|
Bethlen Gabor
Gabriel Bethlen ( hu, Bethlen Gábor; 15 November 1580 – 15 November 1629) was Prince of Transylvania from 1613 to 1629 and Duke of Opole from 1622 to 1625. He was also King-elect of Hungary from 1620 to 1621, but he never took control of the whole kingdom. Bethlen, supported by the Ottomans, led his Calvinist principality against the Habsburgs and their Catholic allies. Early life Gabriel was the elder of the two sons of Farkas Bethlen de Iktár and Druzsiána Lázár de Szárhegy. Gabriel was born in his father's estate, Marosillye (now Ilia in Romania), on 15 November 1580. Farkas Bethlen was a Hungarian nobleman who lost his ancestral estate, Iktár (now Ictar-Budinț in Romania), due to the Ottoman occupation of the central territories of the Kingdom of Hungary. Stephen Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, granted Marosillye to him and made him captain-general of the principality. Druzsiána Lázár was descended from a Székely noble family. Both Farkas Bethlen an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Hungary
The King of Hungary ( hu, magyar király) was the ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Apostoli Magyar Király'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 and used afterwards by all Monarchs of Hungary. The term "King of Hungary" is typically capitalized only as a title applied to a specific person; however, within this article, the terms "Kings of Hungary" or "Junior Kings" (etc.) are also shown in capital letters, as in the manner of philosophical writing which capitalizes concepts such as Truth, Kindness and Beauty. Establishment of the title Before 1000 AD, Hungary was not recognized as a kingdom and the ruler of Hungary was styled Grand Prince of the Hungarians. The first King of Hungary, Stephen I. was crowned on 25 December 1000 (or 1 January 1001) with the crown Pope Sylvester II had sent him and with the consent of Otto III, Holy Roman Emperor. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
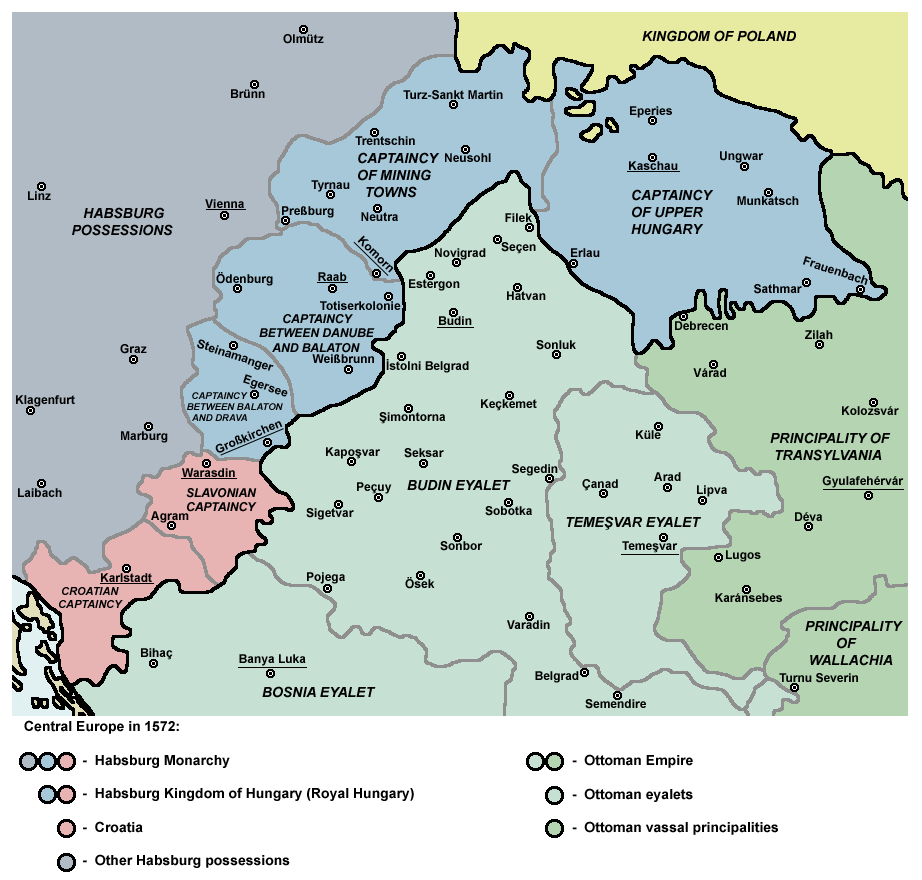
Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary ( hu, Török hódoltság) was the southern and central parts of what had been the Kingdom of Hungary in the late medieval period, which were conquered and ruled by the Ottoman Empire from 1541 to 1699. The Ottoman rule covered almost the entire region of the Great Hungarian Plain (except the northeastern parts) and Southern Transdanubia. The territory was invaded and annexed to the Ottoman Empire by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent between 1521 and 1541. The north-western rim of the Hungarian kingdom remained unconquered and recognised members of the House of Habsburg as Kings of Hungary, giving it the name "Royal Hungary". The boundary between the two thereupon became the frontline in the Ottoman–Habsburg wars over the next 150 years. Following the defeat of the Ottomans in the Great Turkish War, most of Ottoman Hungary was ceded to the Habsburgs under the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. During the period of Ottoman rule, Hungary was divided for administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Racibórz
Duchy of Racibórz (german: Herzogtum Ratibor, cs, Ratibořské knížectví) was one of the duchies of Silesia. Its capital was Racibórz in Upper Silesia. History After Bolesław I the Tall and his younger brother Mieszko I Tanglefoot backed by Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa had retained their Silesian heritage in 1163, the Duchy of Racibórz was formed in 1172 as a territory for Mieszko. It was centered on the towns of Racibórz, Koźle and Cieszyn. Mieszko's small share was enlarged the first time in 1177, when he received the territories of Bytom, Oświęcim, Zator, Pszczyna and Siewierz from his uncle High Duke Casimir II the Just of Poland. In 1202 Mieszko occupied the Duchy of Opole of his deceased nephew Jarosław, forming the united Duchy of Opole and Racibórz. After the death of Mieszko's grandson Duke Władysław Opolski in 1281, his sons again divided the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz and in 1290 the Duchy of Racibórz was recreated again, assigned to Władys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Opole
Duchy of Opole ( pl, Księstwo opolskie; german: Herzogtum Oppeln; cs, Opolské knížectví) was one of the duchies of Silesia ruled by the Piast dynasty. Its capital was Opole (Oppeln, Opolí) in Upper Silesia. Duke Boleslaw III 'the Wrymouth' (r.1102-38; who died a feudatory of the German Emperor) had restored Polish fortunes to some extent but having endured terrific internal strife, he decreed in his Will that the 'kingdom' would be better divided into four hereditary principalities for each of his four sons. A kind of family federation. One became Duke of Great Poland (around Gniezno), another Silesia, another Cracow, another, half-heathen Masovia. The rising local magnates, dowered with estates, preferred provincial princes. But the division of loyalties among these princes brought on a long period of dynastic struggle, intrigue, and national weakness. By this time Silesia, under strong German influence, had been divided into sixteen minuscule principalities and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchies Of Silesia
The Duchies of Silesia were the more than twenty divisions of the region of Silesia formed between the 12th and 14th centuries by the breakup of the Duchy of Silesia, then part of the Kingdom of Poland. In 1335, the duchies were ceded to the Kingdom of Bohemia under the Treaty of Trentschin. Thereafter until 1742, Silesia was one of the Bohemian crown lands and lay within the Holy Roman Empire. Most of Silesia was annexed by the King of Prussia under the Treaty of Berlin in 1742. Only the Duchy of Teschen, the Duchy of Troppau and the Duchy of Nysa remained under the control of the Bohemian crown and as such were known as the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia until 1918. Breakup of Polish Silesia (1138–1335) In the (vain) hope to prevent an inheritance dispute, the Piast prince Bolesław III Wrymouth by his last will and testament had divided Poland into hereditary provinces distributed among his four sons: Masovia, Kujawy, Greater Poland and Silesia. Beside which, the Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia is traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was forced to accept the suzerainty of the Ottoman Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Giurgiu
The Battle of Giurgiu took place on 27–30 October 1595. It was part of the Long Turkish War (1591/1593–1606), a border conflict between the Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire over Balkan territories. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Giurgiu, Battle of Battles involving the Ottoman Empire Battle of Giurgiu Battles involving Wallachia Battles involving Transylvania Battles involving Moldavia Giurgiu Giurgiu (; bg, Гюргево) is a city in southern Romania. The seat of Giurgiu County, it lies in the historical region of Muntenia. It is situated amongst mud-flats and marshes on the left bank of the Danube facing the Bulgarian city ... Military history of Romania History of Muntenia 1595 in the Ottoman Empire 1595 in Europe Battles of the Long Turkish War Michael the Brave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy League Of Pope Clement VIII
The Holy League established in 1594 by Pope Clement VIII was a military alliance of predominantly Christian European countries (Holy League) aimed against the Ottoman Empire during the Long War (1591–1606). The aim of this alliance was to drive the Ottoman Empire out of Europe The coalition was led by Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor. The Holy See took for granted that Poland would join the League, together with all most powerful neighbours of the Ottoman Empire, in spite of their mutual enmities. The league expected an assistance of the Balkan's Christian population. The establishing of this Holy League was only partially successful, while Holy League managed to halt further Ottoman conquests in Europe. Preparations Already in 1583 a group of Cossacks proposed to the Pope to initiate crusade against the Ottomans. Ten years later, Aleksandar Komulović convinced the Pope to support his ambitious plan which also involved Cossacks. His plan was to establish military alliance which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Bocskai
Stephen Bocskai or Bocskay ( hu, Bocskai István; 1 January 155729 December 1606) was Prince of Transylvania and Hungary from 1605 to 1606. He was born to a Hungarian noble family. His father's estates were located in the eastern regions of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary, which developed into the Principality of Transylvania in the 1570s. He spent his youth in the court of the Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian, who was also the ruler of Royal Hungary (the western and northern regions of the medieval kingdom). Bocskai's career started when his underage nephew, Sigismund Báthory, became the ruler of Transylvania in 1581. After the Diet of Transylvania declared Sigismund of age in 1588, Bocskai was one of the few members of Sigismund's council who supported his plan to join an anti-Ottoman coalition. Sigismund made Bocskai captain of Várad (now Oradea in Romania) in 1592. After the pro-Ottoman noblemen forced Sigismund to renounce his throne in 1594, Bocskai supported him in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lăzarea
Lăzarea ( hu, Gyergyószárhegy or colloquially ''Szárhegy'', Hungarian pronunciation: , meaning ''Bald Mountain in Gyergyó'') is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, and is composed of two villages, Ghiduț (''Güdüc'') and Lăzarea. The commune is one of the oldest settlements in the area, and is now a tourist and cultural centre. It has various local attractions, including the Lázár Castle (1450). It is located in the central-north part of the county, at the foot of the Căliman-Harghita Mountains, on the banks of the river Lăzarea. History The history of the village is closely interwoven with that of the Lázár family. Its first written mention is from 1482 when a certain Erzsébet Bíró of Kide warned a Székely named Lázár of '' Zarhegh'' and Péter Szilvási to beware of disposing of the estate of Kide to which she was entitled under the title of bride price and dower. In 157 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
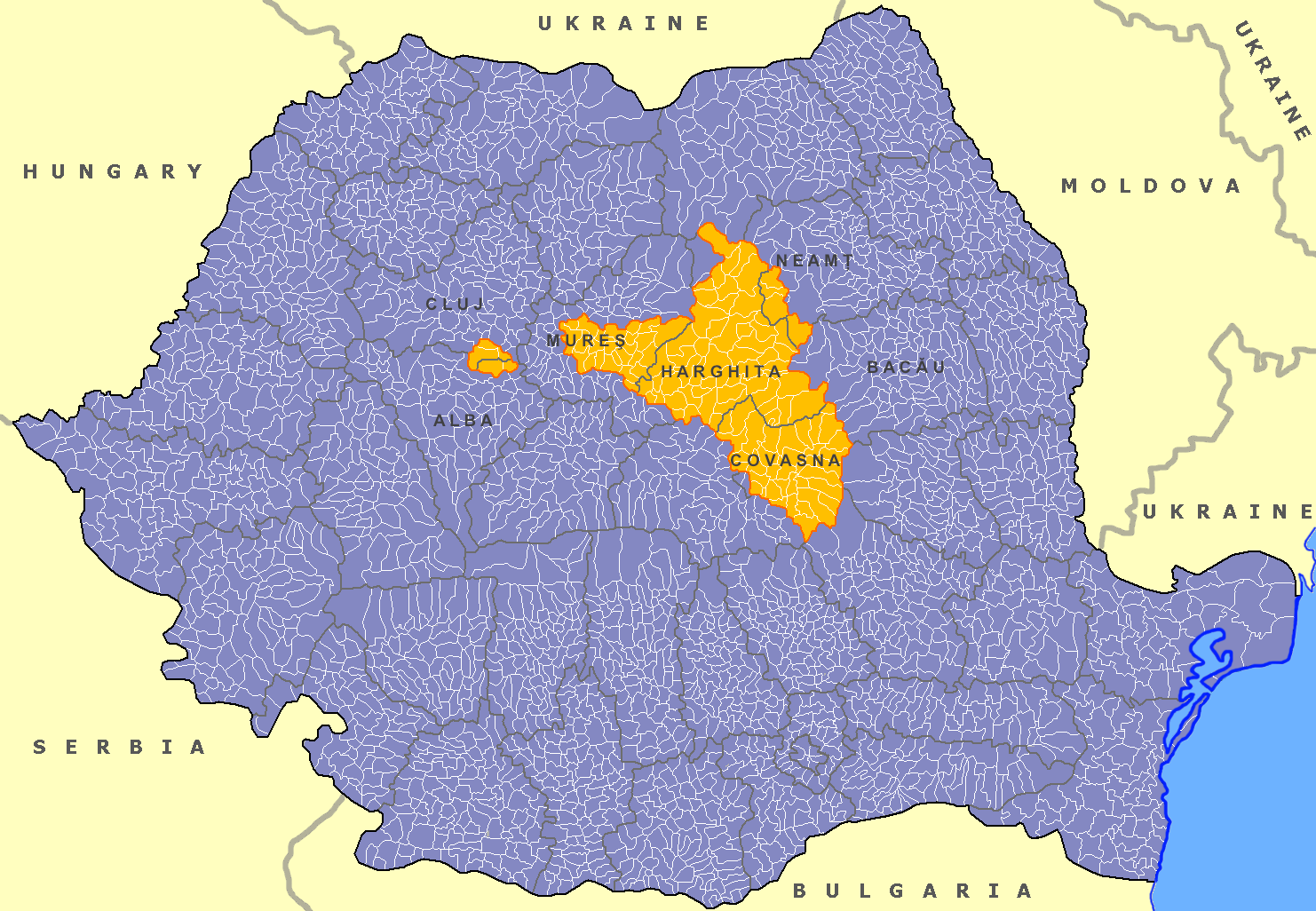
Székely Land
The Székely Land or Szeklerland ( hu, Székelyföld, ; ro, Ținutul Secuiesc and sometimes ; german: Szeklerland; la, Terra Siculorum) is a historic and ethnographic area in Romania, inhabited mainly by Székelys, a subgroup of Hungarians. Its cultural centre is the city of Târgu Mureș (Marosvásárhely), the largest settlement in the region. Székelys (or Szeklers) live in the valleys and hills of the Eastern Carpathian Mountains, corresponding mostly to the present-day Harghita, Covasna, and parts of Mureș counties in Romania. Originally, the name ''Székely Land'' denoted the territories of a number of autonomous Székely seats within Transylvania. The self-governing Székely seats had their own administrative system, and existed as legal entities from medieval times until the 1870s. The privileges of the Székely and Saxon seats were abolished and seats were replaced with counties in 1876. Along with Transylvania and eastern parts of Hungary proper, the Széke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lázár Castle
Lazar Castle ( ro, Castelul Lazar, hu, Lázár-kastély), is a castle located in Lăzarea, Harghita County, Romania. The citadel is named after the Lázár de Szárhegy noble family and it is built in a combination of Romanesque, Gothic, and Renaissance styles. The oldest part of the building dates from 1532, while the rest was added in 1631–1632. See also * List of castles in Romania * Tourism in Romania * Villages with fortified churches in Transylvania The south-eastern Transylvania region in Romania currently has one of the highest numbers of existing fortified churches from the 13th to 16th centuries. It has more than 150 well preserved fortified churches of a great variety of architectural s ... References * Drăguț, Vasile. ''Dicționar enciclopedic de artă medievală românescă.'' București: Editura Științifică și Enciclopedică, 1976. * Ionescu, Grigore. ''Arhitectura pe teritoriul României de-a lungul veacurilor.'' București: Editura Academiei, 1982 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |