|
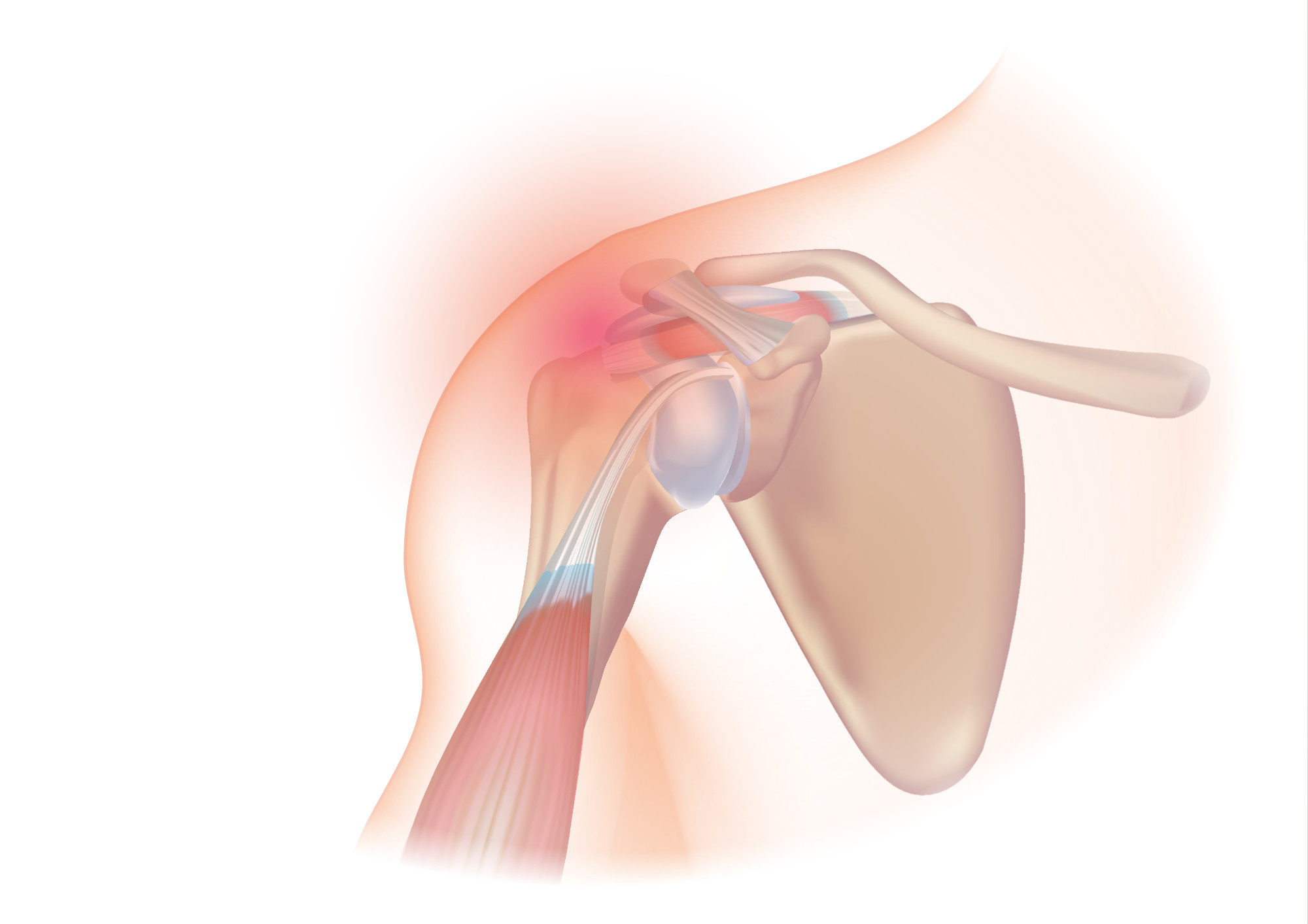
Biceps Tendon Rupture
A biceps tendon rupture or bicep tear is a complete or partial rupture of a tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. It can affect any of the three biceps brachii tendons - the proximal tendon of the short head of the muscle belly, the proximal tendon of the long head of the muscle belly, or the distal tendon. __TOC__ Signs and symptoms When a tendon of the biceps brachii ruptures the muscle belly retracts, meaning that it goes from a lengthened position under tension at two attachments, to a shortened position with a single attachment. This shortened position forms a bulge which is referred to as "Popeye's deformity," due to similarity in appearance to the cartoon character Popeye. Other signs at the time of injury may include ecchymosis, swelling, and/or a sharp pain accompanied by an audible popping sound. The pain may persist for prolonged periods of time depending on the response to the individualized treatment plan. Distal tendon rupture will cause significant weakness with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
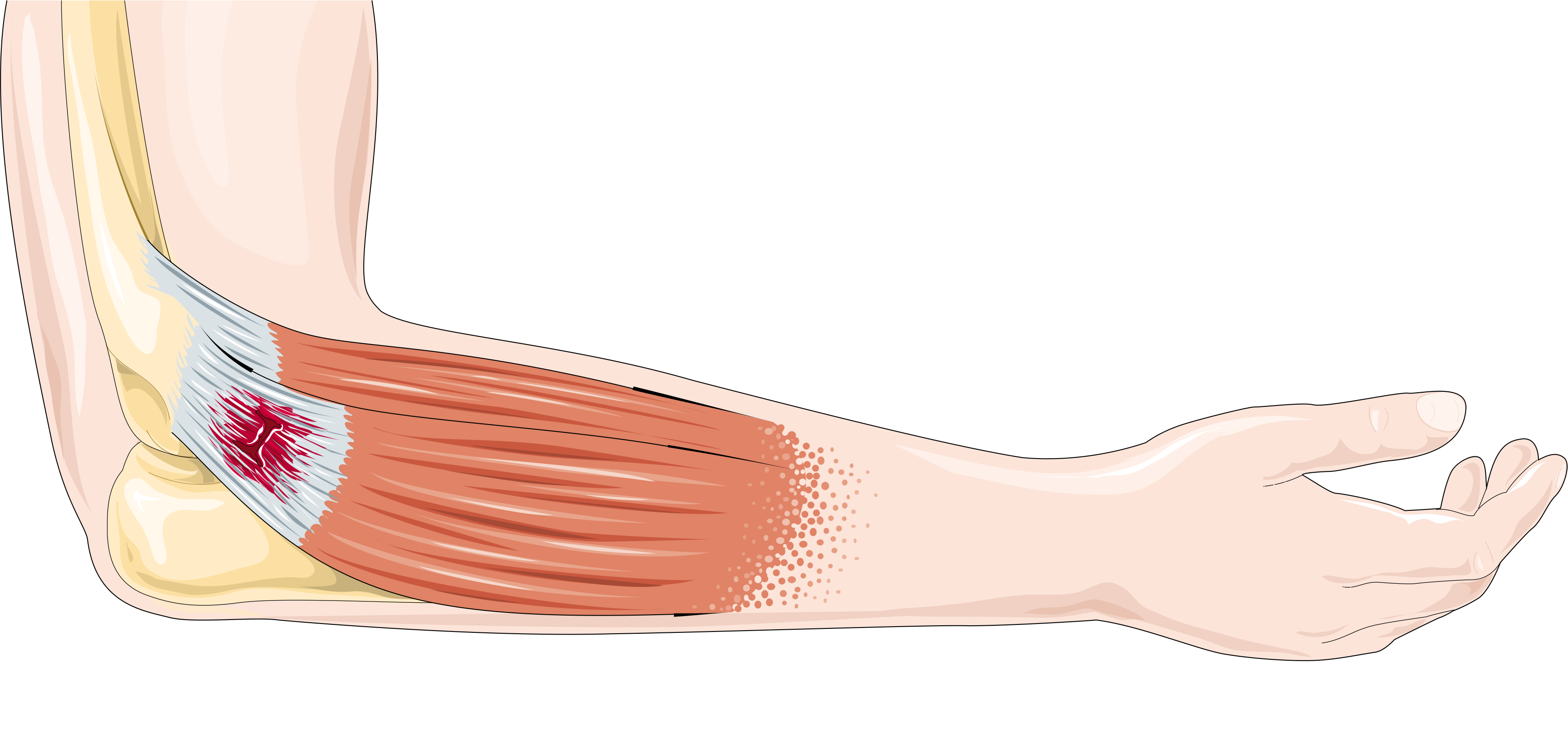
Biceps Brachii Muscle06
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes the forearm and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion). Structure The biceps is one of three muscles in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, along with the brachialis muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, with which the biceps shares a nerve supply. The biceps muscle has two heads, the short head and the long head, distinguished according to their origin at the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of the sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff tear is an injury where one or more of the tendons or muscles of the rotator cuff of the shoulder get torn. Symptoms may include shoulder pain, which is often worse with movement, limited range of motion, or weakness. This may limit people's ability to brush their hair or put on clothing. Clicking may also occur with movement of the arm. Tears may occur as the result of a sudden force or gradually over time. Risk factors include certain repetitive activities, smoking, and a family history of the condition. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, examination, and medical imaging. The rotator cuff is made up of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The supraspinatus is the most commonly affected. Treatment may include pain medication such as NSAIDs and specific exercises. It is recommended that people who are unable to raise their arm above 90 degrees after 2 weeks should be further assessed. In severe cases surgery may be tried, however ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preacher Curl
The term "biceps curl" refers to any of a number of weight training exercises that primarily targets the biceps brachii muscle. It may be performed using a barbell, dumbbell, resistance band, or other equipment. Overview The biceps curl mainly targets the biceps brachii, brachialis and brachioradialis muscles. The biceps is stronger at elbow flexion when the forearm is supinated (palms turned upward) and weaker when the forearm is pronated. The brachioradialis is at its most effective when the palms are facing inward, and the brachialis is unaffected by forearm rotation. Therefore, the degree of forearm rotation affects the degree of muscle recruitment between the three muscles. Form A biceps curl usually starts with the arm in a fully extended position, holding a weight with a supinated (palms facing up) grip. A full repetition consists of bending or "curling" the elbow until it is fully flexed, then slowly lowering the weight to the starting position. The torso should remain u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supinated
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadlift
The deadlift is a weight training exercise in which a loaded barbell or bar is lifted off the ground to the level of the hips, torso perpendicular to the floor, before being placed back on the ground. It is one of the three powerlifting exercises, along with the squat and bench press. Two styles of deadlift are commonly used in competition settings: the sumo deadlift and the standard deadlift. While both of these styles are permitted under the rules of powerlifting competition, only the conventional stance is used in strongman deadlifting contests. Performing Form The conventional deadlift can be broken down into three parts: the setup, the initial pull or drive, and the lockout. Setup: When performing a deadlift, a lifter sets in a position that eccentrically loads the gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus while the muscles of the lumbar contract isometrically in an effort to stabilize the spine. * Set behind the bar with it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentric Training
An eccentric contraction is the motion of an active muscle while it is lengthening under load. Eccentric training is repetitively doing eccentric muscle contractions. For example, in a biceps curl the action of lowering the dumbbell back down from the lift is the eccentric phase of that exercise — as long as the dumbbell is lowered slowly rather than letting it drop (i.e., the biceps are in a state of contraction to control the rate of descent of the dumbbell). An eccentric contraction is one of the distinct phases in the movement of muscles and tendons; they include isometric contraction (no movement), isotonic contraction and concentric contraction (shortening). Eccentric training focuses on slowing down the process of muscle elongation in order to challenge the muscles, which can lead to stronger muscles, faster muscle repair and increasing metabolic rate. Eccentric movement provides a braking mechanism for muscle and tendon groups that are experiencing concentric movement to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone (). (Note that cortisone and aldosterone are isomers.) The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-proliferative, and vasoconstrictive effects. Anti-inflammatory effects are mediated by blocking the action of inflammatory medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis (inflammation of tendons) of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle. This can result in pain, weakness, and loss of movement at the shoulder. Signs and symptoms The most common symptoms in impingement syndrome are pain, weakness and a loss of movement at the affected shoulder. The pain is often worsened by shoulder overhead movement and may occur at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder. The onset of the pain may be acute if due to an injury or insidious if due to a gradual process such as an osteoarthritic spur. The pain has been described as dull rather than sharp, and lingers for long periods of time, making it hard to fall asleep. Other symptoms can include a grinding or popping sensation during movement of the shoulder. The range of motion at the shoulder may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon Rupture
Tendon rupture is a condition in which a tendon separates in whole or in part from tissue to which it is attached, or is itself torn or otherwise divided in whole or in part. Examples include: * Achilles tendon rupture * Biceps tendon rupture * Anterior cruciate ligament injury * Biceps femoris tendon rupture and Quadriceps tendon rupture * Cruciate ligament#Rupture * Patellar tendon rupture Patellar tendon rupture is a tear of the tendon that connects the knee cap (patella) to the tibia. Often there is sudden onset of pain and walking is difficult. In a complete rupture, the ability to extend that knee is decreased. A pop may be felt ... References {{reflist Injuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |