|
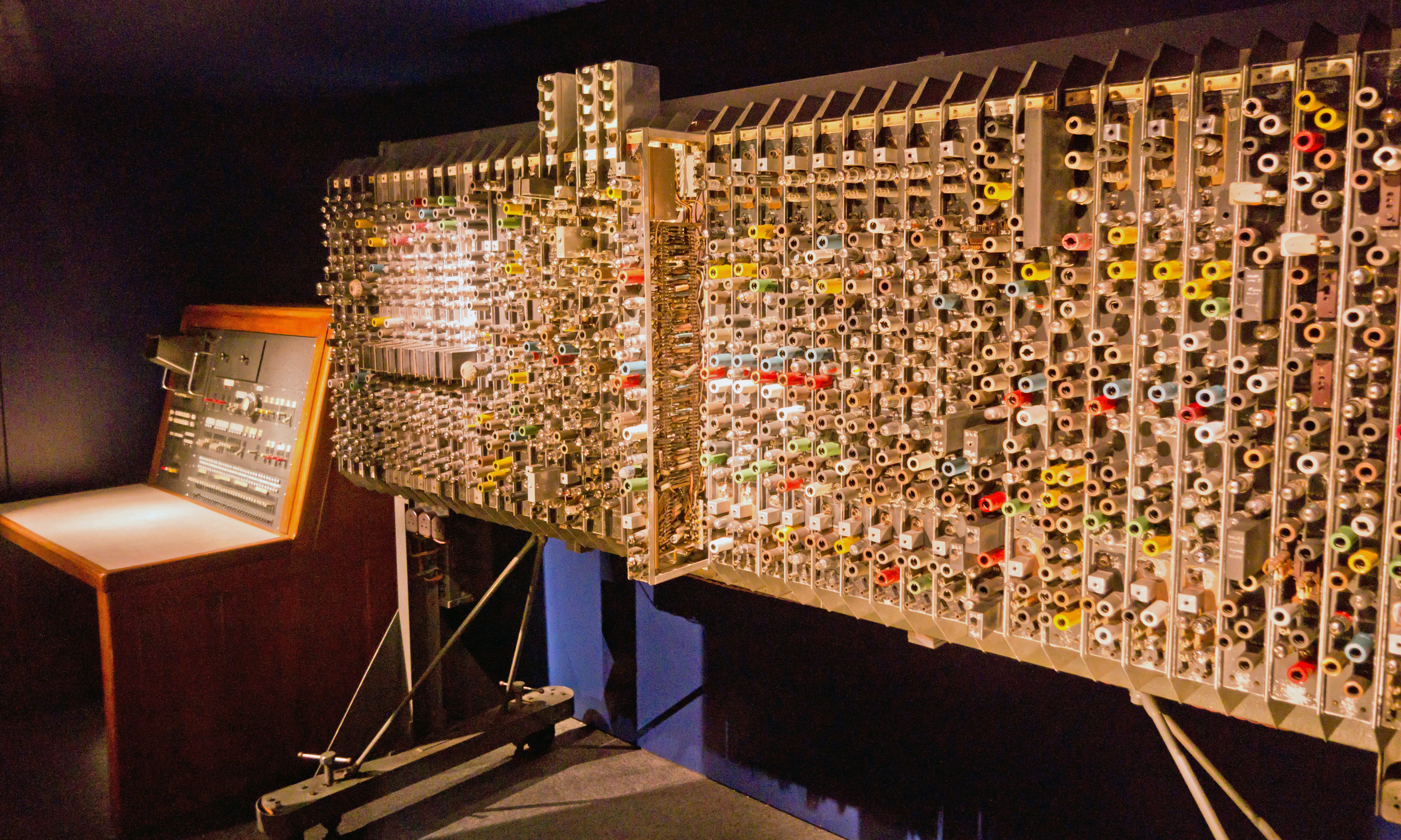
Bendix G15
The Bendix G-15 is a computer introduced in 1956 by the Bendix Corporation, Computer Division, Los Angeles, California. It is about and weighs about . The G-15 has a drum memory of 2,160 29-bit words, along with 20 words used for special purposes and rapid-access storage. The base system, without peripherals, cost $49,500. A working model cost around $60,000 (over $500,000 by today's standards). It could also be rented for $1,485 per month. It was meant for scientific and industrial markets. The series was gradually discontinued when Control Data Corporation took over the Bendix computer division in 1963. The chief designer of the G-15 was Harry Huskey, who had worked with Alan Turing on the ACE in the United Kingdom and on the SWAC in the 1950s. He made most of the design while working as a professor at Berkeley, and other universities. David C. Evans was one of the Bendix engineers on the G-15 project. He would later become famous for his work in computer graphics and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Huskey
Harry Douglas Huskey (January 19, 1916 – April 9, 2017) was an American computer design pioneer. Early life and career Huskey was born in Whittier, in the Smoky Mountains region of North Carolina and grew up in Idaho. He received his bachelor's degree in mathematics and physics at the University of Idaho. He was the first member of his family to attend college. He gained his Master's and then his PhD in 1943 from the Ohio State University on ''Contributions to the Problem of Geöcze''. Huskey taught mathematics to U.S. Navy students at the University of Pennsylvania and then worked part-time on the early ENIAC and EDVAC computers in 1945. This work represented his first formal introduction to computers, according to his obituary in ''The New York Times''. He visited the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the United Kingdom for a year and worked on the Pilot ACE computer with Alan Turing and others. He was also involved with the EDVAC and SEAC computer projects. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Computing Engine
The Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) was a British early electronic serial stored-program computer designed by Alan Turing. It was based on the earlier Pilot ACE. It led to the MOSAIC computer, the Bendix G-15, and other computers. Background The project was managed by John R. Womersley, superintendent of the Mathematics Division of the National Physical Laboratory (NPL). The use of the word ''Engine'' was in homage to Charles Babbage and his Difference Engine and Analytical Engine. Turing's technical design ''Proposed Electronic Calculator'' was the product of his theoretical work in 1936 "On Computable Numbers" (and ) and his wartime experience at Bletchley Park where the Colossus computers had been successful in breaking German military codes. In his 1936 paper, Turing described his idea as a "universal computing machine", but it is now known as the Universal Turing machine. Turing was sought by Womersley to work in the NPL on the ACE project; he accepted and beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milliseconds
A millisecond (from ''milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wavelength of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Memory Access Time
In ordinary language, an average is a single number taken as representative of a list of numbers, usually the sum of the numbers divided by how many numbers are in the list (the arithmetic mean). For example, the average of the numbers 2, 3, 4, 7, and 9 (summing to 25) is 5. Depending on the context, an average might be another statistic such as the median, or mode. For example, the average personal income is often given as the median—the number below which are 50% of personal incomes and above which are 50% of personal incomes—because the mean would be higher by including personal incomes from a few billionaires. For this reason, it is recommended to avoid using the word "average" when discussing measures of central tendency. General properties If all numbers in a list are the same number, then their average is also equal to this number. This property is shared by each of the many types of average. Another universal property is monotonicity: if two lists of numbers ''A'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word (data Type)
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word (the ''word size'', ''word width'', or ''word length'') is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture. The size of a word is reflected in many aspects of a computer's structure and operation; the majority of the registers in a processor are usually word-sized and the largest datum that can be transferred to and from the working memory in a single operation is a word in many (not all) architectures. The largest possible address size, used to designate a location in memory, is typically a hardware word (here, "hardware word" means the full-sized natural word of the processor, as opposed to any other definition used). Documentation for older computers with fixed word size commonly states memory sizes in words ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop is a device which stores a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-precision Floating-point Format
Double-precision floating-point format (sometimes called FP64 or float64) is a floating-point number format, usually occupying 64 bits in computer memory; it represents a wide dynamic range of numeric values by using a floating radix point. Floating point is used to represent fractional values, or when a wider range is needed than is provided by fixed point (of the same bit width), even if at the cost of precision. Double precision may be chosen when the range or precision of single precision would be insufficient. In the IEEE 754-2008 standard, the 64-bit base-2 format is officially referred to as binary64; it was called double in IEEE 754-1985. IEEE 754 specifies additional floating-point formats, including 32-bit base-2 ''single precision'' and, more recently, base-10 representations. One of the first programming languages to provide single- and double-precision floating-point data types was Fortran. Before the widespread adoption of IEEE 754-1985, the representation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processor Register
A processor register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's processor. Registers usually consist of a small amount of fast storage, although some registers have specific hardware functions, and may be read-only or write-only. In computer architecture, registers are typically addressed by mechanisms other than main memory, but may in some cases be assigned a memory address e.g. DEC PDP-10, ICT 1900. Almost all computers, whether load/store architecture or not, load data from a larger memory into registers where it is used for arithmetic operations and is manipulated or tested by machine instructions. Manipulated data is then often stored back to main memory, either by the same instruction or by a subsequent one. Modern processors use either static or dynamic RAM as main memory, with the latter usually accessed via one or more cache levels. Processor registers are normally at the top of the memory hierarchy, and provide the fastest way to access data. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word (computer Architecture)
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word (the ''word size'', ''word width'', or ''word length'') is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture. The size of a word is reflected in many aspects of a computer's structure and operation; the majority of the registers in a processor are usually word-sized and the largest datum that can be transferred to and from the working memory in a single operation is a word in many (not all) architectures. The largest possible address size, used to designate a location in memory, is typically a hardware word (here, "hardware word" means the full-sized natural word of the processor, as opposed to any other definition used). Documentation for older computers with fixed word size commonly states memory sizes in words ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Delay Line
An analog delay line is a network of electrical components connected in cascade, where each individual element creates a time difference between its input and output. It operates on analog signals whose amplitude varies continuously. In the case of a periodic signal, the time difference can be described in terms of a change in the phase of the signal. One example of an analog delay line is a bucket-brigade device. Other types of delay line include acoustic (usually ultrasonic), magnetostrictive, and surface acoustic wave devices. A series of resistor–capacitor circuits (RC circuits) can be cascaded to form a delay. A long transmission line can also provide a delay element. The delay time of an analog delay line may be only a few nanoseconds or several milliseconds, limited by the practical size of the physical medium used to delay the signal and the propagation speed of impulses in the medium. Analog delay lines are applied in many types of signal processing circuits; for ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |