|
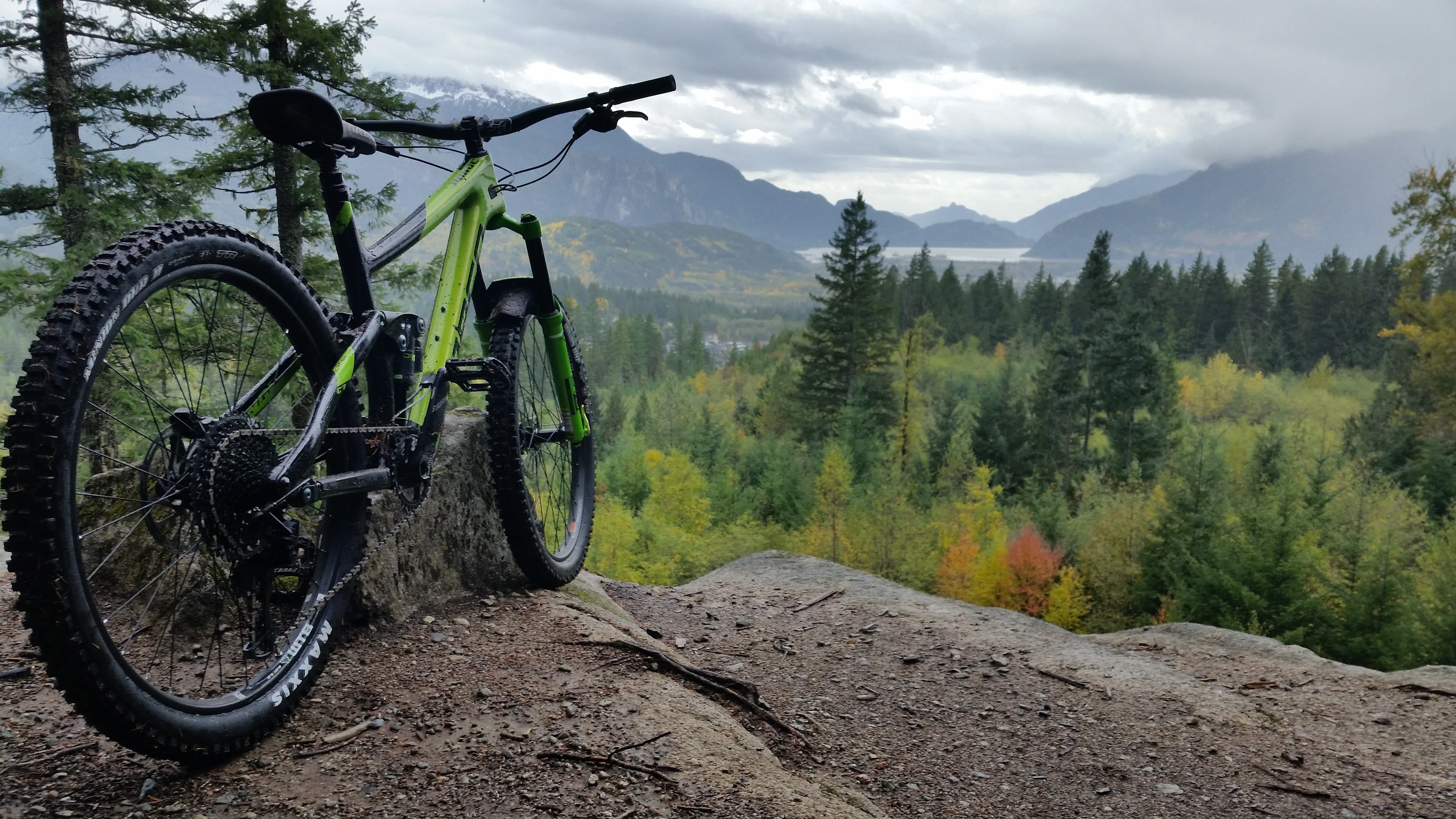
Bicycle Fork
A bicycle fork is the part of a bicycle that holds the front wheel. A fork typically consists of two ''blades'' which are joined at the top by a fork ''crown.'' The crown is often at the front. Most suspension forks have an arch connecting the two side of the lowers (the part connected to the axle.) It is often in front of the stanchions (shaft the lowers slide on) but not always. Above the crown, a ''steerer tube'' attaches the fork to the bicycle and the handlebars (via a stem) allowing the rider to steer the bicycle. The steerer tube of the fork interfaces with the frame via bearings called a headset mounted in the head tube. At the bottom of the fork, ''fork ends'' hold the wheel. Usually, either the axle is bolted to the fork, or a ''quick release skewer'' passes through a hollow axle, clamping the axle to the fork. The term ''fork'' is sometimes also used to describe the part of a bicycle that holds the rear wheel, which on 19th century ''ordinary'' or ''penny-farthin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fox 32 RL Fork
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush''). Twelve species belong to the monophyletic "true foxes" group of genus ''Vulpes''. Approximately another 25 current or extinct species are always or sometimes called foxes; these foxes are either part of the paraphyletic group of the South American foxes, or of the outlying group, which consists of the bat-eared fox, gray fox, and island fox. Foxes live on every continent except Antarctica. The most common and widespread species of fox is the red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') with about 47 recognized subspecies. The global distribution of foxes, together with their widespread reputation for cunning, has contributed to their prominence in popular culture and folklore in many societies around the world. The hunting of foxes with packs of hounds, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headset (bicycle Part)
The headset is the set of components on a bicycle that provides a rotatable interface between the bicycle fork and the head tube of a bicycle frame. The tube through which the steerer of the fork passes is called the head tube. A typical headset consists of two cups that are pressed into the top and bottom of the headtube. Inside the two cups are bearings which provide a low friction contact between the bearing cup and the steerer. Sizes Traditional bicycle head tubes and headsets are sized for a steerer tube (also known as the fork column). Many frame and fork manufacturers are now building their parts around a steerer tube with a diameter of 1⅛ inch. The larger diameter of the head tube and headset gives added stiffness to the steering portion of the bicycle. Common sizes *1" or 1 inch (25.4 mm). This may have a fork crown (The base of the fork steerer tube) of a number of different dimensions. Milling may be necessary to make some headsets fit. ::26.4 mm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannondale Bicycle Corporation
The Cannondale Bicycle Corporation is an American division of Dutch conglomerate Pon Holdings that supplies bicycles. Its headquarters are in Wilton, Connecticut with engineering offices in Freiburg, Germany. Frames are manufactured in Taiwan. History The company was founded in 1971 by Joe Montgomery and Murdock MacGregor to manufacture precast concrete housing. Later Ron Davis came to Cannondale from CBS Laboratories where he was vice-president in charge of the development of microfilm reproduction. Davis had an idea for an internal combustion engine that would use ammonia as fuel. Davis, with MacGregor as his assistant, managed to duplicate and exceed results obtained by Allison Engine, then a division of General Motors. Faced with a commitment to invest a large amount of capital to take the project to a workable model installed in an automobile, Montgomery decided that the company should raise capital by developing and marketing other products that they had conceived. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
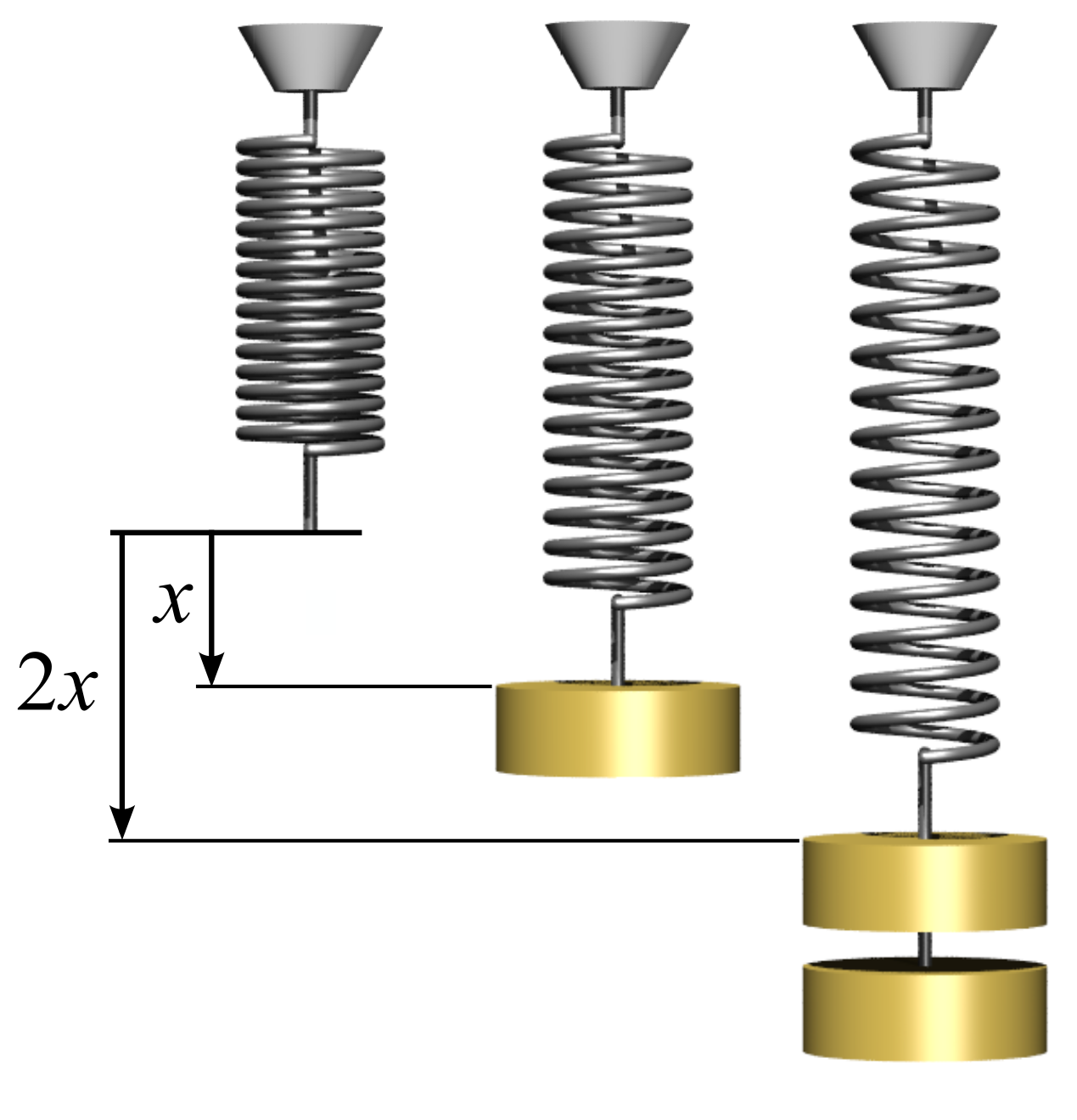
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic polymer'', is often used interchangeably with rubber, although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. At ambient temperatures, such rubbers are thus relatively compliant ( E ≈ 3 M Pa) and deformable. Their primary uses are for seals, adhesives and molded flexible parts. Application areas for different types of rubber are manifold and cover segments as diverse as tires, soles for shoes, and damping and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashpot
A dashpot, also known as a damper, is a mechanical device that resists motion via viscous friction. The resulting force is proportional to the velocity, but acts in the opposite direction, slowing the motion and absorbing energy. It is commonly used in conjunction with a spring. The process and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) symbol for a dashpot is . Types The two most common types of dashpots are linear and rotary. Linear damper Linear dashpots — or linear dampers — are used to exert a force opposite to a translation movement. They are generally specified by stroke (amount of linear displacement) and damping coefficient (force per velocity). Rotary damper Similarly, rotary dampers will tend to oppose any torque applied to them, in an amount proportional to their rotational speed. Their damping coefficients will usually be specified by torque per angular velocity. One can distinguish two kinds of viscous rotary dashpots: * Vane dashpots which have a limited angular ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring (device)
A spring is an elastic object that stores mechanical energy. In everyday use the term often refers to coil springs, but there are many different spring designs. Modern springs are typically manufactured from spring steel, although some non-metallic objects like the bow are also springs. When a conventional spring, without stiffness variability features, is compressed or stretched from its resting position, it exerts an opposing force approximately proportional to its change in length (this approximation breaks down for larger deflections). The ''rate'' or ''spring constant'' of a spring is the change in the force it exerts, divided by the change in deflection of the spring. That is, it is the gradient of the force versus deflection curve. An extension or compression spring's rate is expressed in units of force divided by distance, for example or N/m or lbf/in. A torsion spring is a spring that works by twisting; when it is twisted about its axis by an angle, it produces a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain, such as air or coil-sprung shocks used as suspension, larger and wider wheels and tires, stronger frame materials, and mechanically or hydraulically actuated disc brakes. Mountain biking can generally be broken down into five distinct categories: cross country, trail riding, all mountain (also referred to as "Enduro"), downhill, and freeride. This sport requires endurance, core strength and balance, bike handling skills, and self-reliance. Advanced riders pursue both steep technical descents and high incline climbs. In the case of freeride, downhill, and dirt jumping, aerial maneuvers are performed off both natural features and specially constructed jumps and ramps. Mountain bikers ride on off-road trails su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Absorbers
A shock absorber or damper is a mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy (typically heat) which is then dissipated. Most shock absorbers are a form of dashpot (a damper which resists motion via viscous friction). Description Pneumatic and hydraulic shock absorbers are used in conjunction with cushions and springs. An automobile shock absorber contains spring-loaded check valves and orifices to control the flow of oil through an internal piston (see below). One design consideration, when designing or choosing a shock absorber, is where that energy will go. In most shock absorbers, energy is converted to heat inside the viscous fluid. In hydraulic cylinders, the hydraulic fluid heats up, while in air cylinders, the hot air is usually exhausted to the atmosphere. In other types of shock absorbers, such as electromagnetic types, the dissipated energy can be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Bicycle
A mountain bike (MTB) or mountain bicycle is a bicycle designed for off-road cycling. Mountain bikes share some similarities with other bicycles, but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain, which makes them heavier, more complex and less efficient on smooth surfaces. These typically include a suspension fork, large knobby tires, more durable wheels, more powerful brakes, straight, extra wide handlebars to improve balance and comfort over rough terrain, and wide-ratio gearing optimised for topography and application (e.g., steep climbing or fast descending). Rear suspension is ubiquitous in heavier-duty bikes and now common even in lighter bikes. Dropper posts can be installed to allow the rider to quickly adjust the seat height (an elevated seat position is more effective for pedaling, but poses a hazard in aggressive maneuvers). Mountain bikes are generally specialized for use on mountain trails, single track, fire roads, and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannondale Headshok
The Cannondale Bicycle Corporation is an American division of Dutch conglomerate Pon Holdings that supplies bicycles. Its headquarters are in Wilton, Connecticut with engineering offices in Freiburg, Germany. Frames are manufactured in Taiwan. History The company was founded in 1971 by Joe Montgomery and Murdock MacGregor to manufacture precast concrete housing. Later Ron Davis came to Cannondale from CBS Laboratories where he was vice-president in charge of the development of microfilm reproduction. Davis had an idea for an internal combustion engine that would use ammonia as fuel. Davis, with MacGregor as his assistant, managed to duplicate and exceed results obtained by Allison Engine, then a division of General Motors. Faced with a commitment to invest a large amount of capital to take the project to a workable model installed in an automobile, Montgomery decided that the company should raise capital by developing and marketing other products that they had conceived. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspension Fork
Bicycle suspension is the system, or systems, used to ''suspend'' the rider and bicycle in order to insulate them from the roughness of the terrain. Bicycle suspension is used primarily on mountain bikes, but is also common on hybrid bicycles. Bicycle suspension can be implemented in a variety of ways, and any combination thereof: *Front suspension *Rear suspension *Suspension seatpost *Suspension saddle *Suspension stem (now uncommon) *Suspension hub Bicycles with only front suspension are referred to as hardtail and bicycles with suspension in both the front and rear are referred to as dual or full suspension bikes. When a bicycle has no suspension it is called rigid. Bicycles with only rear suspension are uncommon although the Brompton folding bicycle is equipped with rear only suspension. Although a stiffer frame is usually preferable, no material is infinitely stiff and therefore any frame will exhibit some flexing. Bicycle designers intentionally make frames in such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |