|
Bizen Province
was a province of Japan on the Inland Sea side of Honshū, in what is today the southeastern part of Okayama Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bitchū and Bingo Provinces. Bizen borders Mimasaka, Harima, and Bitchū Provinces. Bizen's original center was in the modern city of Okayama. From an early time Bizen was one of Japan's main centers for sword smithing. Historical record In the 3rd month of the 6th year of the '' Wadō era'' (713), the land of Bizen''-no kuni'' was administratively separated from Mimasaka Province (美作国). In that same year, Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' continued to organize other cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period. In ''Wadō'' 6, Tanba Province (丹波国) was sundered from Tango Province (丹後国); and Hyūga Province (日向国) was divided from Ōsumi Province (大隈国).Titsingh, Isaac. (1834) In ''Wadō'' 5 (712), Mutsu Province (陸奥国) had been severed from Dewa Province (出羽国). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Japan-Bizen
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''province'' has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city". While some provinces were produced artificially by colonial powers, others were formed around local groups with their own ethnic identities. Many have their own powers independent of central or federal authority, especially in Canada and Pakistan. In other countries, like China or France, provinces are the creation of central government, with very little autonomy. Etymology The English word ''province'' is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French , which itself comes from the Latin word , which referred to the sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanba Province
was a province of Japan in the area of central Kyoto and east-central Hyōgo Prefectures. Tanba bordered on Harima, Ōmi, Settsu, Tajima, Wakasa, and Yamashiro Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . In terms of the Gokishichidō system, Tanba was one of the provinces of the San'indō circuit. Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Tanba was ranked as one of the "superior countries" (上国) in terms of importance, and one of the "near countries" (近国) in terms of distance from the capital. The provincial capital is believed to have been located in what is now the city of Kameoka, although the exact location remains uncertain. The ''ichinomiya'' of the province is the Izumo-daijingū also located in Kameoka. The province had an area of . History Before the establishment of the Ritsuryō system, the area was under control of the Tanba Kokuzō and included both the Tanba and Tango areas. The province of Tango was created in 713 during the reign of Empr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobayakawa Hideaki
(1577 – December 1, 1602) was the fifth son of Kinoshita Iesada and the nephew of Toyotomi Hideyoshi. He was gained the rank of ''Saemon no Kami'' (左衛門督) or in China ''Shikkingo'' (執金吾) at genpuku and held the court title of '' Chūnagon'' (中納言), Hideaki was also called ''Kingo Chūnagon'' (金吾中納言). Biography He was adopted by Hideyoshi and called himself ''Hashiba Hidetoshi'' (羽柴 秀俊). He was then again adopted by Kobayakawa Takakage, becoming ''Kobayakawa Hidetoshi'' (小早川 秀俊). He then renamed himself ''Hideaki'' (秀秋) after Takakage's death. Shortly after the Battle of Sekigahara, he renamed one last time to ''Kobayakawa Hideaki'' (小早川 秀詮). During the Battle of Keicho he led reinforcements to rescue Ulsan Castle from the Ming army. Fighting on the front line with a spear, he managed to capture an enemy commander and broke the siege. However, Hideyoshi saw the danger of a reckless charge by the general com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Course of History, Viking Press 1988. p. 68. Hideyoshi rose from a peasant background as a retainer of the prominent lord Oda Nobunaga to become one of the most powerful men in Japan. Hideyoshi succeeded Nobunaga after the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582 and continued Nobunaga's campaign to unite Japan that led to the closing of the Sengoku period. Hideyoshi became the ''de facto'' leader of Japan and acquired the prestigious positions of Chancellor of the Realm and Imperial Regent by the mid-1580s. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea in 1592 to initial success, but eventual military stalemate damaged his prestige before his death in 1598. Hideyoshi's young son and successor Toyotomi Hideyori was displaced by Tokugawa Ieya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Five Elders
The Council of Five Elders (Japanese: 五大老, ''Go-Tairō'') was a group of five powerful feudal lords (Japanese: 大名, ''Daimyō'') formed in 1598 by the Regent (Japanese: 太閤 '' Taikō'') Toyotomi Hideyoshi, shortly before his death the same year. While Hideyoshi was on his deathbed, his son, Toyotomi Hideyori, was still only 5 years old and as such Hideyoshi needed to create the council in order to ensure his heir would be able to succeed him after coming of age. They also acted as advisers for the Five Commissioners (Japanese: 五奉行 ''Go-Bugyō)'', which had also been established by Hideyoshi to govern Kyoto and the surrounding areas. Creation of the Council Leading up to the creation of the council Hideyoshi had been slowly changing in demeanor as the invasions of Korea (in attempt to conquer both Korea and China) were failing. Hideyoshi himself had not joined the Korean Campaigns and assigned vassals in his command to head the campaign. He sent his final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukita Hideie
was the ''daimyō'' of Bizen and Mimasaka Provinces (modern Okayama Prefecture), and one of the council of Five Elders appointed by Toyotomi Hideyoshi. Son of Ukita Naoie, he married Gōhime, a daughter of Maeda Toshiie. Having fought against Tokugawa Ieyasu in the Battle of Sekigahara he was exiled to the island prison of Hachijō-jima, where he died. Biography Hideie's father Ukita Naoie was ''daimyō'' of Bizen province and initially opposed, but later sided with Oda Nobunaga and Toyotomi Hideyoshi. Naoie died in 1581, and Hideie became the head of the Ukita clan. As Hideie was still young (10 years old), it was Hideie's uncle (Ukita Tadaie) who acted as leader of the Ukita army until Hideie coming of age, in particular, Tadaie served on behalf of Hideie as a commander in numerous battles (under Toyotomi Hideyoshi). However, during the siege of Bitchū Takamatsu Castle in 1582, Nobunaga was assassinated on June 2 of that year, but the siege continued until the castle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urakami Clan
Urakami was an area in the northern part of the city of Nagasaki, Japan. History In 1614, by the orders of shōgun leader Tokugawa Ieyasu, Christianity was banned in Japan in order to suppress European influence and to prevent the undermining of the Japanese government. Most Japanese Christians who openly spoke about their religion were open to prosecution and subject to extreme harsh treatment, such as torture or crucifixion. As a result, Urakami became the stronghold for oppressed believers who steadfastly adhered to their religion in secret. During this time period, the Oura Cathedral played the important role as spiritual support for Christians in Urakami. The existence of Christians within the Urakami area resulted the Japanese government to launch a crackdown in order to implement the ban. On September 1, 1790, the first persecution began in Urakami; hidden Christians were discovered and arrested, though there were no deaths. In 1839, a new wave of persecution was launched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sengoku Period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615. The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Various samurai warlords and clans fought for control over Japan in the power vacuum, while the emerged to fight against samurai rule. The arrival of Europeans in 1543 introduced the arquebus into Japanese warfare, and Japan ended its status as a tributary state of China in 1549. Oda Nobunaga dissolved the Ashikaga shogunate in 1573 and launched a war of political unification by force, including the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War, until his death in the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582. Nobunaga's successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi completed his campaign to unify Japan and consolidated his rule with numerous influential reforms. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea in 1592, but their eventual failure damaged his prestige before his death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akamatsu Clan
is a Japanese samurai family of direct descent from Minamoto no Morifusa of the Murakami-Genji. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003)"Akamatsu" at ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 1 retrieved 2013-4-11. History They were prominent shugo-daimyō in Harima during the Sengoku period. During the Ōnin no ran (1467–1477), Akamatsu Masanori was one of the chief generals of the Hosokawa clan. The head of the clan at Shizuoka in Suruga Province became a ''kazoku'' baron in 1887.'''' The Shinmen clan were a branch of the Akamatsu.Yoshikawa, Eiji. (1995) ''Musashi,'' p. 94 Select members of the clan * Akamatsu Norimura (1277–1350). Hall, John Whitney. (1999) ''The Cambridge History of Japan: Medieval Japan,'' Vol. 3, pp. 600-603./ref> * Akamatsu Norisuke (1314–1371). * Akamatsu Mitsusuke (1381–1441). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005) "''Kaikitsu-no-hen,''"''Japan encyclopedia,'' p. 456. * Akamatsu Sada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muromachi Period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi '' shōgun'', Ashikaga Takauji, two years after the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336) of imperial rule was brought to a close. The period ended in 1573 when the 15th and last shogun of this line, Ashikaga Yoshiaki, was driven out of the capital in Kyoto by Oda Nobunaga. From a cultural perspective, the period can be divided into the Kitayama and Higashiyama cultures (later 15th – early 16th centuries). The early years from 1336 to 1392 of the Muromachi period are known as the '' Nanboku-chō'' or Northern and Southern Court period. This period is marked by the continued resistance of the supporters of Emperor Go-Daigo, the emperor behind the Kenmu Restoration. The Sengoku period or Warring States period, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
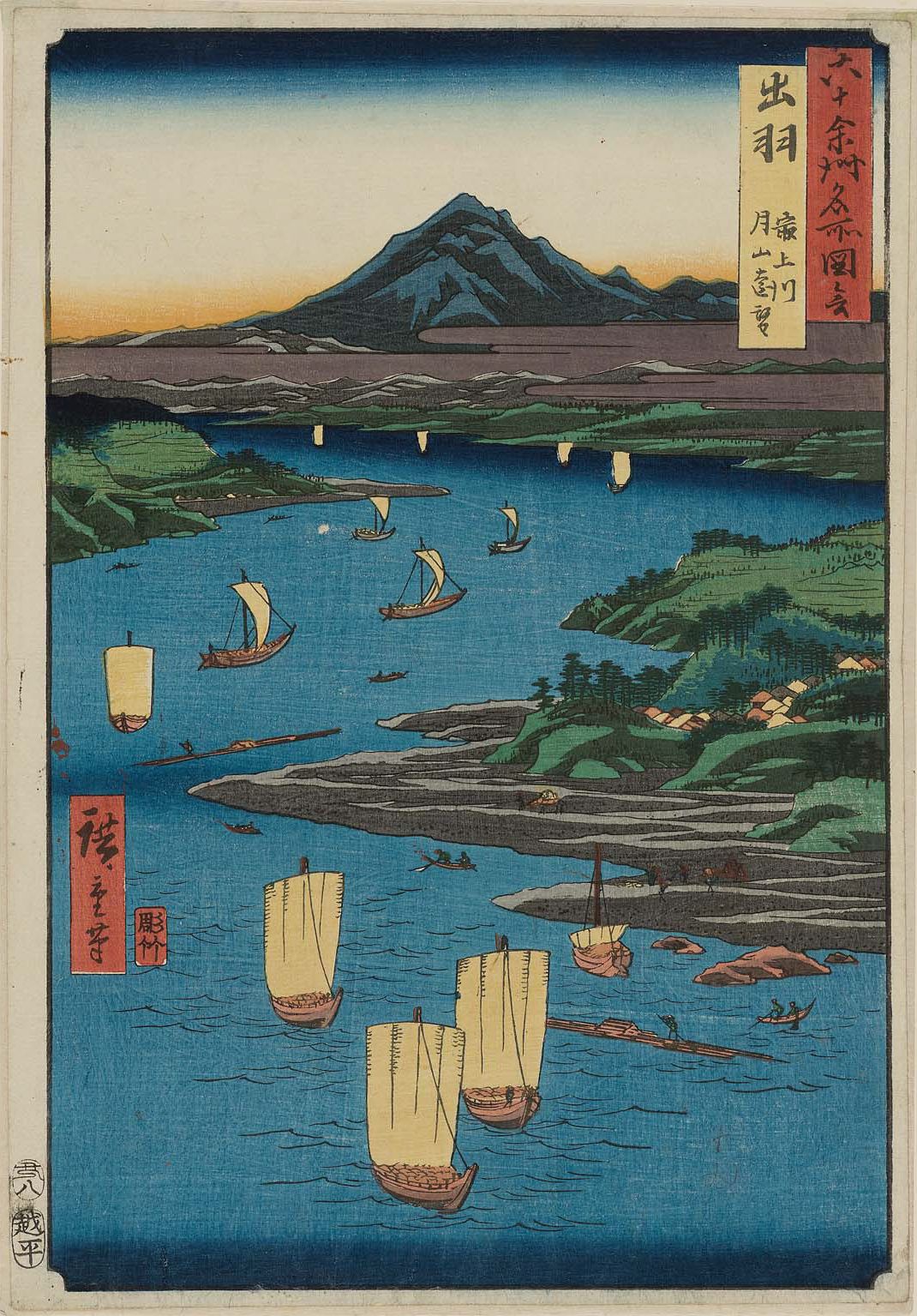
Dewa Province
was a province of Japan comprising modern-day Yamagata Prefecture and Akita Prefecture, except for the city of Kazuno and the town of Kosaka. Dewa bordered on Mutsu and Echigō Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . History Early period Prior to the Asuka period, Dewa was inhabited by Ainu or Emishi tribes, and was effectively outside of the control of the Yamato dynasty. Abe no Hirafu conquered the native Emishi tribes at what are now the cities of Akita and Noshiro in 658 and established a fort on the Mogami River. In 708 AD was created within Echigō Province. The area of Dewa District was roughly that of the modern Shōnai area of Yamagata Prefecture, and was gradually extended to the north as the Japanese pushed back the indigenous people of northern Honshū. Dewa District was promoted to the status of a province () in 712 AD, and gained Okitama and Mogami Districts, formerly part of Mutsu Province. A number of military expeditions were sent to the area, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
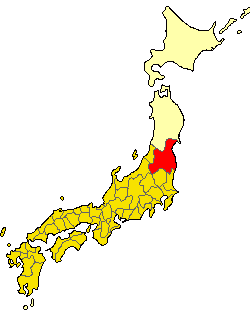
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |