|
Bert Oldfield
William Albert Stanley Oldfield (9 September 1894 – 10 August 1976) was an Australian cricketer and businessman. He played for New South Wales and Australia as a wicket-keeper. Oldfield's 52 stumpings during his Test career remains a record several decades after his final Test. Life and career Oldfield was born in Alexandria, a suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, the seventh child of John William Oldfield, an upholster born in Manchester and his Australian wife Mary Gregory. During World War I, Oldfield served with the first Australian Imperial Force as a Corporal in the 15th Field Ambulance. He was wounded and knocked unconscious at Ypres Salient in 1917, and spent six months recovering from shell shock.''The Oxford Companion to Australian Cricket'', Oxford, Melbourne, 1996, p. 401. At the conclusion of the war he was selected to be part of the Australian Imperial Forces cricket team which played 28 first-class matches in Britain, South Africa and Australia between May 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria, New South Wales
Alexandria is an inner-city suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Alexandria is located 5 kilometres south of the Sydney central business district and is part of the local government area of the City of Sydney. The postcode is 2015. The rough boundaries of Alexandria are Botany Road to the east, Gardeners Road to the south, Mitchell Road and Sydney Park to the west, and Boundary Road to the north. It is approximately 3.5 km south of Central station. History The Parish of Alexandria was established in 1835. The naming of Alexandria and neighbouring Waterloo commemorates the famous British Empire military and naval victories over Napoleon – the Battles of Alexandria and Waterloo. The Iron Duke Hotel in Alexandria is itself named after the Duke of Wellington, as is Wellington Street in Waterloo. It was thought Alexandria may have been named after Princess Alexandra, Queen consort of King Edward VII, however, Alexandra was born on 1 December 1844 and the parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
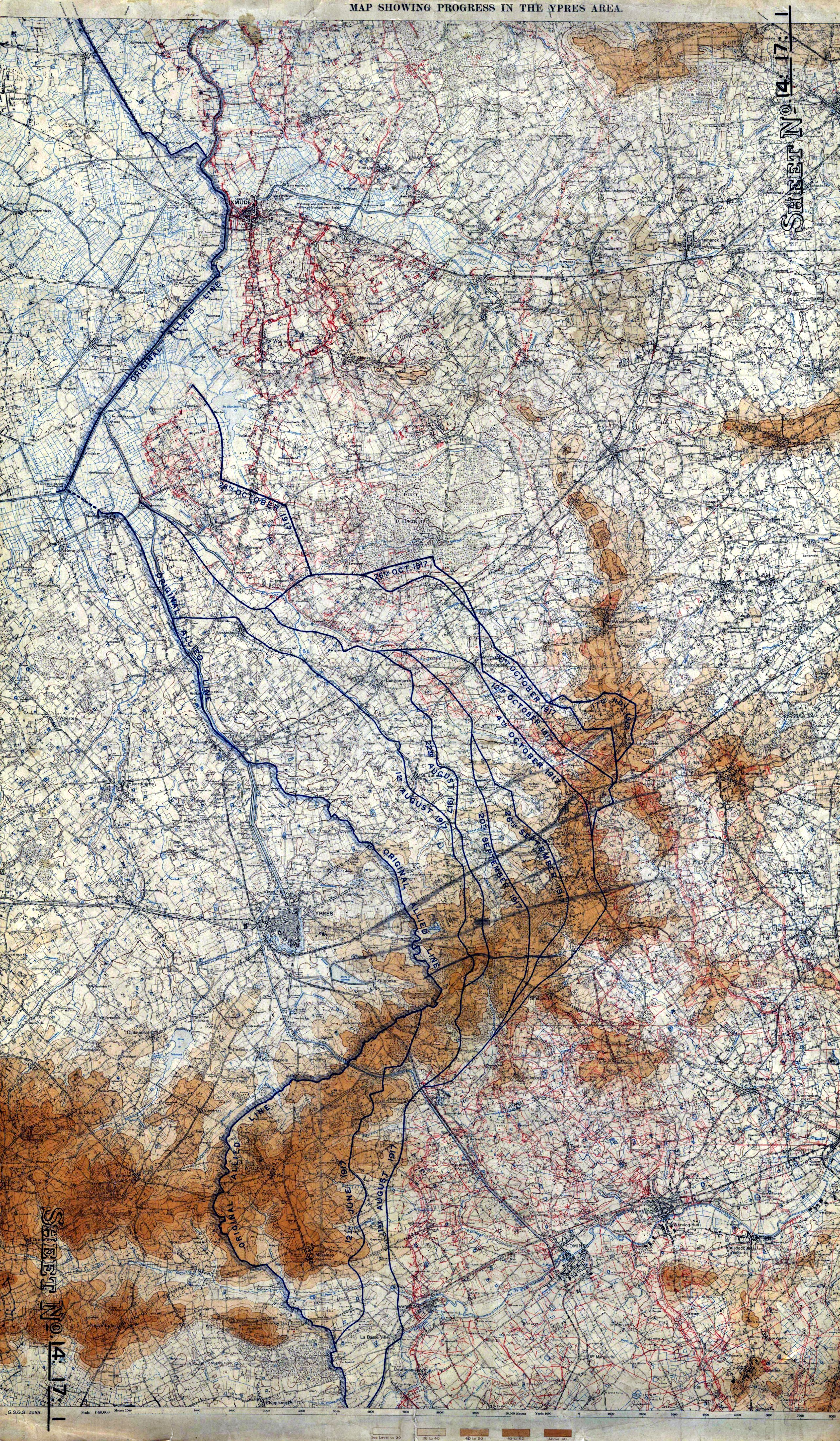
Ypres Salient
The Ypres Salient around Ypres in Belgium was the scene of several battles and an extremely important part of the Western front during the First World War. Ypres district Ypres lies at the junction of the Ypres–Comines Canal and the Ieperlee. The city is overlooked by Kemmel Hill in the south-west and from the east by low hills running south-west to north-east with Wytschaete (Wijtschate), Hill 60 to the east of Verbrandenmolen, Hooge, Polygon Wood and Passchendaele (Passendale). The high point of the ridge is at Wytschaete, from Ypres, while at Hollebeke the ridge is distant and recedes to at Polygon Wood. Wytschaete is about above the plain; on the Ypres–Menin road at Hooge, the elevation is about and at Passchendaele. The rises are slight, apart from the vicinity of Zonnebeke, which has a From Hooge and to the east, the slope is near Hollebeke, it is heights are subtle but have the character of a saucer lip around Ypres. The main ridge has spurs sloping east an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Larwood
Harold Larwood, MBE (14 November 1904 – 22 July 1995) was a professional cricketer for Nottinghamshire County Cricket Club and the England cricket team between 1924 and 1938. A right-arm fast bowler who combined unusual speed with great accuracy, he was considered by many commentators to be the finest and the fastest fast bowler of his generation and one of the fastest bowlers of all time. He was the main exponent of the bowling style known as "bodyline", the use of which during the Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) tour of Australia in 1932–33 caused a furore that brought about a premature and acrimonious end to his international career. A coal miner's son who began working in the mines at the age of 14, Larwood was recommended to Nottinghamshire on the basis of his performances in club cricket, and rapidly acquired a place among the country's leading bowlers. He made his Test debut in 1926, in only his second season in first-class cricket, and was a member of the 1928– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Bowling
Fast bowling (also referred to as pace bowling) is one of two main approaches to bowling in the sport of cricket, the other being spin bowling. Practitioners of pace bowling are usually known as ''fast'' bowlers, ''quicks'', or ''pacemen''. They can also be referred to as a ''seam'' bowler, a ''swing'' bowler or a ''fast bowler who can swing it'' to reflect the predominant characteristic of their deliveries. Strictly speaking, a pure swing bowler does not need to have a high degree of pace, though dedicated medium-pace swing bowlers are rarely seen at Test level in modern times. The aim of pace bowling is to deliver the ball in such a fashion as to cause the batsman to make a mistake. The bowler achieves this by making the hard cricket ball deviate from a predictable, linear trajectory at a sufficiently high speed that limits the time the batsman has to compensate for it. For deviation caused by the ball's stitching (the seam), the ball bounces off the pitch and deflects eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodyline
Bodyline, also known as fast leg theory bowling, was a cricketing tactic devised by the English cricket team for their 1932–33 Ashes tour of Australia. It was designed to combat the extraordinary batting skill of Australia's leading batsman, Don Bradman. A bodyline delivery was one in which the cricket ball was bowled, at pace, at the body of the batsman in the expectation that when he defended himself with his bat a resulting deflection could be caught by one of several fielders standing close by on the leg side. Critics of the tactic considered it intimidating and physically threatening in a game that was traditionally supposed to uphold conventions of sportsmanship. The England team's use of the tactic was perceived by some, both in Australia and England, as overly aggressive or even unfair, and caused controversy that rose to such a level that it threatened diplomatic relations between the two countries before the situation was calmed.Frith, pp. 241–59. Although no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Traditional Owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna people. The area of the city centre and surrounding parklands is called ' in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in honour of Queen Adelaide, the city was founded in 1836 as the planned capital for the only freely-settled British province in Australia. Colonel William Light, one of Adelaide's foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Test, 1932–33 Ashes Series
The Third Test of the 1932–33 Ashes series was one of five Tests in a cricket series between Australia and England. The match was played at the Adelaide Oval in Adelaide from 13 to 19 January 1933, with a rest day on 15 January. England won the match by 338 runs to take a series lead of 2 Tests to 1 with 2 Tests to play. The Test was noted as the one in which the controversy over the use of "bodyline" tactics by the English team came to a head. These tactics, employed by the England fast bowlers Harold Larwood and Bill Voce on the direction of their captain, Douglas Jardine, engendered much ill-feeling. Background In 1932–33, the English team led by Douglas Jardine toured Australia and won the Ashes in a highly acrimonious series known as the "bodyline series". It has been described as the most controversial period in Australian cricket history,Colman, p. 171. and voted the most important Australian moment by a panel of Australian cricket identities. The English team u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Cricket Team In Australia In 1932–33
A cricket team representing England toured Australia in the 1932–33 season. The tour was organised by the Marylebone Cricket Club and matches outside the Tests were played under the MCC name. The tour included five Test matches in Australia, and England won The Ashes by four games to one. The tour was highly controversial because of the bodyline bowling tactics used by the England team under the captaincy of Douglas Jardine. After the Australian tour was over, the MCC team moved on to play in New Zealand, where two further Test matches were played. The MCC team The MCC team was captained by Douglas Jardine, with Bob Wyatt as vice-captain. Pelham Warner and Richard Palairet were joint managers. The team members were: * Douglas Jardine, Surrey, team captain & batsman * Bob Wyatt, Warwickshire, vice-captain & batsman * Gubby Allen, Middlesex, all-rounder * Les Ames, Kent, wicket-keeper * Bill Bowes, Yorkshire, fast bowler * Freddie Brown, Surrey, leg break bowler * George Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Cricket Team In Australia In 1924–25
Marylebone Cricket Club organised the England cricket team's tour of Australia in the 1924–25 season. Australia won the Ashes series 4–1. Test series summary First Test The first Test included a record 127 run tenth wicket partnership between Johnny Taylor and Arthur Mailey which stood as Australia's best for that wicket until Phillip Hughes and Ashton Agar set a new world record by scoring 163 for the tenth wicket against England in the First Test at Trent Bridge in July 2013. Second Test Third Test Fourth Test Fifth Test Ceylon The English team had a stopover in Colombo ''en route'' to Australia and played a one-day single-innings match there against the Ceylon national team, which at that time did not have Test status. References Further reading * Bill Frindall, ''The Wisden Book of Test Cricket 1877–1978'', Wisden, 1979 * Chris Harte, ''A History of Australian Cricket'', Andre Deutsch, 1993 * Ray Robinson, ''On Top Down Under'', Cassell, 1975 * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sammy Carter
Hanson "Sammy" Carter (15 March 1878 – 8 June 1948) was a cricketer who played for Australia and New South Wales. Career Carter attended Sydney Boys High School in 1894. A wicket-keeper, he made his debut for New South Wales in 1897–98, and after two matches in 1901–02 he was selected to tour England in 1902 as the deputy wicket-keeper. He played his first Test in 1907–08, when he played all five Tests against England. He toured England again in 1909, playing all five Tests, and he also played all five Tests when South Africa toured in 1910–11, and when England toured in 1911–12. He resumed his Test career for the last two Tests against England in 1920–21, although he was nearly 43, and toured England in 1921, playing four Tests, and South Africa in 1921–22, playing his last two Tests. In all he took 44 catches and 21 stumpings in 28 Test matches. As a batsman, he is often credited with the invention of the scoop shot that sails over fine-leg. He often made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire County Cricket Club
Lancashire County Cricket Club represents the historic county of Lancashire in English cricket. The club has held first-class status since it was founded in 1864. Lancashire's home is Old Trafford Cricket Ground, although the team also play matches at other grounds around the county. Lancashire was a founder member of the County Championship in 1890 and have won the competition nine times, most recently in 2011. The club's limited overs team is called Lancashire Lightning. Lancashire were widely recognised as the Champion County four times between 1879 and 1889. They won their first two County Championship titles in the 1897 and 1904 seasons. Between 1926 and 1934, they won the championship five times. Throughout most of the inter-war period, Lancashire and their neighbours Yorkshire had the best two teams in England and the Roses Matches between them were usually the highlight of the domestic season. In 1950, Lancashire shared the title with Surrey. The County Championshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Cricket Team
The England cricket team represents England and Wales in international cricket. Since 1997, it has been governed by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), having been previously governed by Marylebone Cricket Club (the MCC) since 1903. England, as a founding nation, is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International (T20I) status. Until the 1990s, Scottish and Irish players also played for England as those countries were not yet ICC members in their own right. England and Australia were the first teams to play a Test match (15–19 March 1877), and along with South Africa, these nations formed the Imperial Cricket Conference (the predecessor to today's International Cricket Council) on 15 June 1909. England and Australia also played the first ODI on 5 January 1971. England's first T20I was played on 13 June 2005, once more against Australia. , England have played 1,058 Test matches, winning 387 and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |