|
Beilul
Beilul ( gez, በይሉል, Bäylul, ar, بيلول, alternatively, Beylul) is a small cape town in the Southern Red Sea Region of Eritrea. Jerónimo Lobo passed Beilul in 1625 and wrote that it was a small port with no more than 50 inhabitants. The route inland led through virtually waterless land and was dangerous because of hostile tribes. When Massawa was occupied by the Ottoman Empire, the Ethiopian Emperor Fasilides tried to develop a new trade route via Baylul. His choice fell on Baylul, because this port was beyond the Ottoman sphere of control and directly opposite the harbor of Mocha in Yemen. In 1642 he sent a message to the Imam of Yemen al-Mu'ayyad Mohammed to gain his support for this project. Since al-Mu'ayyad Mohammed and his son al-Mutawakkil Isma'il assumed that Fasilides was interested in a conversion to Islam, a Yemeni embassy was sent to Gondar in 1646. However, when the Yemenites understood Fasilides' actual motives, their enthusiasm sank and the project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerónimo Lobo
Jerónimo Lobo (1595 – 29 January 1678) was a Portuguese Jesuit missionary. He took part in the unsuccessful efforts to convert Ethiopia from the native Ethiopian church to Roman Catholicism until the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1643. Afterwards he wrote an account of his time in Ethiopia, , which is an important source for the history and culture of that country. Life He was born in Lisbon the third of at least five sons and six daughters to Francisco Lobo da Gama, the Governor of Portuguese Cape Verde, and Maria Brandão de Vasconcelos. He entered the Order of Jesus at the age of 14. In 1621 he was ordained a priest and was ordered as a missionary to India, and after surviving an attack on the fleet carrying him by English and Dutch ships off Portuguese Mozambique a year later, he arrived at Goa in December 1622. With the intention of proceeding to Ethiopia, whose '' Nəgusä nägäst'' Susenyos I had been converted to Roman Catholicism by Pedro Páez, he left Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
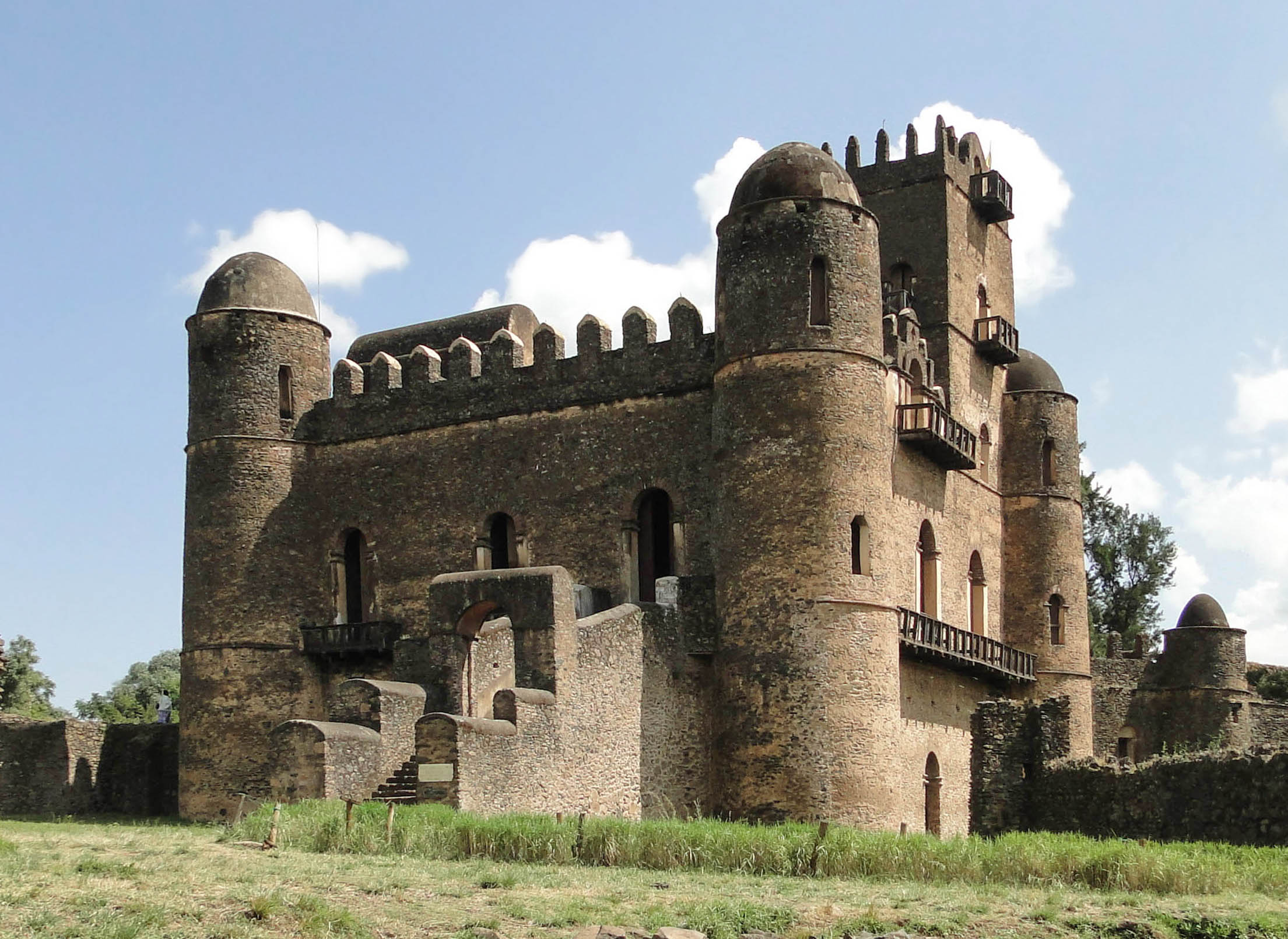
Fasilides
Fasilides ( Ge'ez: ፋሲልደስ; ''Fāsīladas''; 20 November 1603 – 18 October 1667), also known as Fasil, Basilide, or Basilides (as in the works of Edward Gibbon), was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1632 to his death on 18 October 1667, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. His throne name was Alam Sagad (Ge'ez: ዓለም ሰገድ). Of Amhara descent, he was the son of Emperor Susenyos I and Empress Seltan Mogasa (Ge'ez: ሥልጣን ሞገሳ) (throne name) or Wald Sa'ala (Ge'ez: ወልድ ሠዓለ) (name) of Wagda Katata and Merhabete. Emperor Fasilides was born at Magazaz in Bulga, Shewa. His paternal grandfather's name was also Fasilides. He was builder of the Fasil palace. History Fasilides was proclaimed emperor in 1630 during a revolt led by Sarsa Krestos, but did not reach the throne until his father abdicated in 1632. Once he became emperor, Fasilides immediately restored the official status of the traditional Ethiopian Orthodox Church. He sent for a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Red Sea
The Southern Red Sea Region (, it, Regione del Mar Rosso Meridionale, ) is an administrative region of Eritrea. It lies along the southern half of the Red Sea, and contains the coastal city of Assab. It borders the Northern Red Sea Region, and has an area of around . As of 2005, the region had a population of 83,500 compared to a population of 73,700 in 2001. The net growth rate was 11.74 per cent. The total area of the province was 27600.00 km2 and the density was 3.03 persons per km2. Geography The Southern Red Sea Region extends over along Red Sea coast but is only around wide. Forming the major part of the Danakil Desert, its major towns include Asseb, Beilul, Rahaita and T'i'o. The highest point in this region is Mount Ramlu (). It is generally considered one of the hottest, driest and most inhospitable regions in the country. The topography of the region has coastal plains, which are hotter than the regions around the highland plateau. There are two rainy seaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Red Sea Region
The Southern Red Sea Region (, it, Regione del Mar Rosso Meridionale, ) is an administrative region of Eritrea. It lies along the southern half of the Red Sea, and contains the coastal city of Assab. It borders the Northern Red Sea Region, and has an area of around . As of 2005, the region had a population of 83,500 compared to a population of 73,700 in 2001. The net growth rate was 11.74 per cent. The total area of the province was 27600.00 km2 and the density was 3.03 persons per km2. Geography The Southern Red Sea Region extends over along Red Sea coast but is only around wide. Forming the major part of the Danakil Desert, its major towns include Asseb, Beilul, Rahaita and T'i'o. The highest point in this region is Mount Ramlu (). It is generally considered one of the hottest, driest and most inhospitable regions in the country. The topography of the region has coastal plains, which are hotter than the regions around the highland plateau. There are two rainy seaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondar
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on the Lesser Angereb River and southwest of the Simien Mountains. , Gondar has an estimated population of 443,156. Gondar previously served as the capital of both the Ethiopian Empire and the subsequent Begemder Province. The city holds the remains of several royal castles, including those in the Fasil Ghebbi UNESCO World Heritage Site for which Gondar has been called the "Camelot of Africa". History Origins Until the 16th century, the Solomonic Emperors of Ethiopia usually had no fixed capital town, but instead lived in tents in temporary royal camps as they moved around their realms while their family, bodyguard and retinue devoured surplus crops and cut down nearby trees for firewood. One exception to this rule was Debre Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
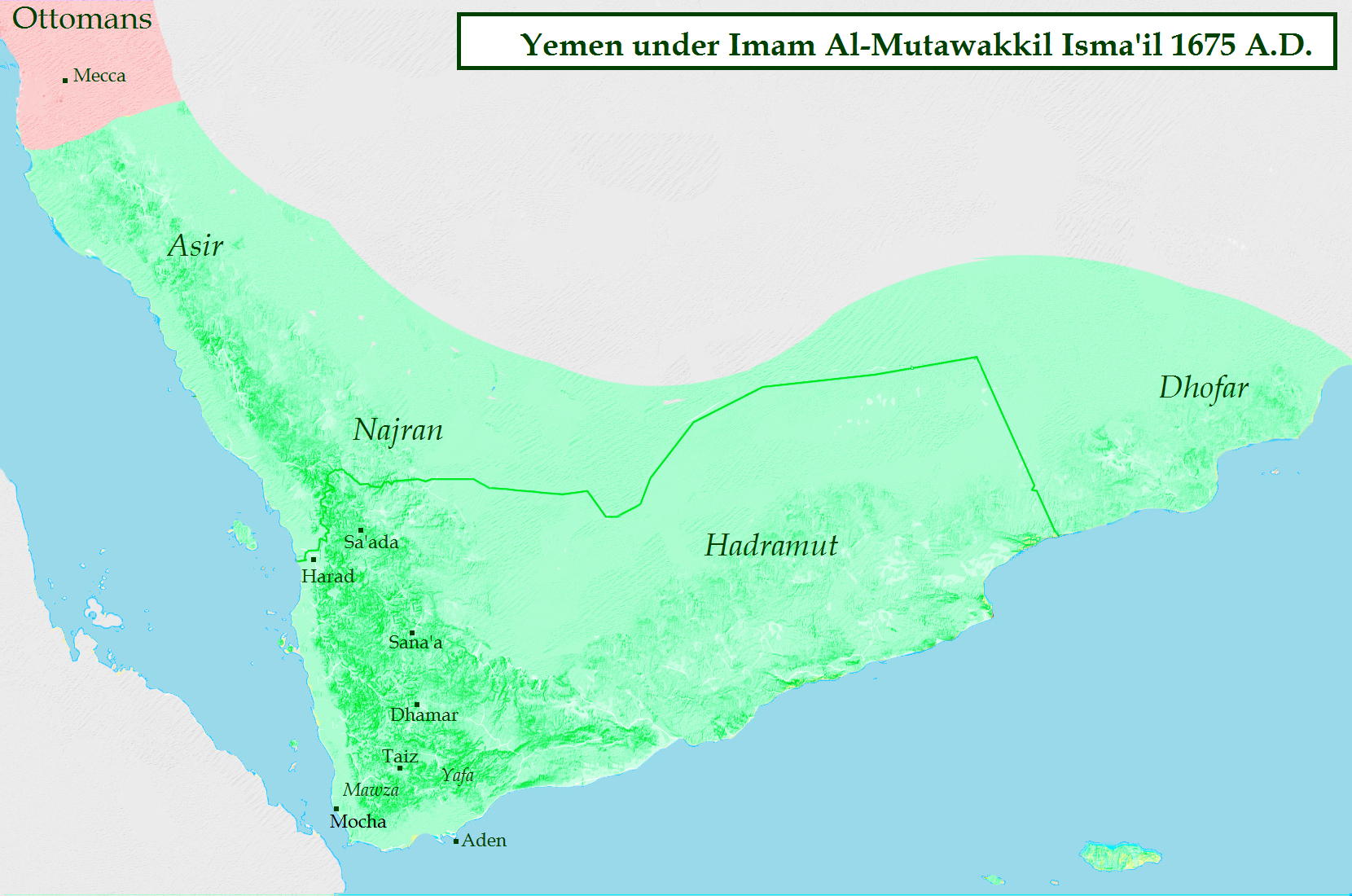
Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il
Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il (c. 1610 – 15 August 1676) was an Imam of Yemen who ruled the country from 1644 until 1676. He was a son of Al-Mansur al-Qasim. His rule saw the biggest territorial expansion of the Zaidiyyah imamate in Greater Yemen. Early reign Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il was the son of the founder of the Qasimid imamate, al-Mansur al-Qasim. In 1644 his elder brother al-Mu'ayyad Muhammad died. With his death, fraternal strife broke out, as several brothers competed for the imamate. In the end, the other brothers submitted to Isma'il. In Zaidi sources, his reign is portrayed in exceedingly positive terms. Yemen was restored to prosperity as the farmers enjoyed excellent harvests. His rule was considered just and incorruptible. Nevertheless, in 1648 a dispute arose between the imam and the various ulema over taxation policy. As Ismail managed to uphold public order in the deeply localized and factionalized Yemeni society, merchants ventured to visit Yemen from other countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mu'ayyad Mohammed
Ibrahim ibn Jaʽfar al-Mutawakkil ( ar, ابراهيم بن جعفر المتوكل; died 866), better known by his ''laqab'' al-Mu'ayyad (, was an Abbasid prince, the third son of the Abbasid caliph al-Mutawakkil, and brother of al-Muntasir and al-Mu'tazz, who both would eventually become caliphs as well. Life Al-Mu'ayyad was the son of Al-Mutawakkil and his concubine, Ishaq. She was an Andulasian, and was one of his favorites. She was the mother of his sons Ibrahim al-Mu'ayyad and Abu Ahmad (the future al-Muwaffaq). The caliph al-Mutawakkil had created a plan of succession that would allow his sons to inherit the caliphate after his death; he would be succeeded first by his eldest son, al-Muntasir, then by al-Mu'tazz and third by al-Mu'ayyad. In 860, al-Mutawakkil had named his three sons heirs and seemed to favour al-Muntasir. However, this appeared to change and al-Muntasir feared his father was going to move against him. With the implicit support of the Turkic faction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and Oman to the Oman–Yemen border, northeast and shares maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia. Yemen is the second-largest Arabs, Arab sovereign state in the peninsula, occupying , with a coastline stretching about . Its constitutionally stated Capital city, capital, and largest city, is Sanaa. As of 2021, Yemen has an estimated population of some 30.4 million. In ancient times, Yemen was the home of the Sabaeans, a trading state that included parts of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. Later in 275 AD, the Himyarite Kingdom was influenced by Judaism. Christianity arrived in the fourth century. Islam spread quickly in the seventh century and Yemenite troops were crucial in the early Islamic conquests. Several Dynasty, dynasties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mocha, Yemen
Mokha ( ar, المُخا, al-Mukhā), also spelled Mocha, or Mukha, is a port city on the Red Sea coast of Yemen. Until Aden and al Hudaydah eclipsed it in the 19th century, Mokha was the principal port for Yemen's capital, Sanaa. Long known for its coffee trade, the city gave its name to Mocha coffee and chocolate. Overview Mocha was the major marketplace for coffee (''Coffea arabica'') from the 15th century until the early 18th century. Even after other sources of coffee were found, ''Mocha'' beans (also called ''Sanani'' or ''Mocha Sanani'' beans, meaning ''from Sana'a'') continued to be prized for their distinctive flavor—and remain so even today. The coffee itself did not grow in Mocha, but was transported from places inland to the port in Mocha, where it was shipped abroad. Mocha's coffee legacy is reflected in the name of the mocha latte and the Moka pot coffee maker. In Germany, traditional Turkish coffee is known as Mokka. According to the Portuguese Jesu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massawa
Massawa ( ; ti, ምጽዋዕ, məṣṣəwaʿ; gez, ምጽዋ; ar, مصوع; it, Massaua; pt, Maçuá) is a port city in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea, located on the Red Sea at the northern end of the Gulf of Zula beside the Dahlak Archipelago.Matt Phillips, Jean-Bernard Carillet, ''Lonely Planet Ethiopia and Eritrea'', (Lonely Planet: 2006), p.340. It has been a historically important port for many centuries. Massawa was the capital of the Italian Colony of Eritrea until the seat of the colonial government was moved to Asmara in 1897. Massawa has an average temperature of nearly , which is one of the highest experienced in the world, and is "one of the hottest marine coastal areas in the world." History Massawa was originally a small seaside village, lying in lands coextensive with the Kingdom of Axum—also known as Kingdom of Zula in antiquity—and overshadowed by the nearby port of Adulis about to the south. Massawa has been ruled or occupied by a succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Eritrea
The regions of Eritrea are the primary geographical divisions through which Eritrea is administered. Six in total, they include the Central, Anseba, Gash-Barka, Southern, Northern Red Sea and Southern Red Sea regions. At the time of independence in 1993 Eritrea was arranged into ten provinces. These provinces were similar to the nine provinces operating during the colonial period. In 1996, these were consolidated into six regions (''zobas''). Gash-Barka Region was the largest and the most densely populated region and is called the "bread-basket". The People's Front for Democracy and Justice or PFDJ (originally Eritrean People's Liberation Front) rules the country and its regions as a single-party totalitarian government. The regional and local elections are conducted on a periodic basis on a restricted framework. All men and women of any ethnic or religious background are eligible to vote. No parties or groups other than PFDJ are allowed to contest and the elections are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_p029_JEBEL_ABOU_ASSAB.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)