|
Benoît Rolland
Benoît Marie Rolland (born 12 September 1954 Paris), is a bow maker and musician, currently established in Boston, Massachusetts. An internationally renowned bow maker, he is a 2012 MacArthur Fellow and a Chevalier des Arts et des Lettres (2017). Biography Early years Rolland was born into a Parisian family of old descent. He received his early musical training at the age of four from his grandmother Germaine Thyssens-Valentin, a renowned concert pianist. During his childhood he frequented her musical salon, where composers such as Olivier Messiaen and other performers gathered. He began to play the violin at age eight and subsequently entered the Versailles conservatory and the Conservatoire de Paris, graduating at age 16. Among his professors were Alfred Loewenguth and Line Talluel. Aside from violin performance, his perfect pitch led to advancement in his ability to read and write music. He honed his skill for musical composition at the Schola Cantorum de Paris (1980–8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow Maker
A bow maker is a person who builds, repairs, and restores ancient or modern bows for bowed string instruments. These include violins, violas, cellos, double basses, viola d'amore, viola da gamba, etc. The French word for bowmaker (bow maker) is archetier for one who makes bows of the string family of instruments such as violin, viola, cello and double bass. Root of the word comes from ''archet''—pronounced —the bow. A bow maker typically uses between 150 and 200 hairs from the tail of a horse for a violin bow. Bows for other members of the violin family typically have a wider ribbon, using more hairs. White hair generally produces a smoother sound and black hair (used mainly for double bass bows) is coarser, producing a rougher sound. Lower quality (inexpensive) bows often use nylon or synthetic hair. Rosin, a hard, sticky substance made from resin (sometimes mixed with wax), is regularly applied to the bow hair to increase friction. In making the stick of a bow, the initia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Suk (violinist)
Josef Suk (8 August 1929 – 7 July 2011) was a Czech violinist, violist, chamber musician and conductor. In his home country he carried the title of National Artist. Youth and studies Josef Suk was born in Prague, the grandson of the composer and violinist Josef Suk, and great-grandson of the composer Antonín Dvořák. After finishing high school in 1945 he entered the Prague Conservatory (1945-1951), where his teachers were Jaroslav Kocián, Norbert Kubát and Karel Šnebergr. The most important of all his teachers was Jaroslav Kocián, who started teaching him privately when Suk was 7 years old. Led by him, Suk mastered the violin art drawing from the spectacular interpretative art of his teacher, who was specific with his noble technique of tone formation. During his studies, in 1949, Suk was sent to Paris and Brussels where he represented successfully the young generation of Czech violinists. After leaving the Prague Conservatory, he spent four terms at the Academy of Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conducting Baton
A baton is a stick that is used by conductors primarily to enlarge and enhance the manual and bodily movements associated with directing an ensemble of musicians. Description Modern batons are generally made of a lightweight wood, fiberglass or carbon fiber which is tapered to a comfortable grip called a "bulb" that is usually made of cork, oak, walnut, rosewood, or occasionally aluminium and that may be tailored to a conductor's needs. Professional conductors often have personal specifications for a baton based on their own physical demands and the nature of the performance: Sir Henry Wood and Herbert von Karajan are some examples. Historic examples of their construction include one given to the French composer Louis-Antoine Jullien in the mid 1850s prior to his first visit to the United States: it is described as "a gorgeous baton made of maplewood, richly mounted in gold and set with costly diamonds." Batons have normally varied in length from about though a range of betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
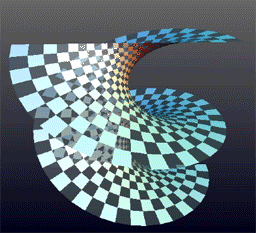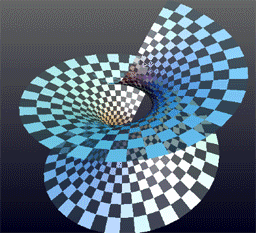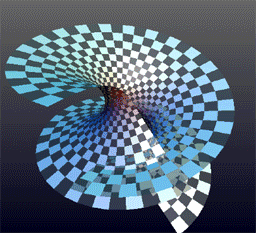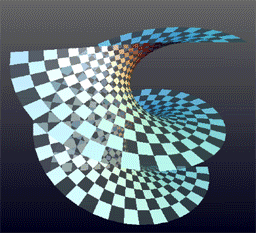
Helicoid
The helicoid, also known as helical surface, after the plane and the catenoid, is the third minimal surface to be known. Description It was described by Euler in 1774 and by Jean Baptiste Meusnier in 1776. Its name derives from its similarity to the helix: for every point on the helicoid, there is a helix contained in the helicoid which passes through that point. Since it is considered that the planar range extends through negative and positive infinity, close observation shows the appearance of two parallel or mirror planes in the sense that if the slope of one plane is traced, the co-plane can be seen to be bypassed or skipped, though in actuality the co-plane is also traced from the opposite perspective. The helicoid is also a ruled surface (and a right conoid), meaning that it is a trace of a line. Alternatively, for any point on the surface, there is a line on the surface passing through it. Indeed, Catalan proved in 1842 that the helicoid and the plane were the only rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow Frog
The bow frog is the end part of a stringed musical instrument's bow that encloses the mechanism responsible for tightening and holding the bow hair ribbon. Most of the bow frogs used in today's classical bows are made of ebony; some synthetic bows have frogs made with materials that imitate ebony, while Baroque bows use frogs made with various woods. Etymology and names The origin of the name ''frog'' is unknown, although it may derive from the use of the frock, the small device that bow makers use to shape it. It is also referred to as the "heel" or "nut" of the bow. The German equivalent ''Frosch'' is the literal equivalent of "frog," while in French and Italian the equivalent of "heel" is used (''talon'' and ''tallone''). French also uses ''hausse''. The foreign language terms sometimes appear in musical instructions, such as ''au talon'', indicating to play with the bow near the frog. However, the English term is also used, such as in the Alfred edition of George Gershwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galliane
A Galliane is a bow frog for stringed instrument bows that sets the hair ribbon at an angle. This kind of frog was first described in ''Scientific American'' in October 2012. It was invented by bow maker Benoit Rolland for violin, viola, cello, and double bass bows. The frog The frog is the part at the end of the bow that encloses the mechanism responsible for tightening and holding the bow hair ribbon. The name ‘frog’ may derive from the use of the frock, the small device that bow makers use to shape it. It is also referred to as the heel of the bow. The evolution of the bow The classical bow was pioneered by François Xavier Tourte, a French master bowmaker from the late 18th and early 19th century. With the help of virtuoso violinist G.B. Viotti he sought to improve upon the limitations of the Baroque bow by lengthening it, strengthening its tip, and introducing a curvature that allowed for greater flexibility and improved the springing action of the bow. Tourte’s craft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Luc Ponty
Jean-Luc Ponty (born 29 September 1942) is a French jazz violinist and composer. Early life Ponty was born into a family of classical musicians in Avranches, France. His father taught violin, his mother taught piano. At sixteen, he was admitted to the Conservatoire National Supérieur de Musique de Paris, graduating two years later with the institution's highest honor, Premier Prix (first prize). He was hired by the Concerts Lamoureux in which he played for three years. While still a member of the orchestra in Paris, Ponty picked up a side job playing clarinet (which his father had taught him) for a college jazz band, that regularly performed at local parties. It proved life-changing. A growing interest in Miles Davis and John Coltrane compelled him to take up tenor saxophone. One night after an orchestra concert, and still wearing his tuxedo, Ponty found himself at a local club with only his violin. Within four years, he was widely accepted as the leading figure in "jazz fid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Tetzlaff
Christian Tetzlaff (born 29 April 1966) is a German violinist. Biography Tetzlaff was born in Hamburg. His parents were amateur musicians and met in a church choir. He began playing the violin and piano at the age of 6, and made his concert debut at 14 years old. He studied with Uwe-Martin Haiberg at the Musikhochschule Lübeck and later with Walter Levin at the University of Cincinnati – College-Conservatory of Music. His breakthrough as a soloist came in 1988, at the age of 22, when he performed Schoenberg's Violin Concerto in critically acclaimed concerts with the Cleveland Orchestra and the Munich Philharmonic. The following year he made his solo recital debut in New York City. He has continued to play as a soloist with major orchestras on stage and in recordings, including Beethoven's works for violin and orchestra performed with the Tonhalle Orchester Zürich under David Zinman. He returned to New York in 2011 for a recital with Antje Weithaas at Zankel Hall. 2012 he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaime Laredo
Jaime Laredo (born June 7, 1941) is a violinist and conductor. He was the conductor and Music Director of the Vermont Symphony Orchestra, and he began his musical career when he was five years old. Laredo was born in Cochabamba, Bolivia. In 1948, he came to North America and took lessons from Antonio de Grassi. He also studied with Frank Houser before moving to Cleveland, Ohio, to study under Josef Gingold in 1953. He studied with Ivan Galamian at the Curtis Institute of Music until his graduation. From 1960 to 1974 he was married to the pianist Ruth Laredo. Laredo is currently a professor at the renowned Cleveland Institute of Music. He served as artistic advisor for the Fort Wayne Philharmonic Orchestra and guest conducted the orchestra on April 18, 2009, in a program featuring his wife, the cellist Sharon Robinson. He was scheduled to again conduct the orchestra for two programs during the 2009–10 season. Laredo and Robinson were also featured soloists in a special conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivry Gitlis
Ivry Gitlis ( he, עברי גיטליס; 25 August 1922 – 24 December 2020) was an Israeli virtuoso violinist and UNESCO Goodwill Ambassador. He performed with the world's top orchestras, including the London Philharmonic, New York Philharmonic, Berlin Philharmonic, Vienna Philharmonic, Philadelphia Orchestra, and Israel Philharmonic Orchestra. Early life and education Yitzhak-Meir (Isaac) Gitlis was born on 25 August 1922 in Haifa, Israel to Jewish parents, who emigrated in 1921 from Kamianets-Podilskyi, Ukraine. Gitlis acquired his first violin when he was five years old and started lessons under Mme Velikovsky together with his friend Zvi Zeitlin. He then studied privately with Mira Ben-Ami, a pupil of Joseph Szigeti. When he was eight, she arranged for him to play for Bronisław Huberman, which prompted a fundraising campaign to allow him to study in France. In 1933, he arrived with his mother in Paris and started to take lessons witMarcel Chailley husband of the pia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mstislav Rostropovich
Mstislav Leopoldovich Rostropovich, (27 March 192727 April 2007) was a Russian cellist and conductor. He is considered by many to be the greatest cellist of the 20th century. In addition to his interpretations and technique, he was well known for both inspiring and commissioning new works, which enlarged the cello repertoire more than any cellist before or since. He inspired and premiered over 100 pieces, forming long-standing friendships and artistic partnerships with composers including Dmitri Shostakovich, Sergei Prokofiev, Henri Dutilleux, Witold Lutosławski, Olivier Messiaen, Luciano Berio, Krzysztof Penderecki, Alfred Schnittke, Norbert Moret, Andreas Makris, Leonard Bernstein, Aram Khachaturian and Benjamin Britten. Rostropovich was internationally recognized as a staunch advocate of human rights, and was awarded the 1974 Award of the International League of Human Rights. He was married to the soprano Galina Vishnevskaya and had two daughters, Olga and Elena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kevlar
Kevlar (para-aramid) is a strong, heat-resistant synthetic fiber, related to other aramids such as Nomex and Technora. Developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPont in 1965, the high-strength material was first used commercially in the early 1970s as a replacement for steel in racing tires. It is typically spun into ropes or fabric sheets that can be used as such, or as an ingredient in composite material components. Kevlar has many applications, ranging from bicycle tires and racing sails to bulletproof vests, all due to its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio; by this measure it is five times stronger than steel. It is also used to make modern marching drumheads that withstand high impact; and for mooring lines and other underwater applications. A similar fiber called Twaron with the same chemical structure was developed by Akzo in the 1970s; commercial production started in 1986, and Twaron is now manufactured by Teijin. History Poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide (K2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |