|
Besanosauridae
''Besanosaurus'' (meaning "Besano ombardy, N. Italy">Italy.html" ;"title="ombardy, N. Italy">ombardy, N. Italylizard") is a genus of large ichthyosaur (a marine reptile, not a dinosaur) that lived during the middle Triassic period, approximately 235 million years ago. This marine reptile came from its own family Besanosauridae and was named by Dal Sasso and Pinna in 1996. The type of species is ''Besanosaurus leptorhynchus'' meaning "long-beaked reptile from Besano." Discovery The bones of ''Besanosaurus'' were first discovered in "Sasso Caldo" quarry in the spring of 1993 by the volunteers of the paleontological group of Besano, a small town in the Lombardy region of north Italy. The fossil was almost completely embedded in the rock and could be first seen only through x-rays; to detect the content of the 38 slabs of stone enclosing the skeleton, 145 radiographs were necessary. The skeleton of ''Besanosaurus'' came to light in the paleontological laboratory of Museo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
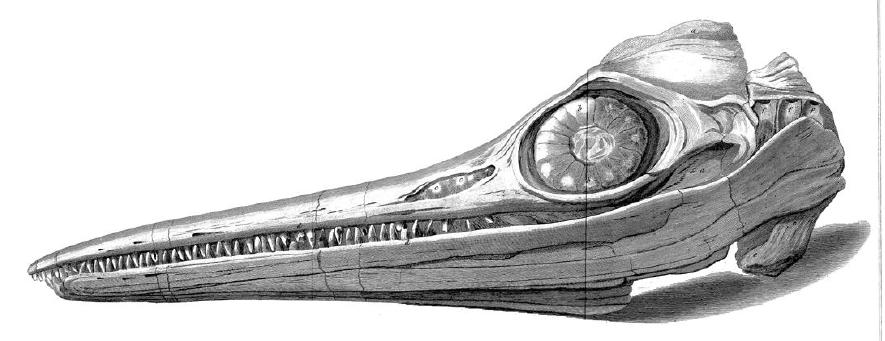
Besanosaurus Leptorhynchus - Skull
''Besanosaurus'' (meaning "Besano ombardy, N. Italy">Italy.html" ;"title="ombardy, N. Italy">ombardy, N. Italylizard") is a genus of large ichthyosaur (a marine reptile, not a dinosaur) that lived during the middle Triassic period, approximately 235 million years ago. This marine reptile came from its own family Besanosauridae and was named by Dal Sasso and Pinna in 1996. The type of species is ''Besanosaurus leptorhynchus'' meaning "long-beaked reptile from Besano." Discovery The bones of ''Besanosaurus'' were first discovered in "Sasso Caldo" quarry in the spring of 1993 by the volunteers of the paleontological group of Besano, a small town in the Lombardy region of north Italy. The fossil was almost completely embedded in the rock and could be first seen only through x-rays; to detect the content of the 38 slabs of stone enclosing the skeleton, 145 radiographs were necessary. The skeleton of ''Besanosaurus'' came to light in the paleontological laboratory of Museo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Besanosaurus Skull Reconstruction
''Besanosaurus'' (meaning "Besano ombardy, N. Italy">Italy.html" ;"title="ombardy, N. Italy">ombardy, N. Italylizard") is a genus of large ichthyosaur (a marine reptile, not a dinosaur) that lived during the middle Triassic period, approximately 235 million years ago. This marine reptile came from its own family Besanosauridae and was named by Dal Sasso and Pinna in 1996. The type of species is ''Besanosaurus leptorhynchus'' meaning "long-beaked reptile from Besano." Discovery The bones of ''Besanosaurus'' were first discovered in "Sasso Caldo" quarry in the spring of 1993 by the volunteers of the paleontological group of Besano, a small town in the Lombardy region of north Italy. The fossil was almost completely embedded in the rock and could be first seen only through x-rays; to detect the content of the 38 slabs of stone enclosing the skeleton, 145 radiographs were necessary. The skeleton of ''Besanosaurus'' came to light in the paleontological laboratory of Museo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauria
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merriamosauria
Merriamosauria is an extinct clade of ichthyosaurs. It was named by Ryosuke Motani in his 1999 analysis of the relationships of ichthyopterygian marine reptiles and was defined in phylogenetic terms as a stem-based taxon including "the last common ancestor of ''Shastasaurus pacificus'' and '' Ichthyosaurus communis'', and all of its descendants." The name honours John Campbell Merriam. Based on this definition, Merriamosauria includes most ichthyosaurs except for several Triassic groups such as the clade Mixosauria, the family Cymbospondylidae, and perhaps the family Toretocnemidae. Merriamosaurs are characterized by features in their pectoral girdles and limb bones, including an extensive connection between the scapula and the coracoid bone, the absence of the first metacarpal and the absence of a pisiform bone. In addition to ''Shastasaurus,'' this clade includes ''Shonisaurus, Guizhouichthyosaurus,'' an unnamed Norian The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Civico Di Storia Naturale Di Milano
The Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano (Milan Natural History Museum) is a museum in Milan, Italy. It was founded in 1838 when naturalist Giuseppe de Cristoforis donated his collections to the city. Its first director was Giorgio Jan. The Museum is located within a 19th-century building in the Indro Montanelli Garden, near the historic city gate of Porta Venezia. The structure was built between 1888 and 1893 in Neo-Romanesque style with Gothic elements. The museum is divided into five different permanent sections: Mineralogy (with a large collection of minerals from all over the world); Paleontology (with several fossils of dinosaurs and other prehistoric organisms); Natural History of Man (dedicated to the origins and evolution of humans with a particular attention to the relationship of the latter with the environment); Invertebrate Zoology (dedicated to mollusks, arthropods and entomology); and Vertebrate Zoology (dedicated to vertebrates, both exotic and Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereo Microscope
The stereo, stereoscopic or dissecting microscope is an optical microscope variant designed for low magnification observation of a sample, typically using light reflected from the surface of an object rather than transmitted through it. The instrument uses two separate optical paths with two objectives and eyepieces to provide slightly different viewing angles to the left and right eyes. This arrangement produces a three-dimensional visualization of the sample being examined."Introduction to Stereomicroscopy" by Paul E. Nothnagle, William Chambers, and , '' |
Mixosaurus
''Mixosaurus'' is an extinct genus of Middle Triassic (Anisian to Ladinian, about 250-240 Mya) ichthyosaur. Its fossils have been found near the Italy–Switzerland border and in South China. The genus was named in 1887 by George H. Baur. The name means "Mixed Lizard", and was chosen because it appears to have been a transitional form between the eel-shaped ichthyosaurs such as ''Cymbospondylus'' and the later dolphin-shaped ichthyosaurs, such as ''Ichthyosaurus''. Baur named ''Mixosaurus'' as a new genus because its forefin was sufficiently different from that of ''Ichthyosaurus''. ''Mixosaurus'' includes 3 species. Previously this number was bigger, and ''Mixosaurus'' was considered as the most common genus of Triassic ichthyosaurs, whose fossils have been found all over the world, including China, Timor, Indonesia, Italy, Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Canada, as well as Alaska and Nevada in the US. Description ''Mixosaurus'' was a small ichthyosaur, measuring between long and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
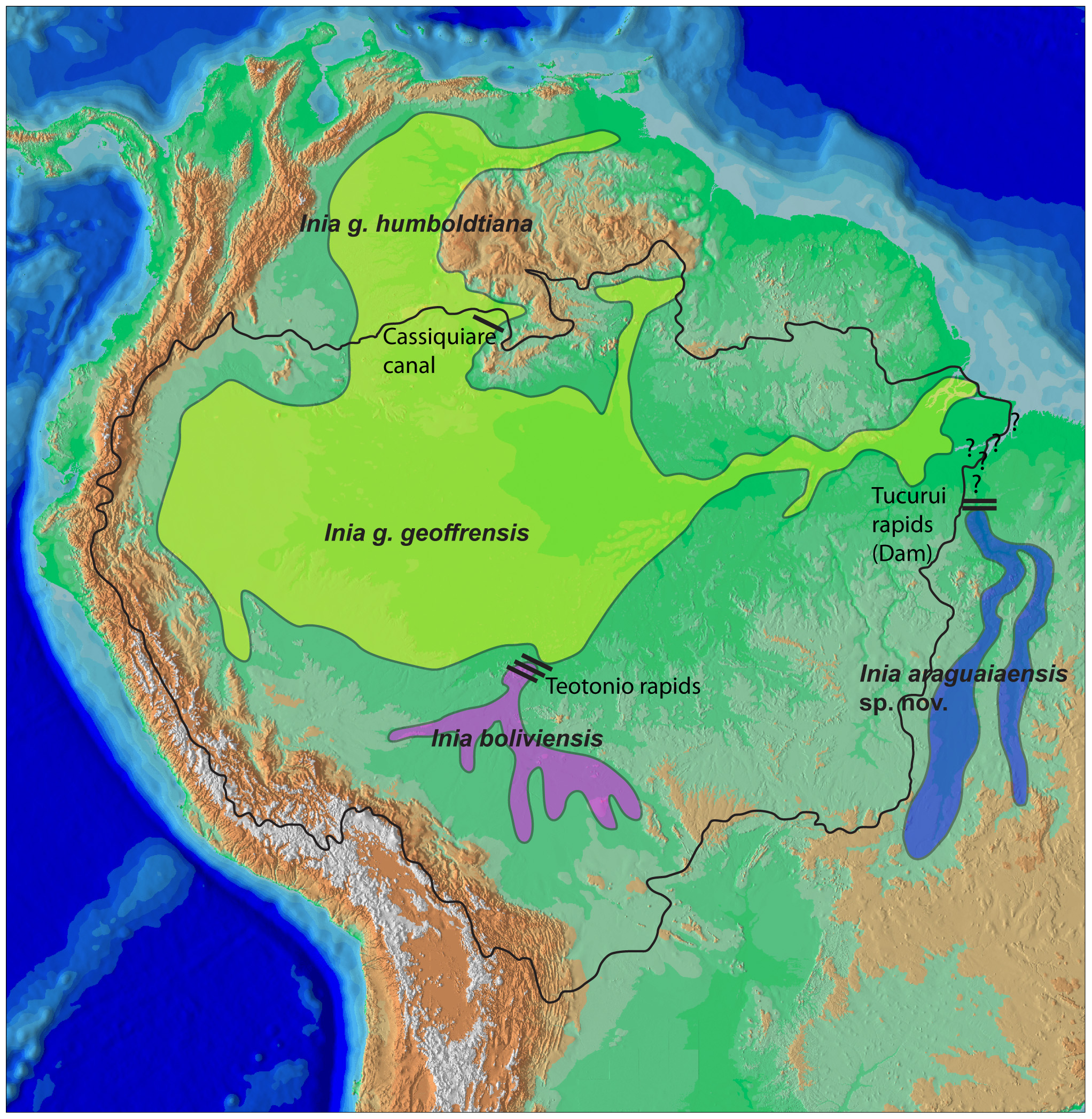
River Dolphins
River dolphins are a polyphyletic group of fully aquatic mammals that reside exclusively in freshwater or brackish water. They are an informal grouping of dolphins, which itself is a paraphyletic group within the infraorder Cetacea. Extant river dolphins are placed in two superfamilies, Platanistoidea and Inioidea. They comprise the families Platanistidae (the South Asian dolphins), the recently extinct Lipotidae (Yangtze river dolphin), Iniidae (the Amazonian dolphins) and Pontoporiidae. There are five extant species of river dolphins. River dolphins, alongside other cetaceans, belong to the clade Artiodactyla, with even-toed ungulates, and their closest living relatives the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. Specific types of Dolphins can be pink. River dolphins are relatively small compared to other dolphins, having evolved to survive in warm, shallow water and strong river currents. They range in size from the long South Asian river dolp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavials
The gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus''), also known as gavial or fish-eating crocodile, is a crocodilian in the family Gavialidae and among the longest of all living crocodilians. Mature females are long, and males . Adult males have a distinct boss at the end of the snout, which resembles an earthenware pot known as a ''ghara'', hence the name "gharial". The gharial is well adapted to catching fish because of its long, narrow snout and 110 sharp, interlocking teeth. The gharial probably evolved in the northern Indian subcontinent. Fossil gharial remains were excavated in Pliocene deposits in the Sivalik Hills and the Narmada River valley. It currently inhabits rivers in the plains of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. It is the most thoroughly aquatic crocodilian, and leaves the water only for basking and building nests on moist sandbanks. Adults mate at the end of the cold season. Females congregate in spring to dig nests, in which they lay 20–95 eggs. They guard t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Picometre, picometers to 10 Nanometre, nanometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 electronvolt, eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet, UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.gif)