|
Bigerriones
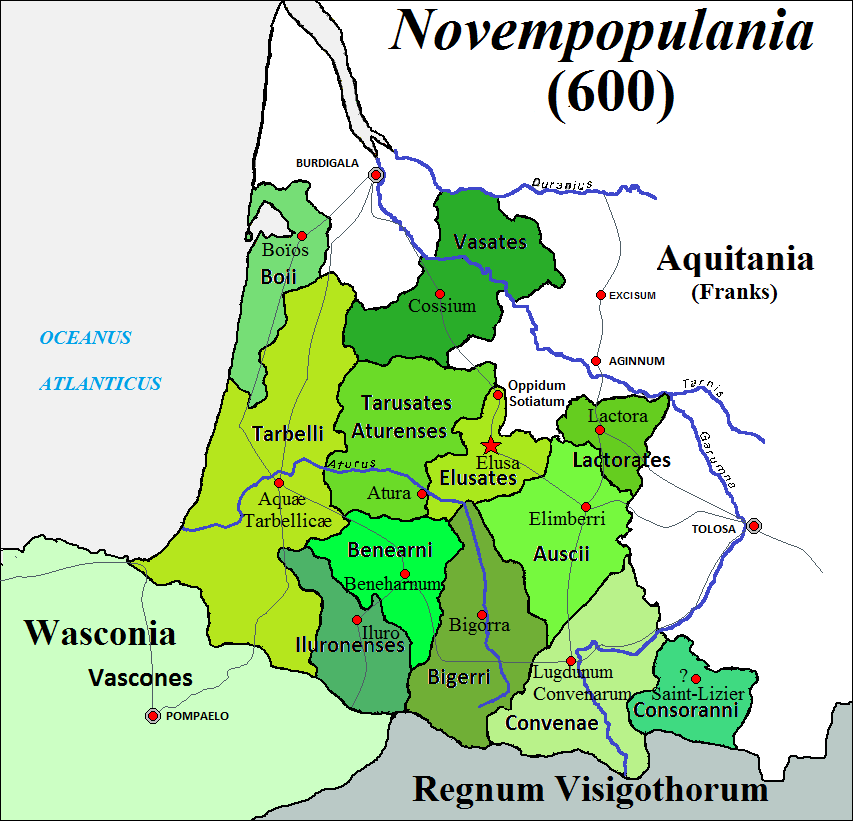
The Bigerriones or Begerri were an Aquitani tribe dwelling in present-day Bigorre during the Iron Age. They were subjugated in 56 BC by the Roman forces of Caesar's legatus P. Licinius Crassus. Name They are mentioned as ''Bigerriones'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), and as ''Begerri'' (var. ''Begerbi'', ''Bebergi'', ''Bergebi'') by Pliny (1st c. AD). The Bigorre region, attested as ''Begorra'' ca. 400 AD, is named after the tribe. Geography The Bigerriones lived in the Bigorre region, in the northern foreland of the Pyrenees. Their territory was located north of the Onobrisates, south of the Atures, Elusates and Auscii, east of the Venarni, and west of the Volcae Tectosages The Volcae () were a Gallic tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedonia c. 270 BC and fought the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC. Tribes known by the name Volcae were found si .... Their chief town was known as Bigorra Cast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitani Tribes Map-fr
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region ''Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such as Julius Caesar and Strabo clearly distinguish the Aquitani from the other peoples of Gaul, and note their similarity to others in the Iberian Peninsula. During the process of Romanization, the Aquitani gradually adopted Latin (Vulgar Latin) and the Roman civilization. Their old language, the Aquitanian language, was a precursor of the Basque language Trask, L. ''The History of Basque'' Routledge: 1997 and the substrate for the Gascon language (one of the Romance languages) spoken in Gascony. History At the time of the Roman conquest, Julius Caesar, who defeated them in his campaign in Gaul, describes them as making up a distinct part of Gaul: Despite apparent cultural and linguistic connections to (Vascones), the area of Aquitania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigorre
Bigorre ({{IPA-fr, biɡɔʁ; Gascon: ''Bigòrra'') is a region in southwest France, historically an independent county and later a French province, located in the upper watershed of the Adour, on the northern slopes of the Pyrenees, part of the larger region known as Gascony. Today Bigorre comprises the centre and west of the ''département'' of Hautes-Pyrénées, with two small exclaves in the neighbouring Pyrénées Atlantiques. Its inhabitants are called '' Bigourdans''. Before the French Revolution, the province of Bigorre had a land area of 2,574 km² (994 sq. miles). Its capital was Tarbes. At the 1999 French census, there lived 177,575 inhabitants on the territory of the former province of Bigorre, which means a density of 69 inh. per km² (179 inh. per sq. mile). The largest urban areas in Bigorre are Tarbes, with 77,414 inhabitants in 1999, Lourdes, with 15,554 inhabitants in 1999, and Bagnères-de-Bigorre, with 11,396 inhabitants in 1999. At the time of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitani
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region ''Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such as Julius Caesar and Strabo clearly distinguish the Aquitani from the other peoples of Gaul, and note their similarity to others in the Iberian Peninsula. During the process of Romanization, the Aquitani gradually adopted Latin (Vulgar Latin) and the Roman civilization. Their old language, the Aquitanian language, was a precursor of the Basque language Trask, L. ''The History of Basque'' Routledge: 1997 and the substrate for the Gascon language (one of the Romance languages) spoken in Gascony. History At the time of the Roman conquest, Julius Caesar, who defeated them in his campaign in Gaul, describes them as making up a distinct part of Gaul: Despite apparent cultural and linguistic connections to (Vascones), the area of Aquitania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elusates
The Elusates were an Aquitani tribe dwelling in the modern Gers department, around present-day Eauze, France during the Iron Age and the Roman period. They were subjugated in 56 BC by the Roman forces of Caesar's legatus P. Licinius Crassus. Name They are mentioned as ''Elusates'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Pliny (1st c. AD), and as Elusa on the ''Tabula Peutingeriana'' (5th c. AD)., s.v. ''Elusates'' and ''Elusa''. The etymology of the ethnonym ''Elusates'' remains uncertain, but the root ''elus(a)''- is generally presumed to be of Aquitanian origin. Alternatively, a connection with the Celtic root *''elu(o)''- ('numerous') has also been proposed. The city of Eauze, attested in the 4th century AD as ''civitas Elusa'', is named after the tribe. Geography The Elusates dwelled south of the Sotiates, north of the Onobrisates, east of the Tarusates, west of the Lactorates, and northwest of the Ausci., Map 25: Hispania Tarraconensis. The pre-Roman oppidum of Esbé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania ( , ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gallia Lugdunensis, Gallia Narbonensis, and Hispania Tarraconensis.John Frederick Drinkwater (1998). "Gaul (Transalpine)". ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Civilization.'' Ed. Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth. Oxford University PressOxford Reference Online Tribes of Aquitania Fourteen Celtic tribes and over twenty Aquitanian tribes occupied the area from the northern slopes of the Pyrenees in the south to the ''Liger'' (Loire) river in the north. The major tribes are listed at the end of this section.''Strabo: The Geography''The Aquitani There were more than twenty tribes of Aquitani, but they were small and lacking in repute; the majority of the tribes lived along the ocean, while the others reached up into the interior and to the sum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitanian Language
The Aquitanian language was the language of the ancient Aquitani, spoken on both sides of the western Pyrenees in ancient Aquitaine (approximately between the Pyrenees and the Garonne, in the region later known as Gascony) and in the areas south of the Pyrenees in the valleys of the Basque Country before the Roman conquest. It probably survived in Aquitania north of the Pyrenees until the Early Middle Ages. Archaeological, toponymical, and historical evidence shows that it was a language or group of languages that represent a precursor of the Basque language. The most important pieces of evidence are a series of votive and funerary texts in Latin, dated to the first three centuries AD, which contain about 400 personal names and 70 names of gods. History Aquitanian and its modern relative, Basque, are commonly thought to be Pre-Indo-European languages, remnants of the languages spoken in Western Europe before the arrival of Indo-European speakers. Some claims have been made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Lézer
Saint-Lézer is a commune in the Hautes-Pyrénées department in south-western France. See also *Communes of the Hautes-Pyrénées department An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, religious ... References Communes of Hautes-Pyrénées {{HautesPyrénées-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcae Tectosages
The Volcae () were a Gallic tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedonia c. 270 BC and fought the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC. Tribes known by the name Volcae were found simultaneously in southern Gaul, Moravia, the Ebro valley of the Iberian Peninsula, and Galatia in Anatolia. The Volcae appear to have been part of the late La Tène material culture, and a Celtic identity has been attributed to the Volcae, based on mentions in Greek and Latin sources as well as onomastic evidence. Driven by highly mobile groups operating outside the tribal system and comprising diverse elements, the Volcae were one of the new ethnic entities formed during the Celtic military expansion at the beginning of the 3rd century BC. Collecting in the famous excursion into the Balkans, ostensibly, from the Greek point of view, to raid Delphi, a branch of the Volcae split from the main group on the way into the Balkans and joined tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auscii
The Auscii or Ausci were an Aquitani tribe dwelling around present-day Auch during the Iron Age. Alongside the Tarbelli, they were one of the most powerful peoples of Aquitania. Name They are mentioned as ''Ausci'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), Pliny (1st c. AD) and Pomponius Mela (mid-1st c. AD), and as ''Au̓skíois'' (Αὐσκίοις) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD)., s.v. ''Auscii''. The ethnonym ''Auscii'' may be related to the prefix ''eusk''-, meaning 'Basque' in the Basque language ('' euskara''). The city of Auch, attested as ''civitas Auscius'' in the early 4th century AD, is named after the tribe. Geography Their territory was located north of the Onobrisates, west of the Cambolectri and Volcae Tectosages, south of the Lactorates, west of the Atures. The chief town of the Auscii was known as Elimberrum (modern Auch), whose name can be compared to the Basque ''ili-berri'' ('new town'). Culture It is believed that the Auscii spoke a form or dialect of the Aquit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |