|
Bioinformatics (journal)
''Bioinformatics'' (sometimes called ''Bioinformatics Oxford journal'') is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research and software in bioinformatics and computational biology. It is the official journal of the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB), together with ''PLOS Computational Biology''. Authors can pay extra for open access and are allowed to self-archive after 1 year. The journal was established as ''Computer Applications in the Biosciences'' (''CABIOS'') in 1985. The founding editor-in-chief was Robert J. Beynon. In 1998, the journal obtained its current name and established an online version of the journal. It is published by Oxford University Press and, as of 2014, the editors-in-chief are Alfonso Valencia and Janet Kelso. Previous editors include Chris Sander, Gary Stormo, Christos Ouzounis, Martin Bishop, and Alex Bateman. In 2014, these five editors were appointed the first Honorary Editors of ''Bioinformatics''. According to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics Journal Cover
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for ''in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable properties (esp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBank DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biweekly Journals
A weekly newspaper is a general-news or current affairs publication that is issued once or twice a week in a wide variety broadsheet, magazine, and digital formats. Similarly, a biweekly newspaper is published once every two weeks. Weekly newspapers tend to have smaller circulations than daily newspapers, and often cover smaller territories, such as one or more smaller towns, a rural county, or a few neighborhoods in a large city. Frequently, weeklies cover local news and engage in community journalism. Most weekly newspapers follow a similar format as daily newspapers (i.e., news, sports, obituaries, etc.). However, the primary focus is on news within a coverage area. The publication dates of weekly newspapers in North America vary, but often they come out in the middle of the week (Wednesday or Thursday). However, in the United Kingdom where they come out on Sundays, the weeklies which are called ''Sunday newspapers'', are often national in scope and have substantial circul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications Established In 1998
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Convention, article 3(3) URL last accessed 2010-05-10.Universal Copyright Convention, Geneva text (1952), article VI . URL last accessed 2010-05-10. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to text, images, or other audio-visual content, including paper ( |
Bioinformatics And Computational Biology Journals
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Conference On Computational Biology
The European Conference on Computational Biology (ECCB) is a scientific meeting on the subjects of bioinformatics and computational biology. It covers a wide spectrum of disciplines, including bioinformatics, computational biology, genomics, computational structural biology, and systems biology. ECCB is organized annually in different European cities. Since 2007, the conference has been held jointly with Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB) every second year. The conference also hosts the European ISCB Student Council Symposium. The proceedings of the conference are published by the journal ''Bioinformatics''. History Formation ECCB was formed with the intent of providing a European conference focusing on advances in computational biology and their application to problems in molecular biology. The conference was initially to be held on a rotating basis, with the idea that previously successful regional conferences (for instance, the German Conference on Bioinformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Systems For Molecular Biology
Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB) is an annual academic conference on the subjects of bioinformatics and computational biology organised by the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB). The principal focus of the conference is on the development and application of advanced computational methods for biological problems. The conference has been held every year since 1993 and has grown to become one of the largest and most prestigious meetings in these fields, hosting over 2,000 delegates in 2004. From the first meeting, ISMB has been held in locations worldwide; since 2007, meetings have been located in Europe and North America in alternating years. Since 2004, European meetings have been held jointly with the European Conference on Computational Biology (ECCB). The main ISMB conference is usually held over three days and consists of presentations, poster sessions and keynote talks. Most presentations are given in multiple parallel tracks; however, key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson Reuters
Thomson Reuters Corporation ( ) is a Canadian multinational media conglomerate. The company was founded in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, where it is headquartered at the Bay Adelaide Centre. Thomson Reuters was created by the Thomson Corporation's purchase of the British company Reuters Group in April 2008. It is majority-owned by The Woodbridge Company, a holding company for the Thomson family. History Thomson Corporation The forerunner of the Thomson company was founded by Roy Thomson in 1934 in Ontario, as the publisher of ''The Timmins Daily Press''. In 1953, Thomson acquired the ''Scotsman'' newspaper and moved to Scotland the following year. He consolidated his media position in Scotland in 1957, when he won the franchise for Scottish Television. In 1959, he bought the Kemsley Group, a purchase that eventually gave him control of the '' Sunday Times''. He separately acquired the ''Times'' in 1967. He moved into the airline business in 1965, when he acquired Britanni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
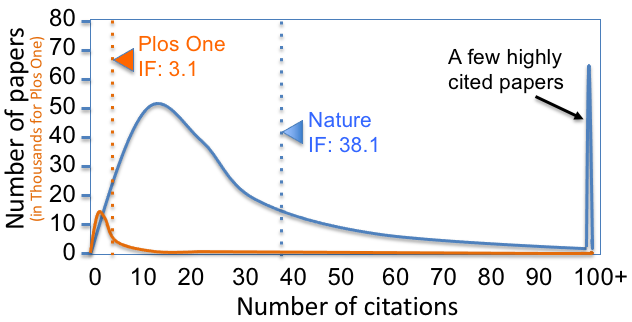
Impact Factor
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science. As a journal-level metric, it is frequently used as a proxy for the relative importance of a journal within its field; journals with higher impact factor values are given the status of being more important, or carry more prestige in their respective fields, than those with lower values. While frequently used by universities and funding bodies to decide on promotion and research proposals, it has come under attack for distorting good scientific practices. History The impact factor was devised by Eugene Garfield, the founder of the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) in Philadelphia. Impact factors began to be calculated yearly starting from 1975 for journals listed in the ''Journal Citation Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Citation Reports
''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publicationby Clarivate Analytics (previously the intellectual property of Thomson Reuters). It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science-Core Collections. It provides information about academic journals in the natural sciences and social sciences, including impact factors. The ''JCR'' was originally published as a part of ''Science Citation Index''. Currently, the ''JCR'', as a distinct service, is based on citations compiled from the '' Science Citation Index Expanded'' and the '' Social Sciences Citation Index''.- - - Basic journal information The information given for each journal includes: * the basic bibliographic information of publisher, title abbreviation, language, ISSN * the subject categories (there are 171 such categories in the sciences and 54 in the social sciences) Citation information * Basic citation data: ** the number of articles published during that year and ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alex Bateman
Alexander George Bateman is a computational biologist and Head of Protein Sequence Resources at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Cambridge, UK. He has led the development of the Pfam biological database and introduced the Rfam database of RNA families. He has also been involved in the use of Wikipedia for community-based annotation of biological databases. Education Bateman received a Bachelor of Science degree in Biochemistry from Newcastle University in 1994. He received his PhD from the University of Cambridge in 1997, for research supervised by Cyrus Chothia on the evolution of the immunoglobulin protein superfamily. During this time, he also worked with Sean Eddy to discover novel protein domains using the HMMER software. Career and research In 1997, Bateman joined the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute to lead the development of the Pfam biological database. In 2003, he introduced the Rfam data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |