|
Bishops Of Rome Under Constantine I
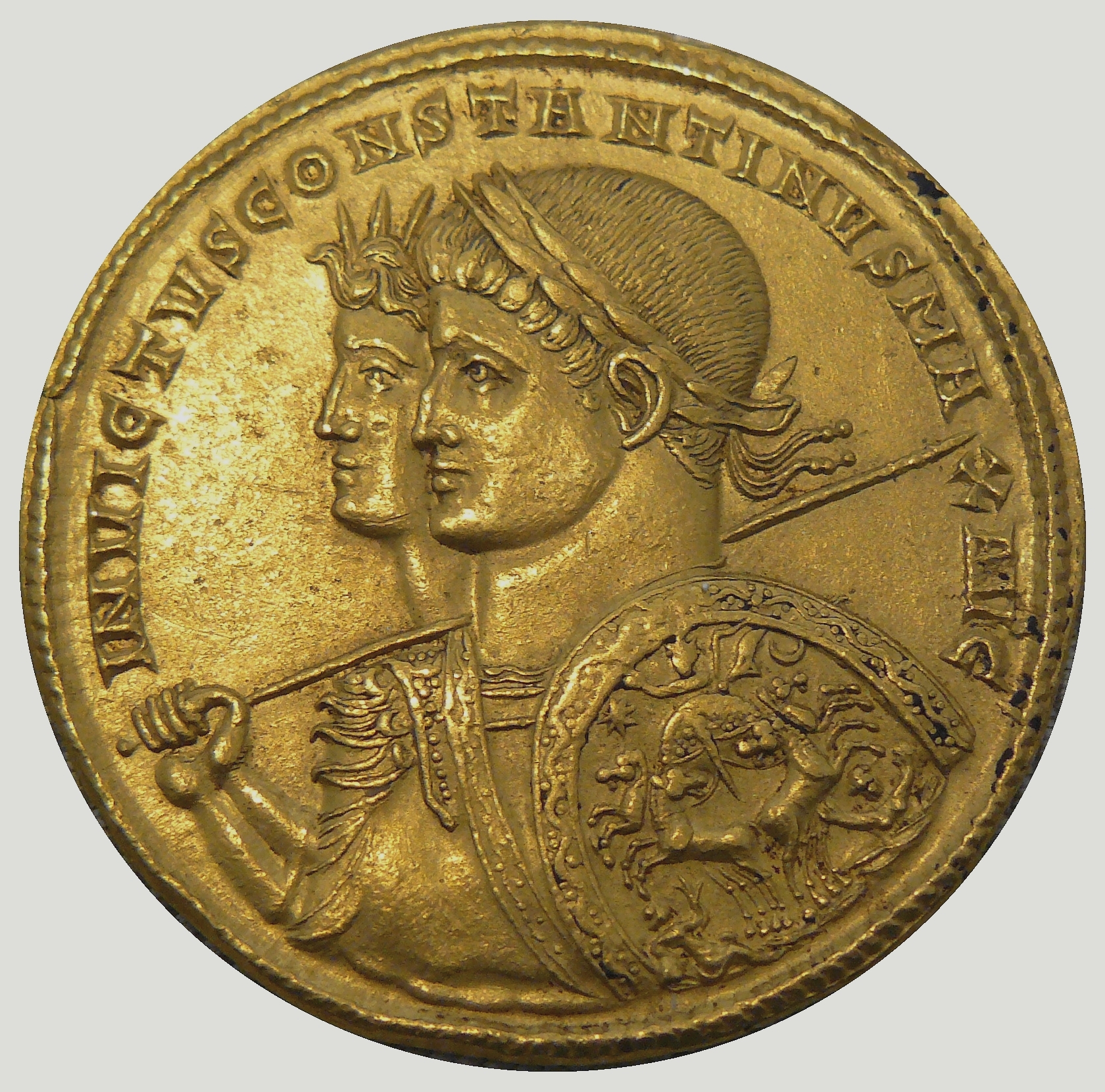
Constantine the Great's (272–337) relationship with the four Bishops of Rome during his reign is an important component of the history of the Papacy, and more generally the history of the Catholic Church. The legend surrounding Constantine I's victory in the Battle of the Milvian Bridge (312) relates his vision of the Chi Rho ( ☧) and the text ''in hoc signo vinces'' in the sky and his reproducing this symbol on the shields of his troops. The following year Constantine and Licinius proclaimed the toleration of Christianity with the Edict of Milan, and in 325 Constantine convened and presided over the First Council of Nicaea, the first ecumenical council. None of this, however, has particularly much to do with the popes, who did not even attend the Council; in fact, the first bishop of Rome to be contemporaneously referred to as "Pope" (πάππας, or ''pappas'') is Damasus I (366-384).Baumgartner, 2003, p. 6. Moreover, between 324 and 330, he built Constantinople as a new c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphael Vision Cross
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. List of works by Raphael, His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual achievement of the Renaissance Neoplatonism, Neoplatonic ideal of human grandeur. Together with Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo, he forms the traditional trinity of great masters of that period. His father was court painter to the ruler of the small but highly cultured city of Urbino. He died when Raphael was eleven, and Raphael seems to have played a role in managing the family workshop from this point. He trained in the workshop of Perugino, and was described as a fully trained "master" by 1500. He worked in or for several cities in north Italy until in 1508 he moved to Rome at the invitation of the pope, to work on the Vatican Palace. He was given a series of important commissions there and elsewhere in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I And Christianity
During the reign of the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great (AD 306–337), Christianity began to transition to the dominant religion of the Roman Empire. Historians remain uncertain about Constantine's reasons for favoring Christianity, and theologians and historians have often argued about which form of early Christianity he subscribed to. There is no consensus among scholars as to whether he adopted his mother Helena's Christianity in his youth, or, as claimed by Eusebius of Caesarea, encouraged her to convert to the faith he had adopted. Constantine ruled the Roman Empire as sole emperor for much of his reign. Some scholars allege that his main objective was to gain unanimous approval and submission to his authority from all classes, and therefore chose Christianity to conduct his political propaganda, believing that it was the most appropriate religion that could fit with the imperial cult. Regardless, under the Constantinian dynasty Christianity expanded throughout the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocletian Persecution
The Diocletianic or Great Persecution was the last and most severe persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. In 303, the emperors Diocletian, Maximian, Galerius, and Constantius issued a series of edicts rescinding Christians' legal rights and demanding that they comply with traditional religious practices. Later edicts targeted the clergy and demanded universal sacrifice, ordering all inhabitants to sacrifice to the gods. The persecution varied in intensity across the empire—weakest in Gaul and Britain, where only the first edict was applied, and strongest in the Eastern provinces. Persecutory laws were nullified by different emperors (Galerius with the Edict of Serdica in 311) at different times, but Constantine and Licinius' Edict of Milan in 313 has traditionally marked the end of the persecution. Christians had been subject to intermittent local discrimination in the empire, but emperors prior to Diocletian were reluctant to issue general laws against the relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Selection Before 1059
The selection of the pope, the bishop of Rome and supreme pontiff of the Roman Catholic Church, prior to the promulgation of '' In nomine Domini'' in 1059 varied throughout history. Popes were often appointed by their predecessors or by political rulers. While some kind of election often characterized the procedure, an election that included meaningful participation of the laity was rare, especially as the popes' claims to temporal power solidified into the Papal States. The practice of papal appointment during this period would later result in the ''jus exclusivae'', i.e., a right to veto the selection that Catholic monarchs exercised into the twentieth century. The absence of an institutionalized procedure of papal succession facilitated religious schism, and the Catholic Church currently regards several papal claimants before 1059 as antipopes. Further, the frequent requirement of political approval of elected popes significantly lengthened periods of ''sede vacante'', i.e., tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Power (Papal)
The temporal power of the Holy See designates the political and secular influence of the Holy See, the leading of a state by the pope of the Catholic Church, as distinguished from its spiritual and pastoral activity. Origins Pope Gregory II's defiance of the Byzantine emperor Leo III the Isaurian as a result of the first iconoclastic controversy (726 AD) in the Byzantine Empire, prepared the way for a long series of revolts, schisms and civil wars that eventually led to the establishment of the temporal power of the popes. For over a thousand years popes ruled as sovereign over an amalgam of territories on the Italian peninsula known as the Papal States, from the capital, Rome. Avignon also came under the jurisdiction of the Papal States in 1348. Early modern period Theologian Robert Bellarmine, in his 16th-century dogmatic work '' Disputationes'' strongly affirmed the authority of the pope as the vicar of Christ. However, he reasoned that since Christ did not ''exerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Miltiades
Pope Miltiades ( grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης, ''Miltiádēs''), also known as Melchiades the African ( ''Melkhiádēs ho Aphrikanós''), was the bishop of Rome from 311 to his death on 10 or 11 January 314. It was during his pontificate that Emperor Constantine the Great issued the Edict of Milan (313), giving Christianity legal status within the Roman Empire. The pope also received the palace of Empress Fausta where the Lateran Palace, the papal seat and residence of the papal administration, would be built. At the Lateran Council, during the schism with the Church of Carthage, Miltiades condemned the rebaptism of apostatised bishops and priests, a teaching of Donatus Magnus. Background The year of Miltiades' birth is unknown but it is known that he was of North African descent and, according to the '' Liber Pontificalis'', compiled from the 5th century onwards, a Roman citizen. Miltiades and his successor, Sylvester I, were part of the clergy of Pope Marcellinus. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Saint Peter's Basilica
Old St. Peter's Basilica was the building that stood, from the 4th to 16th centuries, where the new St. Peter's Basilica stands today in Vatican City. Construction of the basilica, built over the historical site of the Circus of Nero, began during the reign of Emperor Constantine I. The name "old St. Peter's Basilica" has been used since the construction of the current basilica to distinguish the two buildings. History Construction began by orders of the Roman Emperor Constantine I between 318 and 322, and took about 40 years to complete. Over the next twelve centuries, the church gradually gained importance, eventually becoming a major place of pilgrimage in Rome. Papal coronations were held at the basilica, and in 800, Charlemagne was crowned emperor of the Holy Roman Empire there. In 846, Saracens sacked and damaged the basilica. The raiders seem to have known about Rome's extraordinary treasures. Some holy—and impressive—basilicas, such as St. Peter's Basilica, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
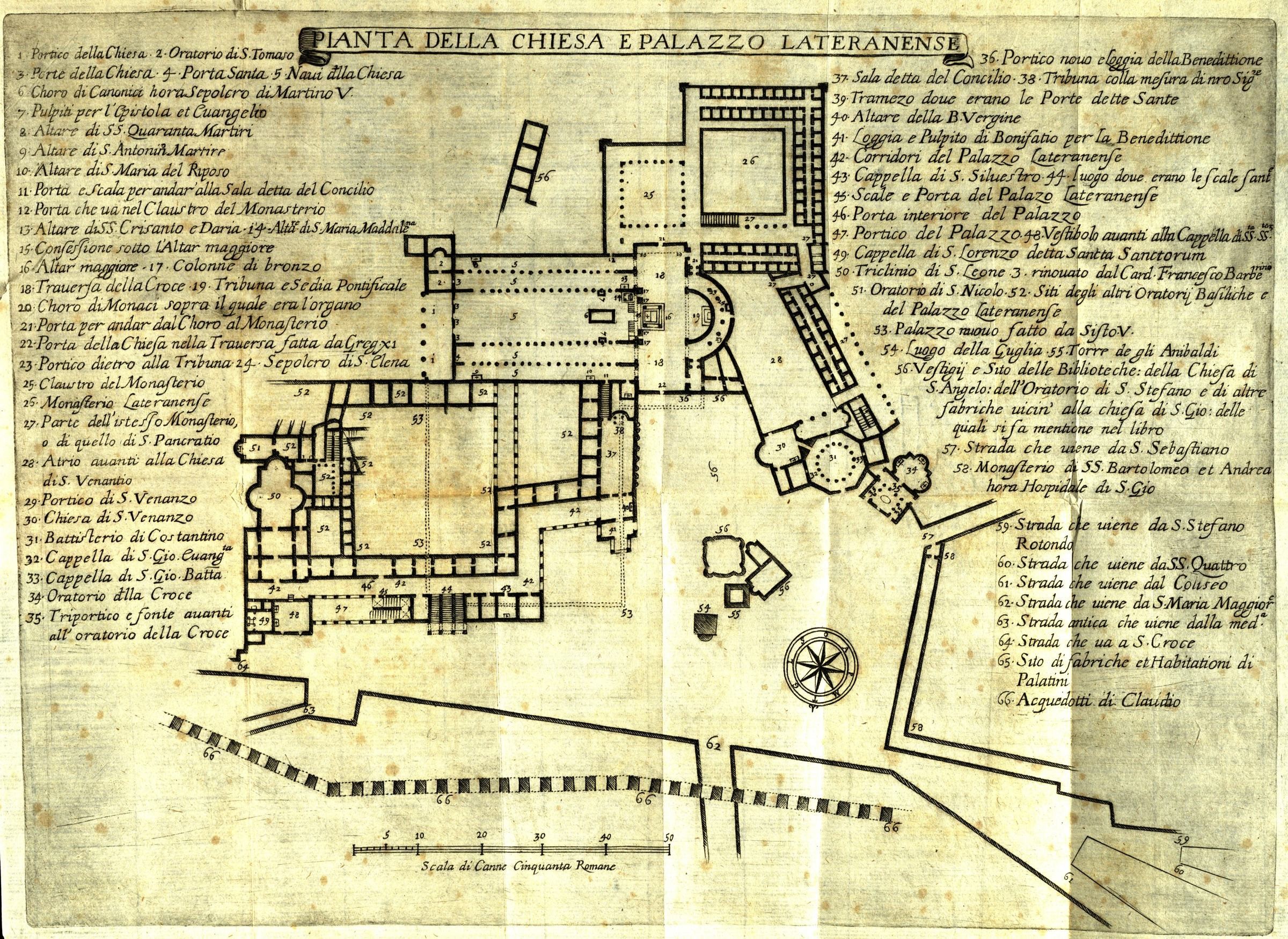
Lateran Palace
The Lateran Palace ( la, Palatium Lateranense), formally the Apostolic Palace of the Lateran ( la, Palatium Apostolicum Lateranense), is an ancient palace of the Roman Empire and later the main papal residence in southeast Rome. Located on St. John's Square in Lateran on the Caelian Hill, the palace is adjacent to the Archbasilica of Saint John Lateran, the cathedral church of Rome. From the fourth century, the palace was the principal residence of the popes, and continued so for about a thousand years until the Apostolic Residence ultimately moved to the Vatican. The palace is now used by the Vatican Historical Museum, which illustrates the history of the Papal States. The palace also houses the offices of the Vicariate of Rome, as well as the residential apartments of the Cardinal Vicar, the pope's delegate for the daily administration of the diocese. Until 1970, the palace was also home to the important collections of the Lateran Museum, now dispersed among other parts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Julius I
Pope Julius I was the bishop of Rome from 6 February 337 to his death on 12 April 352. He is notable for asserting the authority of the pope over the Arian Eastern bishops, as well as a dubious claim that he set 25 December as the official birthdate of Jesus. Pontificate Julius was a native of Rome and was chosen as successor of Pope Mark after the Roman seat had been vacant for four months. Arianism Julius is chiefly known by the part he took in the Arian controversy. After the followers of Eusebius of Nicomedia, who had become the patriarch of Constantinople, renewed their deposition of Athanasius of Alexandria at a synod held in Antioch in 341, they resolved to send delegates to Constans, emperor of the West, and also to Julius, setting forth the grounds on which they had proceeded. Julius, after expressing an opinion favourable to Athanasius, adroitly invited both parties to lay the case before a synod to be presided over by himself. This proposal, however, the Arian Eastern b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Mark
Pope Mark ( la, Marcus) was the bishop of Rome from 18 January to his death on 7 October 336. Little is known of Mark's early life. According to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', he was a Roman, and his father's name was Priscus. Mark succeeded Sylvester I as pope on 18 January 336. Some evidence suggests that the early lists of bishops and martyrs known as the ''Depositio episcoporum'' and ''Depositio martyrum'' were begun during his pontificate. According to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', Pope Mark issued a constitution investing the bishop of Ostia with a pallium and confirming his power to consecrate newly elected popes. Likewise according to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', Pope Mark is credited with the foundation of the Basilica of San Marco, a basilica in Rome, and a cemetery church over the Catacomb of Balbina, just outside the city on lands obtained as a donation from Emperor Constantine. Mark died of natural causes on 7 October and was buried in the catacomb of Balbina. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople (Istanbul), New Rome and ''primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of the several autocephalous churches which compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. The ecumenical patriarch is regarded as the representative and spiritual leader of many Orthodox Christians worldwide. The term ''ecumenical'' in the title is a historical reference to the Ecumene, a Greek designation for the civilised world, i.e. the Roman Empire, and it stems from Canon 28 of the Council of Chalcedon. The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople is one of the most enduring institutions in the world and has had a prominent part in world history. The ecumenical patriarchs in ancient times helped in the spread of Christianity and the resolution of various doctrinal disputes. In the Middle Ages they played a major role in the affairs of the Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_Foto_G._Dall'Orto_28-5-2006.jpg)