|
Bhanu Pratap Jena
Bhanu Pratap Jena (born November 1, 1955) is an American cell biologist and the "George E. Palade University Professor and Distinguished Professor of Physiology" at the Wayne State University School of Medicine, who discovered porosome in mid 1990s & demonstrated it to be the universal secretory machinery in Plasma Membrane. Biography Jena was born in Jajpur, Odisha, India on November 1, 1955, to Manju and Prafulla Jena. He majored in Chemistry, Zoology and Botany from BJB College (B.Sc.,1975) and studied Zoology (Endocrinology) at Utkal University (M.Sc.,1978). Following four years of lectureship at various colleges in Utkal University (1978–82), he received a teaching and research fellowship from Iowa State University in 1982 to pursue studies leading to a doctorate degree. In December 1988, he received his PhD in Zoology (Molecular Endocrinology) from Iowa State. Followed by postdoctoral studies at Iowa State and Yale Universities (1988–1994), he joined Yale University a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jajpur, Odisha
Jajpur (also known as Jajapur) is a town and a municipality in Jajpur district in the Indian state of Odisha. It was the capital of the Kesari dynasty, later supplanted by Cuttack. Now, it is the headquarter of Jajpur district. Etymology and names Jajpur, the place of the ancient Biraja Temple, was originally known as Biraja. Other names of the town in the ancient texts include Viranja, Varanja-nagara, Varaha-tirtha. The Bhauma-Kara kings established their capital city of Guhadevapataka (or Guheshvarapataka), identified with modern Gohiratikar (or Gohiratikra) near Jajpur. The later Somavanshi kings moved their capital from Yayatinagara (modern Binka) to Guheshvarapataka, and renamed the town Abhinava-Yayatinagara ("the new city of Yayati"). Later, the Jajpur town came to be known as Yajanagara. According to one theory, this name is a corruption of "Yayatinagara". Another theory is that it derives from the Brahmanical sacrifices (''Yajna'') that became popular during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
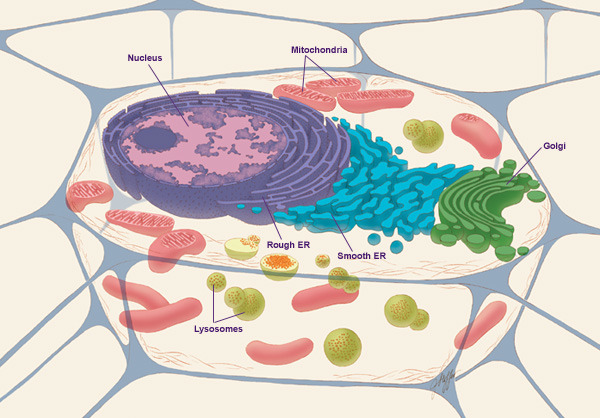
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa State University People
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the east and southeast, Missouri to the south, Nebraska to the west, South Dakota to the northwest, and Minnesota to the north. During the 18th and early 19th centuries, Iowa was a part of Louisiana (New France), French Louisiana and Louisiana (New Spain), Spanish Louisiana; its Flag of Iowa, state flag is patterned after the flag of France. After the Louisiana Purchase, people laid the foundation for an agriculture-based economy in the heart of the Corn Belt. In the latter half of the 20th century, Iowa's agricultural economy transitioned to a diversified economy of advanced manufacturing, processing, financial services, information technology, biotechnology, and Sustainable energy, green energy productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Emigrants To The United States
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1955 Births
Events January * January 3 – José Ramón Guizado becomes president of Panama. * January 17 – , the first nuclear-powered submarine, puts to sea for the first time, from Groton, Connecticut. * January 18– 20 – Battle of Yijiangshan Islands: The Chinese Communist People's Liberation Army seizes the islands from the Republic of China (Taiwan). * January 22 – In the United States, The Pentagon announces a plan to develop intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), armed with nuclear weapons. * January 23 – The Sutton Coldfield rail crash kills 17, near Birmingham, England. * January 25 – The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union announces the end of the war between the USSR and Germany, which began during World War II in 1941. * January 28 – The United States Congress authorizes President Dwight D. Eisenhower to use force to protect Formosa from the People's Republic of China. February * February 10 – The United States Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Membrane
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps. Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic phospholip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Cells
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this way they bring about an integration between the nervous system and the endocrine system, a process known as neuroendocrine integration. An example of a neuroendocrine cell is a cell of the adrenal medulla (innermost part of the adrenal gland), which releases epinephrine, adrenaline to the blood. The adrenal medullary cells are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. These cells are modified postganglionic neurons. Autonomic nerve fibers lead directly to them from the central nervous system. The adrenal medullary hormones are kept in vesicles much in the same way neurotransmitters are kept in neuronal vesicles. Hormonal effects can last up to ten times longer than those of neurotransmitters. Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types. Classification Structure Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. * The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called simple) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
