|
Benahavís
Benahavís is a Spanish town (pueblo) and municipality in the province of Malaga. It is mountain village between Marbella, Estepona, and Ronda, 7 kilometers from the coast. On the southern face of La Serranía de Ronda mountain range, Benahavís is one of the most mountainous villages on the western Costa del Sol, near the resort beaches as well as the spectacular mountains of the Serrania de Ronda. Its terrain is traversed by the Guadalmina, Guadaiza and Guadalmansa Rivers. Places of great natural and historic interest are to be found within its boundaries, such as El Cerro del Duque, Daidin and the Montemayor Castle. During the late 1990s, the Junta de Andalucia constructed a dam on the site of an old marble quarry, and now for much of the year the once ever-flowing Río Guadalmina is a dried-up riverbed. History At the end of the 11th century, Benahavís was founded by Arabs. The village was intimately involved with Andalusia's Arabic past, and particularly with Marbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marbella
Marbella ( , , ) is a city and municipality in southern Spain, belonging to the province of Málaga in the autonomous community of Andalusia. It is part of the Costa del Sol and is the headquarters of the Association of Municipalities of the region; it is also the head of the judicial district that bears its name. Marbella is situated on the Mediterranean Sea, between Málaga and the Strait of Gibraltar, in the foothills of the Sierra Blanca. The municipality covers an area of crossed by highways on the coast, which are its main entrances. In 2018 the population of the city was 141,463 inhabitants, making it the second most populous municipality in the province of Málaga and the eighth in Andalusia. It is one of the most important tourist cities of the Costa del Sol and throughout most of the year is an international tourist attraction, due mainly to its climate and tourist infrastructure. The city also has a significant archaeological heritage, several museums and perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Del Sol Occidental
Costa del Sol Occidental (English: "Western Coast of the Sun") is a Comarcas of Spain, ''comarca'' (county) in Andalusia, southern Spain. It occupies a narrow coastal strip delimited by the cordillera Penibética (Sierra de Mijas, Sierra Alpujata, Sierra Blanca (Andalusia), Sierra Blanca, Sierra Bermeja, Sierra Crestallina) to the north and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. The coast shows a diversity of landscapes: beaches, cliffs, estuaries, bays and dunes. The rivers are short and seasonal, while the agriculture is hampered by the lee wave, lee effect caused by the Baetic System. Municipalities There are 9 municipalities, running along this coast, and listed below from west to east: See also *Baetic System *Costa del Sol References {{coord, 36, 30, 54, N, 4, 52, 40, W, region:ES_type:adm3rd_source:kolossus-cawiki, display=title Comarcas of Andalusia Geography of the Province of Málaga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalmina River
The river Guadalmina (from the Arabic for "Wadi (river) of the port") is a short coastal river of the Mediterranean basin in southern Spain that runs entirely within the Andalusian province of Málaga. Only in length, the Guadalmina rises in the Sierra Bermeja, in the municipality of Igualeja, but its main course begins below the mountains in the municipality of Benahavís, forming a karst aquifer in an area known as ''Las Angosturas'' (the narrows). The river flows into the municipality of Marbella near San Pedro de Alcántara, and serves to delimit its border from that of the municipality of Estepona. The Guadalmina was formerly of defensive strategic importance for the people of Marbella; its waters also served to power watermills for grinding grain into flour. The La Concepción reservoir is the primary water source for this municipality; it is formed by a diversion dam on the Río Verde, where the waters of the rivers Guadalmina, Guadalmansa and Guadaiza join and are capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almáchar
''Almáchar'' is a town and municipality in the province of Málaga, part of the autonomous community of Andalusia in southern Spain. The municipality is situated approximately 35 kilometres from Málaga capital. It has a population of approximately 2,100 residents. It is the capital of the moscatel raisin area. Natives of the area are called Almachareños. Its name comes from the Arabic word ''machar'', which means ''meadow''. Almáchar is situated in the heart of the Axarquía at 200 metres above sea level, 35 kilometres from Málaga city and 14 from Vélez-Málaga Vélez-Málaga () is a municipality and the capital of the Axarquía comarca in the province of Málaga, in the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia. It is the most important city in the comarca. Locally it is referred to as Vélez. Vélez .... It is built on a small hill between the El Borge and Almáchar rivers, close to the Mountains of Málaga and surrounded by vineyards, olive and cereal groves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
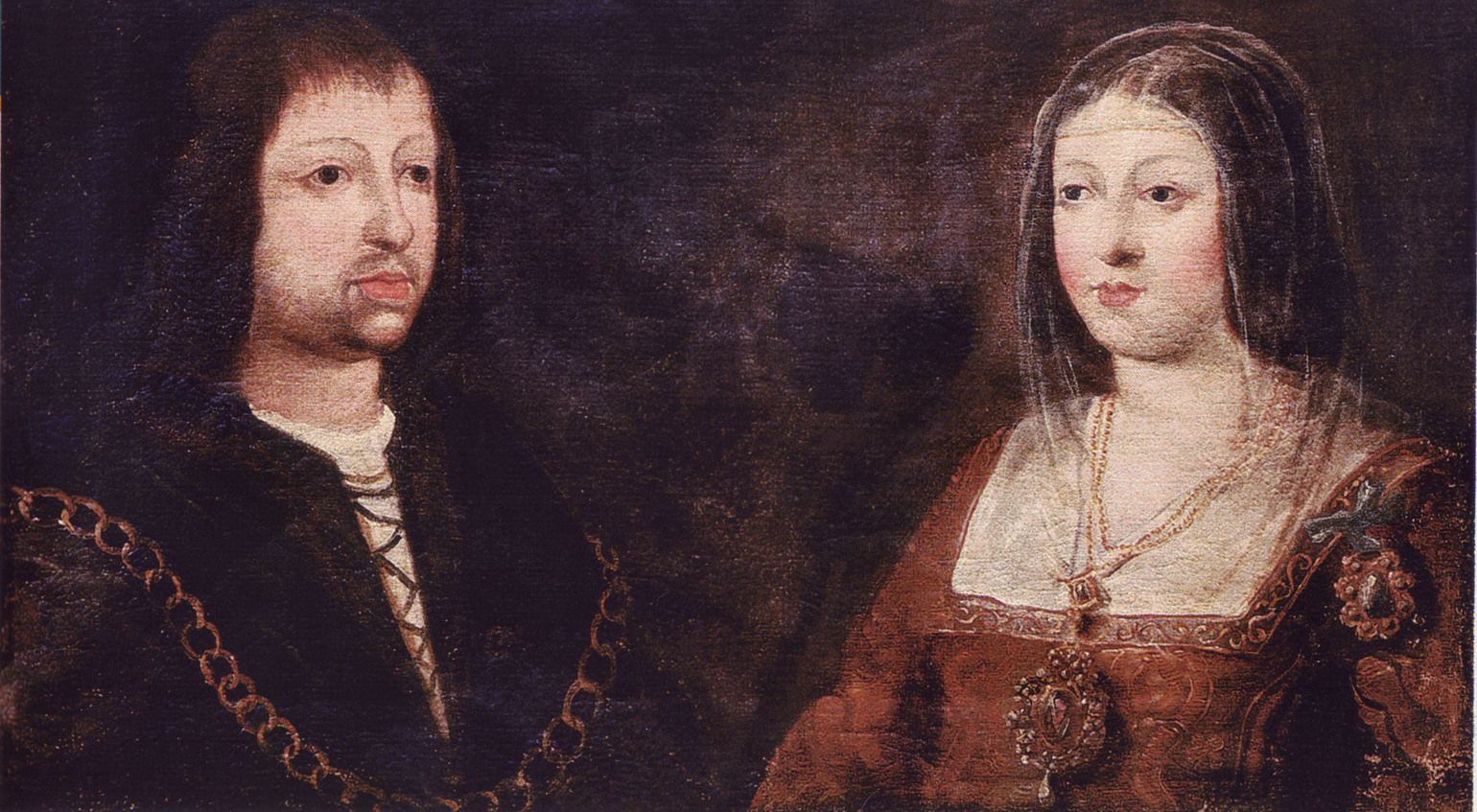
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; to remove the obstacle that this consanguinity would otherwise have posed to their marriage under canon law, they were given a papal dispensation by Sixtus IV. They married on October 19, 1469, in the city of Valladolid; Isabella was eighteen years old and Ferdinand a year younger. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the unification of Spain can essentially be traced back to the marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella. Spain was formed as a dynastic union of two crowns rather than a unitary state, as Castile and Aragon remained separate kingdoms until the Nueva Planta decrees of 1707–16. The court of Ferdinand and Isabella was constantly on the move, in order to bolster local support for the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II Of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He was '' jure uxoris'' King of England and Ireland from his marriage to Queen Mary I in 1554 until her death in 1558. He was also Duke of Milan from 1540. From 1555, he was Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands. The son of Emperor Charles V and Isabella of Portugal, Philip inherited his father's Spanish Empire in 1556 and succeeded to the Portuguese throne in 1580 following a dynastic crisis. The Spanish conquests of the Inca Empire and of the Philippines, named in his honor by Ruy López de Villalobos, were completed during his reign. Under Philip II, Spain reached the height of its influence and power, sometimes called the Spanish Golden Age, and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |