|
Beriev S-13
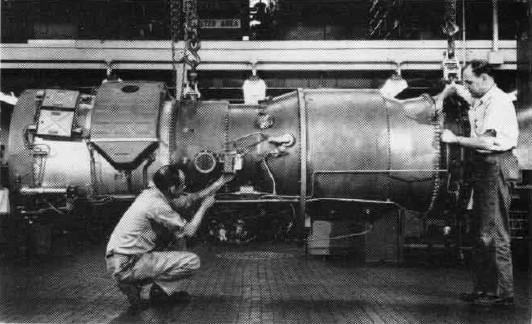
The Beriev S-13 was a Soviet reverse-engineered copy of the Lockheed U-2C, developed in the Soviet Union in the early 1960s. History On 1 May 1960, Francis Gary Powers flew a U-2 espionage mission from northern Pakistan over the Soviet Union. While flying over the Urals, the aircraft came within range of Soviet surface-to-air missiles. The U-2 was hit by an S-75 Dvina missile (NATO code name: SA-2 Guideline) and broke apart, but the debris remained relatively intact. The Soviet Union had its own comparable high altitude reconnaissance aircraft, the Yakovlev Yak-25RW, but for political reasons this high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft was not used outside the borders of the Soviet Union and its main function was to emulate the U-2 to train Soviet air defence forces. The Yakovlev Yak-25RV was unable to reach the U-2's ceiling of . After the U-2 shootdown, the wreckage was examined by Soviet aviation specialists. The investigation, conducted by Georgy Beriev of OKB-49 at Taganr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnaissance Aircraft
A reconnaissance aircraft (colloquially, a spy plane) is a military aircraft designed or adapted to perform aerial reconnaissance with roles including collection of imagery intelligence (including using photography), signals intelligence, as well as measurement and signature intelligence. Modern technology has also enabled some aircraft and UAVs to carry out real-time surveillance in addition to general intelligence gathering. Before the development of devices such as radar, military forces relied on reconnaissance aircraft for visual observation and scouting of enemy movement. An example is the PBY Catalina maritime patrol flying boat used by the Allies in World War II: a flight of U.S. Navy Catalinas spotted part of the Japanese fleet approaching Midway Island, beginning the Battle of Midway. History Prior to the 20th century machines for powered and controllable flight were not available to military forces, but some attempts were made to use lighter than air craft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taganrog
Taganrog ( rus, Таганрог, p=təɡɐnˈrok) is a port city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, on the north shore of the Taganrog Bay in the Sea of Azov, several kilometers west of the mouth of the Don River. Population: History of Taganrog The history of the city goes back to the late Bronze Age–early Iron Age (between the 20th and 10th centuries BC), when it was the earliest Greek settlement in the northwestern Black Sea Region and was mentioned by the Greek historian Herodotus as Emporion Kremnoi. In the 13th century, Pisan merchants founded a colony, Portus Pisanus, which was however short-lived. Taganrog was founded by Peter the Great on 12 September 1698. The first Russian Navy base, it hosted the Azov Flotilla of Catherine the Great (1770–1783), which subsequently became the Russian Black Sea Fleet. Taganrog was granted city status in 1775. By the end of the 18th century, Taganrog had lost its importance as a military base after Crimea and the entire Sea of Azov w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-25; NATO reporting name: Foxbat) is a supersonic interceptor and reconnaissance aircraft that is among the fastest military aircraft to enter service. Designed by the Soviet Union's Mikoyan-Gurevich bureau, it is an aircraft built primarily using stainless steel. It was to be the last plane designed by Mikhail Gurevich, before his retirement. The first prototype flew in 1964 and the aircraft entered service in 1970. It has an operational top speed of Mach 2.83. Although its thrust was sufficient to reach Mach 3.2+, its speed was limited to prevent engines from overheating at higher air speeds and possibly damaging them beyond repair."Intelligence: Big-Mouth Belenko" ''Time'', 11 Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myasishchev M-55
The Myasishchev M-55 (NATO reporting name: ''Mystic-B'') is a high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft developed by OKB Myasishchev in the Soviet Union, similar in mission to the Lockheed ER-2, but with a twin boom fuselage and tail surface design. It is a twin-engined development of the Myasishchev M-17 Stratosphera with a higher maximum take-off weight. Design and development During the 1950s and 1960s the United States instituted several programs using high-altitude reconnaissance balloons, released over friendly territory to ascend into the jetstream and be transported over the Soviet Union and People's Republic of China.Taylor, Michael J. H. ''Brassey's World Aircraft & Systems Directory 1999–2000'', 2000. , p. 157. ''Subject 34'' To combat these high-altitude balloons, Myasishchev proposed ''Subject 34'' a single-seat turbojet-powered twin-boom high-aspect-ratio aircraft, nicknamed ''Chaika'' ("Seagull" in Russian) due to its anhedral wing design. Armament of the single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsybin RSR
The Tsybin RSR (''Reactivnyy Strategicheskiy Razvedchik'', Cyrillic ''Реактивный Стратегический Разведчик'', Russian for "jet strategic reconnaissance") was a Soviet design for an advanced, long-range, Mach 3 strategic reconnaissance aircraft. Development and design In 1954, the design bureau headed by Pavel Tsybin started development of a ramjet-powered supersonic strategic bomber, the RS. This design proved impracticable, and a smaller derivative, the 2RS was proposed, which would achieve intercontinental range by being air-launched from a modified Tupolev Tu-95 bomber.Butowski 1998. p. 39–40. This too was unsuccessful, with the aircraft unable to return to base if used on an intercontinental mission, while being incapable of carrying a thermonuclear bomb.Gunston 1995, p. 376. The design was therefore revised again to a reconnaissance aircraft capable of operating from conventional runways, the RSR. As ramjets could not be used for take-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a long-range, high-altitude, Mach 3+ strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed and manufactured by the American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation. It was operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and NASA. The SR-71 was developed as a black project from the Lockheed A-12 reconnaissance aircraft during the 1960s by Lockheed's Skunk Works division. American aerospace engineer Clarence "Kelly" Johnson was responsible for many of the aircraft's innovative concepts. The shape of the SR-71 was based on that of the A-12, which was one of the first aircraft to be designed with a reduced radar cross-section. Initially, a bomber variant of the A-12 was requested by Curtis LeMay, before the program was focused solely on reconnaissance. Mission equipment for the reconnaissance role included signals intelligence sensors, side looking airborne radar, and a camera; the SR-71 was both longer and heavier than the A-12, allowing it to hold mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces were formed from components of the Imperial Russian Air Service in 1917, and faced their greatest test during World War II. The groups were also involved in the Korean War, and dissolved along with the Soviet Union itself in 1991–92. Former Soviet Air Forces' assets were subsequently divided into several air forces of former Soviet republics, including the new Russian Air Force. "March of the Pilots" was its song. Origins The ''All-Russia Collegium for Direction of the Air Forces of the Old Army'' (translation is uncertain) was formed on 20 December 1917. This was a Bolshevik aerial headquarters initially led by Konstantin Akashev. Along with a general postwar military reorganisation, the collegium was reconstituted as the "Workers' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.6 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Kazan is the fifth-largest city in Russia, and the most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. Kazan became the capital of the Khanate of Kazan and was conquered by Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century, becoming a part of Russia. The city was seized and largely destroyed during Pugachev's Rebellion of 1773–1775, but was later rebuilt during the reign of Catherine the Great. In the following centuries, Kazan grew to become a major industrial, cultural and religious centre of Russia. In 1920, after the Russian SFSR became a part of the Soviet Union, Kazan became the capital of the Tat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-16
The JSC Precision Engineering Design Bureau named after A. E. Nudelman (russian: Конструкторское бюро точного машиностроения им. А. Э. Нудельмана, Konstruktorskoye Byuro Tochnogo Mashinostroeniya im. A. E. Nudelmana), shortened to "KB Tochmash" (russian: КБ Точмаш, KB Tochmash), is a missile design bureau located in Moscow. It was founded in 1934 under the designation OKB-16 under the leadership of Yakov Taubin, but after his arrest and execution, leadership fell to Alexander Nudelman, who would lead it until 1987. Products KB Tochmash has designed many weapon systems, including the following: Gun systems * Nudelman-Suranov NS-37 Autocannon * Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 Autocannon * Nudelman-Suranov NS-45 Autocannon * Nudelman N-37 Autocannon * Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 Autocannon * Nudelman-Rikhter NR-30 Autocannon * Rikhter R-23 Autocannon * Nudelman-Nemenov NN-30 CIWS * AGS-17 Automatic Grenade Launcher Rockets * S-5 * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney J75-P-13
The Pratt & Whitney J75 (civilian designation: JT4A) is an axial-flow turbojet engine first flown in 1955. A two-spool design in the 17,000 lbf (76 kN) thrust class, the J75 was essentially the bigger brother of the Pratt & Whitney J57 (JT3C). It was known in civilian service as the JT4A, and in a variety of stationary roles as the GG4 and FT4. Design and development In military use, the J75 was used on the Convair F-106 Delta Dart, Lockheed U-2, and Republic F-105 Thunderchief. It was also utilized in the prototype and experimental Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow, Lockheed A-12, Martin P6M SeaMaster, North American YF-107, and Vought XF8U-3 Crusader III. Before the arrival of the Pratt & Whitney JT3D turbofan engine, the JT4A was used to power certain Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 models, bringing improved field performance in the medium-range Boeing 707-220 and Douglas DC-8-20, and intercontinental range in the Boeing 707-320 and the Douglas DC-8-30. By late 1959, P&W had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ministers Of The Soviet Union
The Council of Ministers of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( rus, Совет министров СССР, r=Sovet Ministrov SSSR, p=sɐˈvʲet mʲɪˈnʲistrəf ɛsɛsɛˈsɛr; sometimes abbreviated to ''Sovmin'' or referred to as the ''Soviet of Ministers''), was the ''de jure'' government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), comprising the main executive and administrative agency of the USSR from 1946 until 1991. During 1946 the Council of People's Commissars was reorganized as the Council of Ministers. Accordingly, the People's Commissariats were renamed as Ministries. The council issued declarations and instructions based on and in accordance with applicable laws, which had obligatory jurisdictional power in all republics of the Union. However, the most important decisions were made by joint declarations with the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Soviet Union (CPSU), which was ''de facto'' more powerful than the Council of Ministers. During 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)