|
Bian Zhang
Bian Zhang (died 186), originally named Bian Yun, was an official who lived in the Eastern Han dynasty of China. He served as the Prefect of Xin'an County. In 185, Beigong Boyu of the Qiang tribe rebelled in Liang Province. Beigong Boyu took Bian Zhang and Han Sui, another Han official, hostage and stopped all attempts to return them. Bian Zhang was forced to participate in the rebellion or else he would be killed. He became the overall commander of the rebels, but was defeated in battle with Dong Zhuo and Sun Jian and died of illness shortly after,''Zizhi Tongjian'' vol. 58. or according to other sources, killed by Han. See also * Lists of people of the Three Kingdoms References * Fan, Ye (5th century). '' Book of the Later Han'' (''Houhanshu''). * Sima, Guang (1084). ''Zizhi Tongjian ''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song (960–1127), Northern Song dynasty in the form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Ling Of Han
Emperor Ling of Han (156 – 13 May 189), personal name Liu Hong, was the 12th and last powerful emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty. Born the son of a lesser marquis who descended directly from Emperor Zhang (the third Eastern Han emperor), Liu Hong was chosen to be emperor in 168 around age 12 after the death of his predecessor, Emperor Huan, who had no son to succeed him. He reigned for about 21 years until his death in 189. Emperor Ling's reign saw another repetition of corrupt eunuchs dominating the eastern Han central government, as was the case during his predecessor's reign. Zhang Rang, the leader of the eunuch faction (十常侍), managed to dominate the political scene after defeating a faction led by Empress Dowager Dou's father, Dou Wu, and the Confucian scholar-official Chen Fan in 168. After reaching adulthood, Emperor Ling was not interested in state affairs and preferred to indulge in women and a decadent lifestyle. At the same time, corrupt officials in the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bian (surname)
Bian is the romanization of several Chinese surnames, including Biàn 卞, Biān 边, Biǎn 扁, Biàn 弁, Biàn 汴, etc. Biān 边 is the most common of these names, while Biàn 卞 is the second-most common. Notable people named Bian 卞 Biàn It is the 86th name on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem.K. S. Tom. 989(1989). Echoes from Old China: Life, Legends and Lore of the Middle Kingdom. University of Hawaii Press. . As of 2018, it is the 269th most common surname in China. * Bian He, discoverer of the Heshibi *Empress Dowager Bian to Cao Cao * Empress Bian to Cao Mao * Empress Bian to Cao Huan * Bian Zhilin, poet in 20th century * Bian Zhongyun, deputy principal beaten to death with wooden sticks by a group of students during Beijing's Red August at the beginning of the Cultural Revolution *Bian Yingui, physicist specializing in fluid mechanics and aerodynamics * Bian Xiaoxuan, historian in Chinese literature *Bian Liunian, Chinese musician, composer, and musical director ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
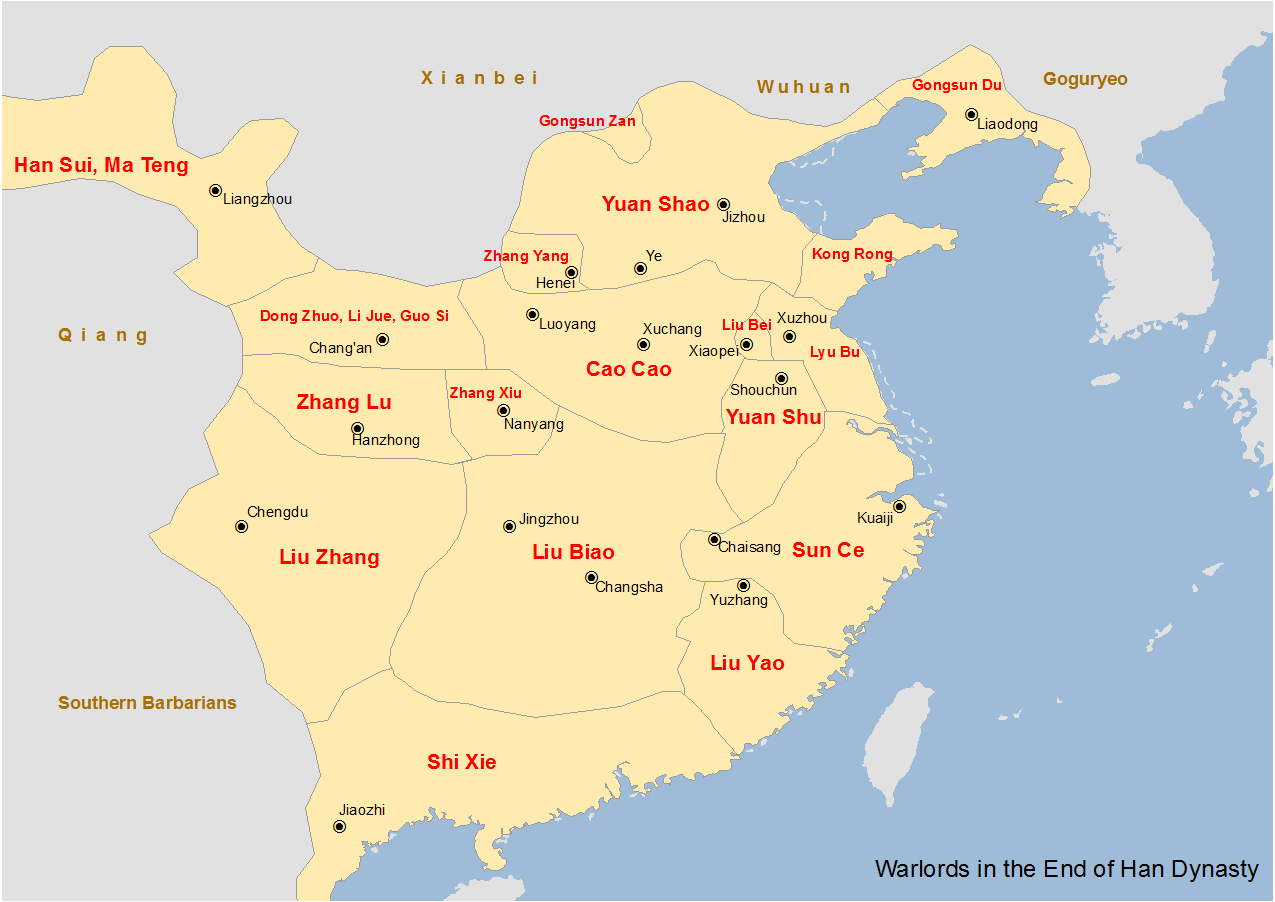
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xin'an County
Xin'an County () is a county in the west of Henan Province, bordering Shanxi Province to the north across the Yellow River. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Luoyang, and contains its northernmost point. History In ancient China, Xin'an was a county located to the west of Luoyang, former capital of the Zhou Dynasty (1049-256 BCE). The archaeological site of the Hanguguan gate dates back to this time and is thus enlisted by UNESCO as part of the world heritage site A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ... “ Silk Roads”. Administrative divisions As 2012, this county is divided to 10 towns and 1 township. ;Towns ;Townships * Caocun Township () Climate References Luoyang County-level divisions of Henan {{Henan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Province
Liang Province or Liangzhou () was a province in the northwest of ancient China, in the approximate location of the modern-day province of Gansu. It was bordered in the east by Sili Province. History Establishment The province was first conquered by the Han Chinese in the 120s BCE during the Han–Xiongnu War, and settled in the decades thereafter. The Hexi Corridor served to connect China proper with the Western Regions, which helped secure important parts of the Silk Road into Central Asia. Qiang rebellions In 107 CE, the Xianlian Qiang rebelled against Han authority. After heavy fighting, and proposals to abandon Liang Province, this First Great Qiang Rebellion was quelled in 118. Efforts were made to resettle the province from 129 to 144, although large parts of Liang remained without effective government. General Duan Jiong conducted another successful campaign against Qiang rebels in 167–169, committing a massacre at Shoot-Tiger Valley. End of Han rule In 184, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dong Zhuo
Dong Zhuo () (died 22 May 192), courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minister of the imperial government. Yet he forced the young Emperor Shao of Han to abdicate and replaced him with his half-brother Emperor Xian of Han while he sought to become the de facto ruler of China in the boy-emperor's name. The Eastern Han dynasty regime survived in name only. Dong Zhuo seized control of the imperial capital Luoyang in 189 when it entered a state of turmoil following the death of Emperor Ling of Han and a massacre of the eunuch faction by the court officials led by General-in-Chief He Jin. Dong Zhuo subsequently deposed Liu Bian (Emperor Shao) and replaced him with his half-brother, the puppet Emperor Xian of Han. Dong Zhuo's rule was brief and characterized by cruelty and tyranny. In the following year, a coalition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Jian
Sun Jian () () (155–191?), courtesy name Wentai, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He allied himself with Yuan Shu in 190 when warlords from eastern China formed a coalition to oust Dong Zhuo, a tyrannical warlord who held the puppet Emperor Xian in his power. Although he controlled neither many troops nor much land, Sun Jian's personal bravery and resourcefulness were feared by Dong Zhuo, who placed him among Yuan Shao, Yuan Shu and Liu Biao as the most influential men at that time. After the coalition disbanded in the next year, China fell into massive civil war. In 191, Sun Jian was killed in battle during an offensive campaign against Liu Biao. Sun Jian was also the father of Sun Quan, one of the central figures of the Three Kingdoms era who eventually established the Eastern Wu state and declared himself its first emperor in 229, whereupon Sun Jian was given the posthumous title Emperor Wuli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of People Of The Three Kingdoms
The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and those found in other cultural references to the Three Kingdoms are listed separately in List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms. Notes The states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu were officially established in 220, 221, and 229 respectively. Therefore, certain people in the list who died before these years have their respective lords' names, in place of either of the three states, listed in the allegiance column. Take Guan Yu for example — he died before Liu Bei established Shu Han in 221, so his allegiance is listed as "Liu Bei" instead of "Shu Han". See also * List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms The following is a list of fictional people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan Ye (historian)
Fan Ye (398 – 23 January 446), courtesy name Weizong (蔚宗), was a Chinese historian and politician of the Liu Song dynasty during the Southern and Northern dynasties period. He was the compiler of the historical text ''Book of the Later Han''. The fourthThe age order of Fan Ye and his brothers was listed in Fan Tai's biography in ''Book of Song'' (volume 60) son of Fan Tai (范泰), Fan Ye was born in present-day Shaoxing, Zhejiang, but his ancestral home was in Nanyang, Henan. He was a noted atheist who heavily criticised Buddhism, Yin and Yang, and the concept of the Mandate of Heaven. To this end, he cited Zhang Heng's scientific studies as evidence. Fan has a biography in the ''Book of Song'' (volume 69). References Sources * Tan, Jiajian"Hou Hanshu" ("Book of Later Han") ''Encyclopedia of China The ''Encyclopedia of China'' () is the first large-entry modern encyclopedia in the Chinese language. The compilation began in 1978. Published by the Encyclopedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later or Eastern Han. The book was compiled by Fan Ye and others in the 5th century during the Liu Song dynasty, using a number of earlier histories and documents as sources. Background In 23 CE, Han dynasty official Wang Mang was overthrown by a peasants' revolt known as the Red Eyebrows. His fall separates the Early (or Western) Han Dynasty from the Later (or Eastern) Han Dynasty. As an orthodox history, the book is unusual in being completed over two hundred years after the fall of the dynasty. Fan Ye's primary source was the ''Dongguan Han Ji'' (東觀漢記; "Han Records of the Eastern Lodge"), which was written during the Han dynasty itself. Contents References Citations Sources ; General * Chavannes, Édouard (1906).T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Guang
Sima Guang (17 November 1019 – 11 October 1086), courtesy name Junshi, was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer. He was a high-ranking Song dynasty scholar-official who authored the monumental history book ''Zizhi Tongjian''. Sima was a political conservative who opposed Wang Anshi's reforms. Early life Sima Guang was named after his birthplace Guāng Prefecture, where his father Sima Chi () served as a county magistrate in Guangshan County. The Simas were originally from Xia County in Shǎn Prefecture, and claimed descent from Cao Wei's official Sima Fu in the 3rd century. A famous anecdote relates how the young Sima Guang once saved a playmate who had fallen into an enormous vat full of water. As other children scattered in panic, Sima Guang calmly picked up a rock and smashed a hole in the base of the pot. Water leaked out, and his friend was saved from drowning. At age 6, Sima Guang once heard a lecture on the 4th-century BC history book '' Zuo Zhuan''. Fascinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |