|
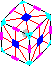
Bevel Cube
The Helicopter Cube is a Rubik's Cube-like puzzle invented by Adam G. Cowan in 2005 and built in 2006. It is also in the shape of a cube. At first glance, the Helicopter Cube may seem like a combination of the 2x2x2 and the Skewb, but it actually cuts differently, and twists around cube edges rather than cube faces. The purpose of the puzzle is to scramble the colors, and then restore them back to their original state of a single color per face. Description The Helicopter Cube is made in the shape of a cube, cut into 8 corner pieces and 24 face center pieces. Each corner piece has 3 colors, and each face center piece has only a single color. Unlike the Rubik's Cube, its faces do not rotate; rather, the pieces are scrambled by rotating around a cube edge. When twisting the puzzle, a 180° turn exchanges two corner pieces and swaps two pairs of face center pieces, but preserves the cube shape. The entire puzzle can be scrambled in this way. However, it is also possible to twist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of Large Numbers
Two naming scales for large numbers have been used in English and other European languages since the early modern era: the long and short scales. Most English variants use the short scale today, but the long scale remains dominant in many non-English-speaking areas, including continental Europe and Spanish-speaking countries in Latin America. These naming procedures are based on taking the number ''n'' occurring in 103''n''+3 (short scale) or 106''n'' (long scale) and concatenating Latin roots for its units, tens, and hundreds place, together with the suffix ''-illion''. Names of numbers above a trillion are rarely used in practice; such large numbers have practical usage primarily in the scientific domain, where powers of ten are expressed as ''10'' with a numeric superscript. Indian English does not use millions, but has its own system of large numbers including lakhs and crores. English also has many words, such as "zillion", used informally to mean large but unspecified amoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square One (puzzle)
The Square-1 is a variant of the Rubik's Cube. Its distinguishing feature among the numerous Rubik's Cube variants is that it can change shape as it is twisted, due to the way it is cut, thus adding an extra level of challenge and difficulty. The Super Square One and Square Two puzzles have also been introduced. The Super Square One has two additional layers that can be scrambled and solved independently of the rest of the puzzle, and the Square Two has extra cuts made to the top and bottom layer, making the edge and corner wedges the same size. History The Square-1 (full name "''Back to Square One''") or alternatively, "''Cube 21''", was invented by Karel Hršel and Vojtěch Kopský in 1990. Application for a Czechoslovak patent was filed on 8 November 1990, then filed as a "priority document" on January 1, 1991. The patent was finally approved on 26 October 1992, with patent number CS27726 On March 16, 1993, the object itself was patented in the US with patent number US5,1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schönflies Notation
The Schoenflies (or Schönflies) notation, named after the German mathematician Arthur Moritz Schoenflies, is a notation primarily used to specify point groups in three dimensions. Because a point group alone is completely adequate to describe the symmetry of a molecule, the notation is often sufficient and commonly used for spectroscopy. However, in crystallography, there is additional translational symmetry, and point groups are not enough to describe the full symmetry of crystals, so the full space group is usually used instead. The naming of full space groups usually follows another common convention, the Hermann–Mauguin notation, also known as the international notation. Although Schoenflies notation without superscripts is a pure point group notation, optionally, superscripts can be added to further specify individual space groups. However, for space groups, the connection to the underlying symmetry elements is much more clear in Hermann–Mauguin notation, so the latter not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann–Mauguin Notation
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann (who introduced it in 1928) and the French mineralogist Charles-Victor Mauguin (who modified it in 1931). This notation is sometimes called international notation, because it was adopted as standard by the ''International Tables For Crystallography'' since their first edition in 1935. The Hermann–Mauguin notation, compared with the Schoenflies notation, is preferred in crystallography because it can easily be used to include translational symmetry elements, and it specifies the directions of the symmetry axes. Point groups Rotation axes are denoted by a number ''n'' — 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ... (angle of rotation ''φ'' = ). For improper rotations, Hermann–Mauguin symbols show rotoinversion axes, unlike Schoenflies and Shubnikov notations, that shows rotation-reflection axes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Finite Spherical Symmetry Groups
Finite spherical symmetry groups are also called point groups in three dimensions. There are five fundamental symmetry classes which have triangular fundamental domains: dihedral, cyclic, tetrahedral, octahedral, and icosahedral symmetry. This article lists the groups by Schoenflies notation, Coxeter notation, orbifold notation, and order. John Conway uses a variation of the Schoenflies notation, based on the groups' quaternion algebraic structure, labeled by one or two upper case letters, and whole number subscripts. The group order is defined as the subscript, unless the order is doubled for symbols with a plus or minus, "±", prefix, which implies a central inversion. Hermann–Mauguin notation (International notation) is also given. The crystallography groups, 32 in total, are a subset with element orders 2, 3, 4 and 6.Sands, 1993 Involutional symmetry There are four involutional groups: no symmetry (C1), reflection symmetry (Cs), 2-fold rotational symmetry (C2), and cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R2er2e
R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Ireland ''or'' . The letter is the eighth most common letter in English and the fourth-most common consonant (after , , and ). The letter is used to form the ending "-re", which is used in certain words such as ''centre'' in some varieties of English spelling, such as British English. Canadian English also uses the "-re" ending, unlike American English, where the ending is usually replaced by "-er" (''center''). This does not affect pronunciation. Name The name of the letter in Latin was (), following the pattern of other letters representing continuants, such as F, L, M, N and S. This name is preserved in French and many other languages. In Middle English, the name of the letter changed from to , following a pattern exhibited in many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mer2e
Mer or MER may refer to: Business * Management expense ratio * Market exchange rate * Merrill Lynch's former NYSE stock symbol People * Francis Mer (born 1939), a French businessman, industrialist and politician, former Minister of the Economy * Gideon Mer (1894-1961), an Israeli scientist working mostly on the eradication of malaria * M.E.R. (Maria Elizabeth Rothmann), an Afrikaner writer * Mer (community), a community found primarily in the Indian state of Gujarat Places * Mer, Loir-et-Cher, a commune in the Loir-et-Cher département of France * Merionethshire, historic county in Wales, Chapman code MER * Murray Island, Queensland, known locally as Mer, an Australian island Sports * Meralco Bolts, a team in the Philippine Basketball Association Science * Mer, a synonym for repeat unit in chemistry * ''Mer'', a type of geometric isomer of octahedral complexes (see ''fac''–''mer'' isomerism) * -mer, an affix meaning "part", used in several words in chemistry and biology * M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mfr2e , a Scottish commercial radio station based in Inverness
* Music for Relief, a charity organisation founded by Linkin Park
* Myofascial release
* Météo-France
{{disambiguation ...
MFR may refer to: * Rogue Valley International–Medford Airport, IATA code * Marine Forces Reserve * Medical first responder * Melt flow rate of thermoplastic polymers * Member of the Order of the Federal Republic, one of the Nigerian National Honours * Methanofuran, a chemical compound * Minimum funding requirement * Mixed Flow Reactor, a type of chemical reactor * Moray Firth Radio MFR is an Independent Local Radio station based in Inverness, owned and operated by Bauer as part of the Hits Radio Network. It broadcasts to Moray, the Scottish Highlands and South West Aberdeenshire. As of December 2022, the station has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |