|
Beta Gruis
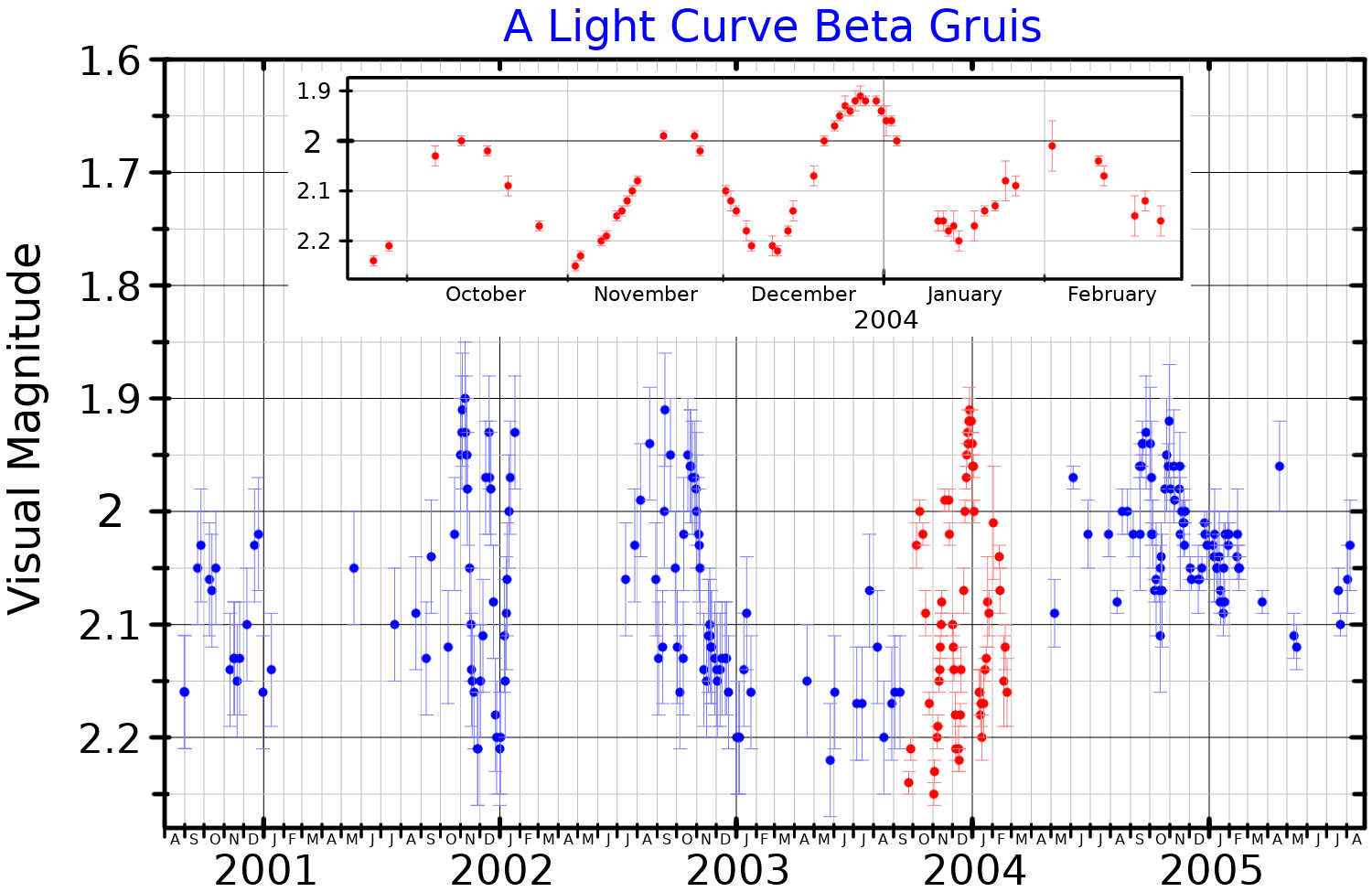
Beta Gruis (β Gruis, abbreviated Beta Gru, β Gru), formally named Tiaki , is the second brightest star in the southern constellation of Grus. It was once considered the rear star in the tail of the constellation of the (Southern) Fish, Piscis Austrinus: it, with Alpha, Delta, Theta, Iota, and Lambda Gruis, belonged to Piscis Austrinus in medieval Arabic astronomy. Nomenclature ''β Gruis'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Gruis'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional Tuamotuan name of ''Tiaki''. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Tiaki'' for this star on 5 September 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Crane'', refers to an asterism consisting of Beta Gruis, Alpha Gruis, Epsilon Gruis, Eta Gruis, Delta Tucanae, Zeta Gruis, Iota Gruis, Theta Gruis, Delta² Gruis and Mu¹ Gruis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grus (constellation)
Grus (, or colloquially ) is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the crane, a type of bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Grus first appeared on a celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas ''Uranometria'' of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave Bayer designations to its stars in 1756, some of which had been previously considered part of the neighbouring constellation Piscis Austrinus. The constellations Grus, Pavo, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds". The constellation's brightest star, Alpha Gruis, is also known as Alnair and appears as a 1.7-magnitude blue-white star. Beta Gruis is a red giant variable star with a minimum magnitude of 2.3 and a maximum magnitude of 2.0. Six star systems have been foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation, is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for '' Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; both mean 'hunter'), or * choosing a new name based on some attribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu1 Gruis
Mu1 Gruis, Latinized from μ1 Gruis, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.79. The distance to this system, as determined using an annual parallax shift of 11.44 mas as seen from the Earth, is around 275 light years. It is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −5 km/s. The pair orbit each other with a period of 19 years and an eccentricity of 0.56. The yellow-hued primary component is an evolved giant star with stellar classification of G III and visual magnitude 5.20. With the supply of hydrogen at its core exhausted, it cooled and expanded; at present it has nine times the girth of the Sun. The star is radiating 67 times the luminosity of the Sun from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 5,422 K. The secondary component is magnitude 6.68 and classed as a G-type star, although its color index an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta2 Gruis
Delta2 Gruis, Latinized from δ2 Gruis, is a solitary, red-hued star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of about 4. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.88 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located around 330 light years from the Sun. It is moving further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +3 km/s. This is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of M4.5 IIIa. It is a pulsating variable with multiple periods, including 20.6, 24.1, 24.5, and 32.3 days. The strongest period is 33.3 days with an amplitude of 0.043 magnitude. It has a magnitude 9.71 visual companion at an angular separation of 60.4 arc seconds along a position angle In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Gruis
Zeta Gruis, Latinised from ζ Gruis, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.12. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 24.5 mas as seen from the Earth, the system is located about 133 light-years from the Sun. This is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of , where the suffix notation indicates underabundances of iron and cyanogen in the spectrum. Having exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core, the star has expanded and cooled; at present it has 10 times the girth of the Sun. The star is radiating 46 times the luminosity of the Sun The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal ... from its swollen photosphere at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Tucanae
Delta Tucanae (δ Tuc, δ Tucanae) is a common proper motion pair located in the southwestern corner of the southern constellation of Tucana. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 13.00 mas as seen from Earth, is approximately 250 light years from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.48. As of 2013, the two components had an angular separation of 7.0 arc seconds along a position angle of 282°. The brighter primary, component A, is blue-white hued star a visual magnitude of 4.52. It is a B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B9 Vn, where the 'n' suffix indicates "nebulous" absorption lines due to the star's rotation. It is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 224 km/s, which is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is an estimated 12% larger than the polar radius. The star has about three times the mass of the Sun and is around 232 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Gruis
Eta Gruis, Latinized from η Gruis, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.85. Based upon an annual parallax shift of as seen from the Earth, the system is located about 460 light years from the Sun. The star is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +28 km/s. This object is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of , where the suffix notation indicates this is an intermediate CN star. It is a periodic microvariable with an amplitude of 0.0055 magnitude and a frequency of 0.36118 cycles per day. With the supply of hydrogen exhausted at its core, the star has expanded and cooled, now having 31 times the Sun's girth. It is radiating 338.5 times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,420 K. Eta Gruis has a magnitude 11.5 visual companion located at an angu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Gruis
ε Gruis, Latinised as Epsilon Gruis, is a blue-white hued star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 3.5. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 25.30 mas as measured from Earth, it is located around 129 light years from the Sun. The system may be moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of about −0.4 km/s. This is an A-type subgiant of spectral type A2IVn, a star that has used up its core hydrogen and has begun to expand off the main sequence. At the estimated age of 249 million years, it is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 235 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is an estimated 18% larger than the polar radius. The star displays an infrared excess, suggesting the presence of a circumstellar disk A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Constellations
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" (Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming Dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Series A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e.g. Shangh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |