|
Bisoxazoline Ligand
In chemistry, bis(oxazoline) ligands (often abbreviated BOX ligands) are a class of privileged chiral ligands containing two oxazoline rings. They are typically C2‑symmetric and exist in a wide variety of forms; with structures based around CH2 or pyridine linkers being particularly common (often generalised BOX and PyBOX respectively). The coordination complexes of bis(oxazoline) ligands are used in asymmetric catalysis. These ligands are examples of C2-symmetric ligands. Synthesis The synthesis of oxazoline rings is well established and in general proceeded via the cyclisation of a 2‑amino alcohol with any of a number of suitable functional groups. In the case of bis(oxazoline)s, synthesis is most conveniently achieved by using bi-functional starting materials; as this allows both rings to be produced at once. Of the materials suitable, dicarboxylic or di nitrile compounds are the most commonly available and hence the majority bis(oxazoline) ligands are produced from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valinol
Valinol is an organic compound named after, and commonly produced from, the amino acid valine. The compound is chiral and is produced almost exclusively as the S‑isomer (also designated as the L‑isomer), due to the abundant supply of S-valine. It is part of a broader class of amino alcohols. Synthesis Valinol can be generated by converting the carboxylic group of valine to an alcohol with a strong reducing agent such as lithium aluminium hydride, or with NaBH4 and I2 (forming the borane–tetrahydrofuran complex). In both cases the valinol produced can be subsequently purified by short path distillation. Reactions Valinol is mainly used to prepare chiral oxazolines, a process which can be achieved via a variety of methods. These oxazolines are principally used as ligands in asymmetric catalysis Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Metal
A noble metal is ordinarily regarded as a metallic chemical element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its raw form. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals (ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium) are most often so classified. Silver, copper and mercury are sometimes included as noble metals, however less often as each of these usually occurs in nature combined with sulfur. In more specialized fields of study and applications the number of elements counted as noble metals can be smaller or larger. In physics, there are only three noble metals: copper, silver and gold. In dentistry, silver is not always counted as a noble metal since it is subject to corrosion when present in the mouth. In chemistry, the term noble metal is sometimes applied more broadly to any metallic or semimetallic element that does not react with a weak acid and give off hydrogen gas in the process. This broader set includes copper, mercury, tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Synthesis
Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereomeric) products in unequal amounts." Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer. Enantiomers are stereoisomers that have opposite configurations at every chiral center. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that differ at one or more chiral centers. Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity. Overview Many of the building blocks of biological systems such as sugars and amino acids are produced exclusively as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Pyramidal Molecular Geometry
In molecular geometry, square pyramidal geometry describes the shape of certain compounds with the formula where L is a ligand. If the ligand atoms were connected, the resulting shape would be that of a pyramid with a square base. The point group symmetry involved is of type C4v. The geometry is common for certain main group compounds that have a stereochemically-active lone pair, as described by VSEPR theory. Certain compounds crystallize in both the trigonal bipyramidal and the square pyramidal structures, notably . As a transition state in Berry pseudorotation As a trigonal bipyramidal molecule undergoes Berry pseudorotation, it proceeds via an intermediary stage with the square pyramidal geometry. Thus even though the geometry is rarely seen as the ground state, it is accessed by a low energy distortion from a trigonal bipyramid. Pseudorotation also occurs in square pyramidal molecules. Molecules with this geometry, as opposed to trigonal bipyramidal, exhibit heavier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Stereochemical Model
A box (plural: boxes) is a container used for the storage or transportation of its contents. Most boxes have flat, parallel, rectangular sides. Boxes can be very small (like a matchbox) or very large (like a shipping box for furniture), and can be used for a variety of purposes from functional to decorative. Boxes may be made of a variety of materials, both durable, such as wood and metal; and non-durable, such as corrugated fiberboard and paperboard. Corrugated metal boxes are commonly used as shipping containers. Most commonly, boxes have flat, parallel, rectangular sides, making them rectangular prisms; but boxes may also have other shapes. Rectangular prisms are often referred to colloquially as "boxes." Boxes may be closed and shut with flaps, doors, or a separate lid. They can be secured shut with adhesives, tapes, or more decorative or elaborately functional mechanisms, such as a catch, clasp or lock. Types Packaging Several types of boxes are used in packaging an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazarov Cyclization
The Nazarov cyclization reaction (often referred to as simply the Nazarov cyclization) is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of cyclopentenones. The reaction is typically divided into ''classical'' and ''modern'' variants, depending on the reagents and substrates employed. It was originally discovered by Ivan Nikolaevich Nazarov (1906–1957) in 1941 while studying the rearrangements of allyl vinyl ketones. As originally described, the Nazarov cyclization involves the activation of a divinyl ketone using a stoichiometric Lewis acid or protic acid promoter. The key step of the reaction mechanism involves a cationic 4π- electrocyclic ring closure which forms the cyclopentenone product (See Mechanism below). As the reaction has been developed, variants involving substrates other than divinyl ketones and promoters other than Lewis acids have been subsumed under the name Nazarov cyclization provided that they follow a similar mechanistic pathway. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Addition
In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael addition is a reaction between a Michael donor (an enolate or other nucleophile) and a Michael acceptor (usually an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl) to produce a Michael adduct by creating a carbon-carbon bond at the acceptor's β-carbon. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions and is widely used for the mild formation of carbon-carbon bonds. The Michael addition is an important atom-economical method for diastereoselective and enantioselective C–C bond formation, and many asymmetric variants exist : In this general Michael addition scheme, either or both of R and R' on the nucleophile (the Michael donor) represent electron-withdrawing substituents such as acyl, cyano, nitro, or sulfone groups, which make the adjacent methylene hydrogen acidic enough to form a carbanion when reacted with the base, ''B:''. For the alkene (the Michael acceptor), the R" substituent is usually a carbonyl, which makes the compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
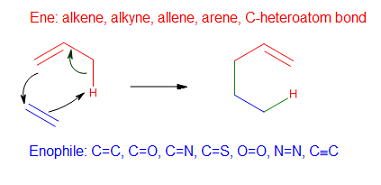
Ene Reaction
In organic chemistry, the ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction by its discoverer Kurt Alder in 1943) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position. This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been also developed, which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products. Ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannich Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Mannich reaction is a three-component organic reaction that involves the amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl () functional group by formaldehyde () and a primary or secondary amine () or ammonia (). The final product is a β-amino-carbonyl compound also known as a Mannich base. Reactions between aldimines and α-methylene carbonyls are also considered Mannich reactions because these imines form between amines and aldehydes. The reaction is named after Carl Mannich. center, 500px, Scheme 1 - Ammonia or an amine reacts with formaldehyde and an alpha acidic proton of a carbonyl compound to a beta amino carbonyl compound. The Mannich reaction starts with the nucleophilic addition of an amine to a carbonyl group followed by dehydration to the Schiff base. The Schiff base is an electrophile which reacts in a second step in an electrophilic addition with an enol formed from a carbonyl compound containing an acidic alpha-proton. The Mann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |