|
Belaci
The Belaci were a small Gallic tribe dwelling in the Alpes Cottiae, around present-day Oulx, during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Belacorum'' on the Arch of Susa. CIL 5:7231., s.v. ''Belaci''. The ethnonym Belaci is possibly Celtic, stemming from the root ''belo''- ('strong') extended by the suffix -''aco''-. Variants beginning with ''V''- may also occur in inscriptions, as in ''Vellaconis, Velaci, Velaco, Velagenius, Vilagenio, Vilagenia, Velagenus'', or ''Velacena''. The toponym Beaulard, located in their territory, derives from an earlier ''Belas''. Geography The Belaci dwelled around the settlements of Ad Martis (modern Oulx) and Diovia (Bardonecchia). Their territory was located north of the Segovii, south of the Medulli, west of the Segusini, and east of the Graioceli., Map 17: Lugdunum. Their chief town, Ad Martis, was situated on the road crossing through the Alpes Cottiae above Segusio, at the confluence of the Dora di Bardonecchia and the Dora Ripa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segovii
The Segovii (Gaulish: *''Segouioi'', 'the victorious, powerful') were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the Alpes Cottiae, around present-day Cesana Torinese and Montgenèvre, during the Iron Age. Name They are attested as ''Segoviorum'' on the Arch of Susa., s.v. ''Segovii''. The ethnonym ''Segovii'' is a latinized form of Gaulish *''Segouioi''. It derives from the root ''sego''-, meaning 'victory, force'. It is comparable with the feminine forms ''Segouia'' (Segovia) and ''Segauias'' (now Göfis). Geography The Segovii dwelled around the towns of Gaesao/Tyrium (modern Cesana Torinese) and Druantium (Montgenèvre; also named *''Alpis Cottia'' and ''Summae Alpes''). Their territory was located south of the Belaci, north of the Brigianii and Quariates, and east of the Ucenni., Map 17: Lugdunum. The settlement of Ad Fines (modern Fenils) may have been the border between the territories of the Segovii and Belaci. History They are mentioned on the Arch of Susa, erected by Cottius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segusini
The Segusini (Gaulish: *''Segusinoi'', 'those of Segusio') were a Gallic tribe dwelling around present-day Susa, in the Alpes Cottiae, during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Segosianō̃n'' (Σεγοσιανῶν) Strabo (early 1st c. AD), as ''Segousianō̃n'' (Σεγουσιανῶν) Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), as ''Segusinorum'' on the Arch of Susa, and as ''Segusinae'' on an inscription., s.v. ''Segusini''. The ethnonym ''Segusini'' is a latinized form of Gaulish *''Segusinoi''. It means 'the people of Segusio', itself from the root ''sego''- ('victory, force'). Geography The Segusini dwelled in the valley of the Duria, around Segusio (modern Susa). Their territory was located east of the Medulli and Belaci, south of the Acitavones, and east of the Iemerii and Taurini., Map 17: Lugdunum. Their chief town, Segusio, controlled the route over Mont Genèvre and served as the gateway into the Italian Peninsula. Segusio possessed Latin law probably from the time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
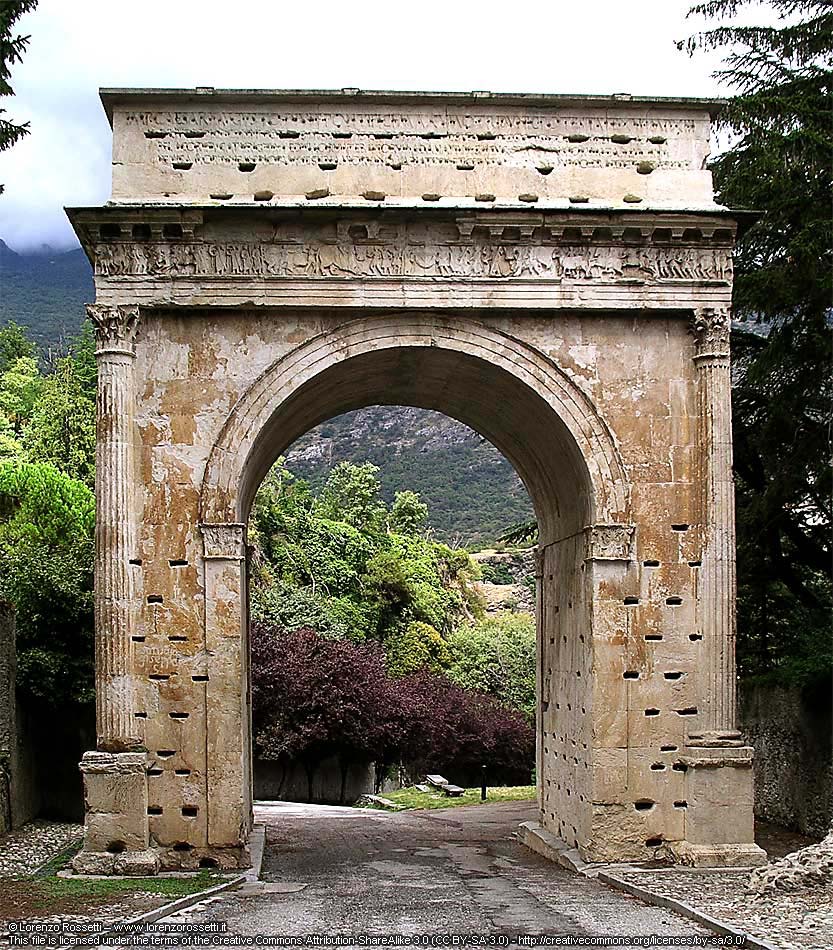
Arch Of Augustus (Susa)
The Arch of Augustus is an important monument constructed in the city of Susa, Piedmont, in the province of Turin. It was originally built at the end of the 1st century BC to record the renewed alliance between Emperor Augustus and Marcus Julius Cottius, a Celto-Ligurian ruler who had been made king and Roman prefect of the Cottian Alps. The arch, together with other remains from the period, such as the Roman amphitheatre and a Roman aqueduct, underscore the importance that the city of Susa had during the Roman period. Description From above, the arch forms a rectangle 11.93 metres long and 7.3 metres wide. It rests on two large bases and there is only one archway. The white marble of the arch was sourced from a nearby quarries at Fornesto and Tre Piloni. The arch has a unique arcade, in which the archivolt is supported by pilasters. The entablature rests on four Corinthian columns placed at the extremities of each corner, such that a quarter of each drum is embedded in the mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugdunum
Lugdunum (also spelled Lugudunum, ; modern Lyon, France) was an important Roman city in Gaul, established on the current site of Lyon. The Roman city was founded in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus, but continued an existing Gallic settlement with a likely population of several thousands. It served as the capital of the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis and was an important city in the western half of the Roman Empire for centuries. Two emperors, Claudius and Caracalla, were born in Lugdunum. In the period 69–192 AD, the city's population may have numbered 50,000 to 100,000, and possibly up to 200,000 inhabitants. The original Roman city was situated west of the confluence of the Rhône and Saône, on the Fourvière heights. By the late centuries of the empire much of the population was located in the Saône River valley at the foot of Fourvière. Name The Roman city was founded as ''Colonia Copia Felix Munatia'', a name invoking prosperity and the blessing of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Celtic Peoples
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cottius
Marcus Julius Cottius was King of the Celtic and Ligurian inhabitants of the mountainous Roman province then known as '' Alpes Taurinae'' and now as the Cottian Alps early in the 1st century BC. Son and successor to King Donnus, he negotiated a dependent status with Emperor Augustus that preserved considerable autonomy for his country, making him a Roman governor, and adopted Roman citizenship. Early relationship with Rome The friendship between Cottius's realm and Rome goes back at least to the reign of his father King Donnus; there is numismatic evidence which suggests that Donnus established friendly relations with Julius Caesar. As Caesar needed to cross the Cottii Regnum in 58 BC on his way to Gaul, he made an agreement with King Donnus to have his troops transported on his road as well as having a new paved road being built.Cornwell, H., Alpine Reactions to Roman Power, in Varga, R., Rusu-Bolindeț, V., (eds) Official Power and Local Elites in the Roman Provinces, p. 59 Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars (mythology)
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Mars ( la, Mārs, ) was the god of war and also an agricultural guardian, a combination characteristic of early Rome. He was the son of Jupiter and Juno, and was pre-eminent among the Roman army's military gods. Most of his festivals were held in March, the month named for him ( Latin ''Martius''), and in October, which began the season for military campaigning and ended the season for farming. Under the influence of Greek culture, Mars was identified with the Greek god Ares,''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. whose myths were reinterpreted in Roman literature and art under the name of Mars. The character and dignity of Mars differed in fundamental ways from that of his Greek counterpart, who is often treated with contempt and revulsion in Greek literature. Mars's altar in the Campus Martius, the area of Rome that took its name from him, was supposed to have been dedicated by Numa, the peace-lov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dora Riparia
The Dora Riparia (; pms, Dòira Rivaira; french: Doire Ripaire or ''Doire''; la, Duria minor) is an alpine river, a left-hand tributary of the Po. It is long (of which 5 km in France), with a drainage basin. It originates in the Cottian Alps, close to the Col de Montgenèvre in France, where it is called the Piccola Dora. Its name becomes the Dora Riparia after the confluence with the Ripa in the Argentera Valley and the Thuras de Bousson close to Cesana. Further down the valley, in Oulx, the river grows thanks to its main upper tributary, the Dora di Bardonecchia, and before Susa is augmented by the Galambra and Cenischia. After Susa, it only receives minor tributaries: from the left, Gravio by Condove, Sessi by Caprie, and Messa by Almese, from the right Scaglione by Meana and Gravio by Villar Focchiardo. It runs through the Susa Valley, and after having crossed part of the plain of the Po and the territories of the comunes of Avigliana, Alpignano, Pianezza and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dora Di Bardonecchia
The Dora di Bardonecchia is a short tributary of the Dora Riparia river, lying entirely within the upper Susa Valley in the Metropolitan City of Turin, Piedmont, Italy. Geography It originates just outside Bardonecchia from the confluence of mountain streams from the valleys of Rochemolles, Frejus, Rho, and Valle Stretta. It follows the valley for about and joins the Dora Riparia northeast of Oulx. Several major road and rail lines run parallel to the river: the A32 motorway from Torino to Bardonecchia; state highway SS535, ''Strada Statale di Bardonecchia''; the international double-track Fréjus railway, the main line of the Rome-Torino-Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ... run. Notes Other projects Rivers of the Alps Rivers of the Province of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segusio
Susa ( lat, Segusio, french: Suse, frp, Suisa) is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Turin, Piedmont (Italy), Piedmont, Italy. In the middle of Susa Valley, it is situated on at the confluence of the Cenischia with the Dora Riparia, a tributary of the Po River, at the foot of the Cottian Alps, 51 km (32 mi) west of Turin. History Susa ( la, Segusio) was founded by the Ligures. It was the capital of the Segusini (also known as Cottii). In the late 1st century BC it became voluntarily part of the Ancient Rome, Roman Empire. Remains of the Roman city have been found in the excavations of the central square, the Piazza Savoia. Susa was the capital of the province of Alpes Cottiae. According to the medieval historian Rodulfus Glaber, Susa was "the oldest of Alpine towns". In the Middle and Modern ages, Susa remained important as a hub of roads connecting southern France to Italy. Taking part of the county or march of Turin (sometimes "march of Susa"). In 1167 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy ( Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and into the Balkans, leading to war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settled in Anatolia, becoming known as Galatians. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graioceli
The Graioceli were a small Gallic tribe dwelling in the valley of Maurienne, in the modern region of Savoie, during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Graioceli'' (var. ''graiocaeli, gaioceli'') by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC)., s.v. ''Graioceli''. The etymology of the ethnonym ''Graioceli'' remains unclear. It possibly contains a divine name *''Graios'' (found in ''Herculi''/''Herculeio Graio'') attached to the Gaulish root ''ocel''-, meaning 'peak, summit, promontory'. The same stem is also present in the name of the '' Alpes Graiae''. Geography The Graioceli dwelled in the Maurienne Valley, around the modern towns of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne and Saint-Jean-d'Arves. Their territory was located the southeast of the Allobroges, south of the Ceutrones, north of the Ucennii, and west of the Medulli., Map 17: Lugdunum. History In the mid-first century BC, the Graioceli are mentioned by Julius Caesar as a tribe hostile to Rome. In what appears to be a concerted attack, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


