|
Big Hill
The Big Hill on the Canadian Pacific Railway main line in British Columbia, Canada, was the most difficult piece of railway track on the Canadian Pacific Railway's route. It was situated in the rugged Canadian Rockies west of the Continental Divide of the Americas and Kicking Horse Pass. Even though the Big Hill was replaced by the Spiral Tunnels in 1909, the area has long been a challenge to the operation of trains and remains so to this day. Construction To complete the Pacific railway as quickly as possible, a decision was made to delay blasting a lengthy tunnel through Mount Stephen and instead build a temporary line over it. Instead of the desired 2.2% grade (116 feet to the mile) a steep 4.5% (some sources say 4.4%) grade was built in 1884. This was one of the steepest adhesion railway lines anywhere. (4.5% = 1 in 22.22). It descended from Wapta Lake to the base of Mount Stephen, along the Kicking Horse River to a point just west of Field, then rose again to meet the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Hill CPR
Big or BIG may refer to: * Big, of great size or degree Film and television * ''Big'' (film), a 1988 fantasy-comedy film starring Tom Hanks * ''Big!'', a Discovery Channel television show * ''Richard Hammond's Big'', a television show presented by Richard Hammond * ''Big'' (TV series), a 2012 South Korean TV series * ''Banana Island Ghost'', a 2017 fantasy action comedy film Music * '' Big: the musical'', a 1996 musical based on the film * Big Records, a record label * ''Big'' (album), a 2007 album by Macy Gray * "Big" (Dead Letter Circus song) * "Big" (Sneaky Sound System song) * "Big" (Rita Ora and Imanbek song) * "Big", a 1990 song by New Fast Automatic Daffodils * "Big", a 2021 song by Jade Eagleson from ''Honkytonk Revival'' *The Notorious B.I.G., an American rapper Places * Allen Army Airfield (IATA code), Alaska, US * BIG, a VOR navigational beacon at London Biggin Hill Airport * Big River (other), various rivers (and other things) * Big Island (disambigua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
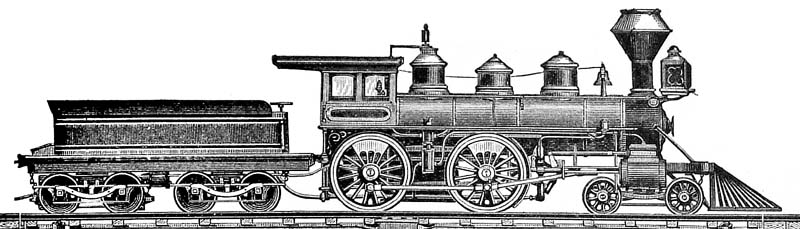
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Greater Vancouver, Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2.6million in 2021, making it the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada#List, third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley Regional District, Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 people per square kilometre, and fourth highest in North America (after New York City, San Francisco, and Mexico City). Vancouver is one of the most Ethnic origins of people in Canada, ethnically and Languages of Canada, linguistically diverse cities in Canada: 49.3 percent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruling Gradient
The term ruling grade is usually used as a synonym for "steepest climb" between two points on a railroad. More simply, the steepest grade to be climbed dictates how powerful the motive power (or how light the train) must be in order for the run to be made without assistance. Even if 99% of the line could be run with a low-powered (and inexpensive) locomotive, if at some point on the line there is a steeper gradient than such train would be able to climb, this gradient "rules" that a more powerful locomotive must be used, in spite of it being far too powerful for the rest of the line. This is why special "helper engines" (also dubbed "Bankers") are often stationed near steep grades on otherwise mild tracks. It is cheaper than running a too-powerful locomotive over the entire track mileage just in order to make the grade, especially when multiple trains run over the line each day (to help justify the fixed daily cost of the helper operation). In the 1953 edition of ''Railway Engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Ogden (British Columbia)
Mount Ogden is a mountain in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. Description Mount Ogden is a summit located in Yoho National Park. The peak is situated 3.5 km west of the Continental Divide in the Waputik Range. Takakkaw Falls is six km to the northwest, and Sherbrooke Lake lies immediately below the southeast slope. Precipitation runoff from Mount Ogden drains west into the Yoho River and east into Sherbrooke Creek, which are both tributaries of the Kicking Horse River. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises over 1,300 meters (4,265 feet) above Yoho Valley in two kilometers (1.2 mile). Mt. Ogden is visible from the Trans-Canada Highway ( Highway 1) which traverses the southern base of the mountain. The nearest higher peak is Mount Niles, to the north. History The name "Ogden Mountain" was adopted June 30, 1904, and the toponym was changed to "Mount Ogden" June 30, 1911. The mountain is named after Isaac Gouverneur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Mountain (Yoho)
Cathedral Mountain is a complex massif located six kilometres northwest of Lake O'Hara in Yoho National Park, in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. Its shape and structure conjures up a resemblance to a gothic cathedral that has inspired many artists, including Group of Seven's Arthur Lismer, to paint it back in 1928. This picturesque mountain is visible from Highway 1, the Trans-Canada Highway near Kicking Horse Pass. Its nearest higher peak is Mount Stephen, to the west. To prevent damage to its operations, CP Rail pumps overflow from ''Teacup Lake'' down the west face of Cathedral in order to minimize the subglacial lake's discharging in a phenomenon known as a jökulhlaup. History The name Cathedral Mountain was in use as early as 1884 and appeared on George Dawson's 1886 map. The first ascent of Cathedral Mountain was made in 1901 by James Outram, with guides Joseph Bossoney, and Christian Klucker. The mountain's name was officially adopted in 1924 when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogers Pass (British Columbia)
Rogers Pass is a high mountain pass through the Selkirk Mountains of British Columbia, but the term also includes the approaches used by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) and the Trans-Canada Highway. In the heart of Glacier National Park, this tourism destination since 1886 is a National Historic Site. Topography Rogers Pass is the lowest route between the Sir Donald and Hermit ranges of the Selkirks, providing a shortcut along the southern perimeter of the Big Bend of the Columbia River from Revelstoke on the west to Donald, near Golden, British Columbia, Golden, on the east. The pass is formed by the headwaters of the Illecillewaet River to the west and by the Beaver River (Columbia River), Beaver River to the east. These rivers are tributaries of the Columbia, which arcs to the north. Railway Proposal & planning During the 1870s, when the transcontinental was being planned, the preferred route through the Canadian Rockies was the northerly Yellowhead Pass. After awarding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Schwitzer
John Edward Schwitzer (April 1870 – January 1911) was assistant chief engineer for the Canadian Pacific Railway in the early 1900s. He was known for two major projects on the CPR, both that removed costly bottlenecks on the routes. One of those was the Lethbridge Viaduct or High Level Bridge in Lethbridge, Alberta, which was built over the Oldman River valley to shorten the CP Crowsnest Line between Lethbridge and Fort Macleod by over 8 km. This eliminated a problematic series of smaller wood bridges used on the old route. A smaller bridge, similar to the one in Lethbridge, was built near Monarch, Alberta as part of the rerouting. Another project which he is most noted for was the Spiral Tunnels, which eliminated the infamous Big Hill, where the mainline dropped on a 4.4% grade near Field, British Columbia. The tunnels allowed the grade to drop to 2.2%, making it a more safer and less-costly route. Both projects were completed in 1909, months apart from each other. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral (railway)
A spiral (sometimes called a spiral loop or just loop) is a technique employed by railways to ascend steep hills. A railway spiral rises on a steady curve until it has completed a loop, passing over itself as it gains height, allowing the railway to gain vertical elevation in a relatively short horizontal distance. It is an alternative to a zig-zag, and avoids the need for the trains to stop and reverse direction while ascending. If the train is longer than the length of each loop it may be possible to view it looping above itself. The term "loop" is also often used for a railway that curves sharply and goes back on itself: if the railway crosses itself, then it forms a spiral or helix; otherwise, it forms the much more common horseshoe curve or bend. List of spirals Argentina * Two spirals between Tacuara and Meseta at and on the heritage ''Tren a las Nubes'' section of the Salta–Antofagasta railway part of the General Manuel Belgrano Railway. Australia * Spiral on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Spiral Tunnels Map
Old or OLD may refer to: Places *Old, Baranya, Hungary *Old, Northamptonshire, England *Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD) *OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Maine, United States People *Old (surname) Music *OLD (band), a grindcore/industrial metal group * ''Old'' (Danny Brown album), a 2013 album by Danny Brown * ''Old'' (Starflyer 59 album), a 2003 album by Starflyer 59 * "Old" (song), a 1995 song by Machine Head *''Old LP'', a 2019 album by That Dog Other uses * ''Old'' (film), a 2021 American thriller film *''Oxford Latin Dictionary'' *Online dating *Over-Locknut Distance (or Dimension), a measurement of a bicycle wheel and frame *Old age See also *List of people known as the Old * * *Olde, a list of people with the surname *Olds (other) Olds may refer to: People * The olds, a jocular and irreverent online nickname for older adults * Bert Olds (1891–1953), Australian rules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Exits Lower Spiral
Power most often refers to: * Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work" ** Engine power, the power put out by an engine ** Electric power * Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events ** Abusive power Power may also refer to: Mathematics, science and technology Computing * IBM POWER (software), an IBM operating system enhancement package * IBM POWER architecture, a RISC instruction set architecture * Power ISA, a RISC instruction set architecture derived from PowerPC * IBM Power microprocessors, made by IBM, which implement those RISC architectures * Power.org, a predecessor to the OpenPOWER Foundation * SGI POWER Challenge, a line of SGI supercomputers Mathematics * Exponentiation, "''x'' to the power of ''y''" * Power function * Power of a point * Statistical power Physics * Magnification, the factor by which an optical system enlarges an image * Optical power, the degree to which a lens converges or diverges light Social sciences and politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |