|
Bernard Kennedy
Bernard Peter Mel Kennedy (born 20 May 1952) is an Irish psychoanalyst, poet, and priest. Early life, family and education Bernard Peter Mel Kennedy was born on 20 May 1952 in Rathfarnham, Dublin to William Augustine Kennedy and Alice Kennedy (née Hughes). Kennedy was ordained in 1979 at Dublin's Holy Cross Seminary (previously known as Clonliffe College). He holds a Master of Arts (MA) in psychoanalytic studies from the University of Sheffield, having matriculated in 2000 and graduated in 2002 with a thesis titled ''On freudian understanding of Sexuality''; he holds a Master of Science (MSc) in psychoanalytic psychotherapy from University College Dublin, which he attended from 2002 to 2004 and for which his thesis was titled ''On Homosexuality and the relation to the father''. His Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) focuses on symptomatology in the works of Freud and Lacan in a 2006 thesis titled ''The Freudian Understanding of the Symptom''. Career Priesthood and theology Beginning in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Very Reverend
The Very Reverend is a Style (manner of address), style given to members of the clergy. The definite article "The" should always precede "Reverend" as "Reverend" is a style or fashion and not a title. Catholic In the Catholic Church, the style is given, by custom, to priests who hold positions of particular note: e.g. vicars general, episcopal vicars, judicial vicars, ecclesiastical judges, vicars forane (deans or archpriests), provincials of religious orders, rectors or presidents of cathedrals, seminaries or colleges/universities, priors of monasteries, Canon (priest), canons, for instance. (The style is ignored if the holder is a monsignor or a bishop; otherwise, a priest who is "Very Reverend" continues to be addressed as Father.) Monsignors of the grade of Chaplain of His Holiness were formerly styled as ''The Very Reverend Monsignor'', while honorary prelates and protonotary apostolics were styled ''The Right Reverend Monsignor''. Now, apart from legitimate custom or acquire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mater Misericordiae University Hospital
The Mater Misericordiae University Hospital ( ga, Ospidéal an Mater Misercordiae), commonly known as the Mater ( "matter"), is a major teaching hospital, based at Eccles Street, Phibsborough, on the northside of Dublin, Ireland. It is managed by Ireland East Hospital Group. History The hospital was founded as an initiative of Catherine McAuley of the Sisters of Mercy and was officially opened by Daniel Murray, Archbishop of Dublin, on 24 September 1861. ''Mater misericordiae'' means "Mother of Mercy" in Latin, a title of the Virgin Mary and alludes to its founders, the Sisters of Mercy. Electric light, a major step in the improvement of endoscopy, was first used by Sir Francis Cruise, to allow cystoscopy, hysteroscopy and sigmoidoscopy as well as the examination of the nasal (and later thoracic) cavities at the hospital in 1865. It became the first hospital in Ireland to remain open 24 hours a day when it dealt with a cholera epidemic in 1886. In 2003, the National Pulmonary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
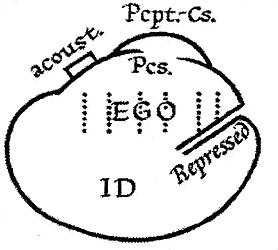
Id, Ego And Super-ego
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ego (Freudian)
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolic Order
The Symbolic (or Symbolic Order of the Borromean knot) is the order in the unconscious that gives rise to subjectivity and bridges intersubjectivity between two subjects; an example is Jacques Lacan's idea of desire as the desire of the Other, maintained by the Symbolic's subjectification of the Other into speech. In the later psychoanalytic theory of Lacan, it is linked by the '' sinthome'' to the Imaginary and the Real. Overview In Lacan's theory, the unconscious is the discourse of the Other and thus belongs to the Symbolic. It is also the realm of the Law that regulates desire in the Oedipus complex, and is determinant of subjectivity. A formative moment in the development of the Symbolic in a subject is the Other giving rise to the ''objet petit (a)utre'', establishing lack, demand and need. However, when it becomes an empty signifier, psychosis, which Freud had failed to tackle in theory, develops from an unstable metonymic sliding of the signified (i.e., for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castration Complex
The castration complex is a concept developed by Sigmund Freud, first presented in 1908, initially as part of his theorisation of the transition in early childhood development from the polymorphous perversity of infantile sexuality to the ‘infantile genital organisation’ which forms the basis for adult sexuality. The trauma induced by the child’s discovery of anatomical difference between the sexes (presence or absence of the penis) gives rise to the fantasy of female emasculation or castration. Phallic stage According to Freud the early stages of the child’s psychosexual development are characterised by polymorphous perversity and a bisexual disposition, and are the same for both sexes. Up to and including the phallic stage of this development the penis and clitoris are the leading erogenous zones. Once the castration complex is initiated with the child’s discovery and puzzlement over the anatomical difference between the sexes (presence or absence of the penis), it mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgenerational Trauma
Transgenerational trauma is the psychological and physiological effects that the trauma experienced by people has on subsequent generations in that group. The primary modes of transmission are the uterine environment during pregnancy causing epigenetic changes in the developing embryo, and the shared family environment of the infant causing psychological, behavioral and social changes in the individual. The term intergenerational transmission refers to instances whereby the traumatic effects are passed down from the directly traumatized generation 0to their offspring 1 and transgenerational transmission is when the offspring 1then pass the effects down to descendants who have not been exposed to the initial traumatic event - at least the grandchildren 2of the original sufferer for males, and their great-grandchildren 3for females. Collective trauma is when psychological trauma experienced by communities and identity groups is carried on as part of the group's collective memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influential and important writers of the 20th century. Joyce's novel ''Ulysses'' (1922) is a landmark in which the episodes of Homer's ''Odyssey'' are paralleled in a variety of literary styles, particularly stream of consciousness. Other well-known works are the short-story collection ''Dubliners'' (1914), and the novels ''A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man'' (1916) and ''Finnegans Wake'' (1939). His other writings include three books of poetry, a play, letters, and occasional journalism. Joyce was born in Dublin into a middle-class family. He attended the Jesuit Clongowes Wood College in County Kildare, then, briefly, the Christian Brothers-run O'Connell School. Despite the chaotic family life imposed by his father's unpredictable finances, he excelled at the Jesuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mother Teresa
Mary Teresa Bojaxhiu, MC (; 26 August 1910 – 5 September 1997), better known as Mother Teresa ( sq, Nënë Tereza), was an Indian-Albanian Catholic nun who, in 1950, founded the Missionaries of Charity. Anjezë Gonxhe Bojaxhiu () was born in Skopjeat the time, part of the Ottoman Empire. After eighteen years, she moved to Ireland and then to India, where she lived most of her life. Saint Teresa of Calcutta; was canonised on 4 September 2016. The anniversary of her death is her feast day. After Mother Teresa founded her religious congregation, it grew to have over 4,500 nuns and was active in 133 countries . The congregation manages homes for people who are dying of HIV/AIDS, leprosy, and tuberculosis. The congregation also runs soup kitchens, dispensaries, mobile clinics, children's and family counselling programmes, as well as orphanages and schools. Members take vows of chastity, poverty, and obedience and also profess a fourth vow: to give "wholehearted free ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desire (Lacanian)
In philosophy, desire has been identified as a recurring philosophical problem. It has been variously interpreted as what compels someone towards the highest state of human nature or consciousness, as well as being posited as either something to be eliminated or a powerful source of potential. In Plato's ''The Republic'', Socrates argued that individual desires must be postponed in the name of a higher ideal. Similarly, within the teachings of Buddhism, craving, identified as the most potent form of desire, is thought to be the cause of all suffering, which can be eliminated to attain greater happiness (Nirvana). While on the path to liberation, a practitioner is advised to "generate desire" for skillful ends. History Ancient Greece In Aristotle's ''De Anima'' the soul is seen to be involved in motion, because animals desire things and in their desire, they acquire locomotion. Aristotle argued that desire is implicated in animal interactions and the propensity of animals to motio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacanianism
Lacanianism or Lacanian psychoanalysis is a theoretical system that explains the mind, behaviour, and culture through a structuralist and post-structuralist extension of classical psychoanalysis, initiated by the work of Jacques Lacan from the 1950s to the 1980s. Lacanian perspectives contend that the world of language, the Symbolic, structures the human mind, and stress the importance of desire, which is conceived of as endless and impossible to satisfy. Contemporary Lacanianism is characterised by a broad range of thought and extensive debate between Lacanians. Lacanianism has been particularly influential in post-structuralism, literary theory and feminist theory, as well as in various branches of critical theory, including queer theory. Equally, it has been criticised by the post-structuralists Deleuze and Guattari and by various feminist theorists. Its clinical relevance is limited and outside France it has had no influence on psychiatry. There is a Lacanian strand in left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archdiocese Of Dublin
The Archbishop of Dublin is an archepiscopal title which takes its name after Dublin, Ireland. Since the Reformation, there have been parallel apostolic successions to the title: one in the Catholic Church and the other in the Church of Ireland. The archbishop of each denomination also holds the title of Primate of Ireland. History The diocese of Dublin was formally established by Sigtrygg (Sitric) Silkbeard, King of Dublin in 1028, . ''Diocese of Dublin and Glendalough''. Retrieved on 31 March 2010. and the first bishop, , was consecrated in about the same year. The diocese of Dublin was subject to the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |