. The technique is based on the principle that when excitation light is totally internally reflected in a transparent solid coverglass at its interface with a liquid medium, an electromagnetic field, also known as an evanescent wave, is generated at the solid-liquid interface with the same frequency as the excitation light. The intensity of the evanescent wave exponentially decays with distance from the surface of the solid so that only fluorescent molecules within a few hundred nanometers of the solid are efficiently excited. Two-dimensional images of the fluorescence can then be obtained, although there are also mechanisms in which three-dimensional information on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evanescent Wave
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evanescent": Having P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Polarisation Interferometry
Dual-polarization interferometry (DPI) is an analytical technique that probes molecular layers adsorbed to the surface of a waveguide using the evanescent wave of a laser beam. It is used to measure the conformational change in proteins, or other biomolecules, as they function (referred to as the conformation activity relationship). Instrumentation DPI focuses laser light into two waveguides. One of these functions as the "sensing" waveguide having an exposed surface while the second one functions to maintain a reference beam. A two-dimensional interference pattern is formed in the far field by combining the light passing through the two waveguides. The DPI technique rotates the polarization of the laser, to alternately excite two polarization modes of the waveguides. Measurement of the interferogram for both polarizations allows both the refractive index and the thickness of the adsorbed layer to be calculated. The polarization can be switched rapidly, allowing real-time measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Crystal Microbalance
A quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) (also known as ''quartz microbalance'' (QMB), sometimes also as ''quartz crystal nanobalance'' (QCN)) measures a mass variation per unit area by measuring the change in frequency of a quartz crystal resonator. The resonance is disturbed by the addition or removal of a small mass due to oxide growth/decay or film deposition at the surface of the acoustic resonator. The QCM can be used under vacuum, in gas phase ("gas sensor", first use described by King) and more recently in liquid environments. It is useful for monitoring the rate of deposition in thin film deposition systems under vacuum. In liquid, it is highly effective at determining the affinity of molecules ( proteins, in particular) to surfaces functionalized with recognition sites. Larger entities such as viruses or polymers are investigated as well. QCM has also been used to investigate interactions between biomolecules. Frequency measurements are easily made to high precision (discussed be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer Mechanics
Lipid bilayer mechanics is the study of the physical material properties of lipid bilayers, classifying bilayer behavior with stress and strain rather than biochemical interactions. Local point deformations such as membrane protein interactions are typically modelled with the complex theory of biological liquid crystals but the mechanical properties of a homogeneous bilayer are often characterized in terms of only three mechanical elastic moduli: the area expansion modulus Ka, a bending modulus Kb and an edge energy \Lambda. For fluid bilayers the shear modulus is by definition zero, as the free rearrangement of molecules within plane means that the structure will not support shear stresses. These mechanical properties affect several membrane-mediated biological processes. In particular, the values of Ka and Kb affect the ability of proteins and small molecules to insert into the bilayer. Bilayer mechanical properties have also been shown to alter the function of mechanically acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer Phase Behavior
One property of a lipid bilayer is the relative mobility (fluidity) of the individual lipid molecules and how this mobility changes with temperature. This response is known as the phase behavior of the bilayer. Broadly, at a given temperature a lipid bilayer can exist in either a liquid or a solid phase. The solid phase is commonly referred to as a “gel” phase. All lipids have a characteristic temperature at which they undergo a transition ( melt) from the gel to liquid phase. In both phases the lipid molecules are constrained to the two dimensional plane of the membrane, but in liquid phase bilayers the molecules diffuse freely within this plane. Thus, in a liquid bilayer a given lipid will rapidly exchange locations with its neighbor millions of times a second and will, through the process of a random walk, migrate over long distances.H. C. Berg, "Random Walks in Biology". Extended Paperback Ed. ed. 1993, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. Motion constraints In contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Force Microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. Overview Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. The information is gathered by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe. Piezoelectric elements that facilitate tiny but accurate and precise movements on (electronic) command enable precise scanning. Despite the name, the Atomic Force Microscope does not use the Nuclear force. Abilities The AFM has three major abilities: force measurement, topographic imaging, and manipulation. In force measurement, AFMs can be used to measure the forces between the probe and the sample as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Experiment
A long-term experiment is an experimental procedure that runs through a long period of time, in order to test a hypothesis or observe a phenomenon that takes place at an extremely slow rate. What duration is considered "long" depends on the academic discipline. For example, several agricultural field experiments have run for more than 100 years, but much shorter experiments may qualify as "long-term" in other disciplines. An experiment is "a set of actions and observations", implying that one or more treatments (fertilizer, subsidized school lunches, etc.) is imposed on the system under study. Long-term experiments therefore contrast with nonexperimental long-term studies in which manipulation of the system studied is impossible (e.g. Jupiter's Great Red Spot) or undesirable (e.g. field observations of chimpanzee behavior). In physics The Oxford Electric Bell has been ringing at Oxford University since 1840, although there is some reason to believe it may be 15 years older. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)