|
Becoming Madame Mao
''Becoming Madame Mao'' is a historical novel by Anchee Min detailing the life of Jiang Qing. She became Madame Mao after her marriage to Mao Zedong. In this story Min tries to cast a sympathetic light on one of the most controversial political figures in the People's Republic of China. Plot summary Madame Mao is born to a very poor family around 1910 (early enough to have had her feet bound although due to a severe infection the bindings were taken off). She has an abusive father who kicks her and her concubine mother out of the house at an early age. Her mother ends up as a concubine and servant and the young 'Madame Mao' runs away to her grandparents. Anchee Min, the author, seems to attribute a lot of Madame Mao's later actions to her childhood—and that a lot of her incessant claims to power actually come from a need to be desired and to feel close to Mao rather than a deep need for power herself. Madame Mao's dream is to become an actress but she only achieves mediocre suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchee Min
Anchee Min (; born January 14, 1957, in Shanghai, China) is a Chinese-American author who lives in San Francisco and Shanghai. Min has published two memoirs, '' Red Azalea'' and ''The Cooked Seed: A Memoir'', and six historical novels. Her fiction emphasizes strong female characters, such as Jiang Qing, the wife of chairman Mao Zedong, and Empress Dowager Cixi, the last ruling empress of China. Life Min was born in Shanghai on January 14, 1957. Her parents were both teachers. She was nine years old when the Cultural Revolution began. As a child, she was a member of the Little Red Guards and was made to report her favorite teacher, who was accused of being an anti-Maoist, to the authorities. When Min was 17, she was sent to a collective farm near the East China Sea, where she endured horrific conditions and worked 18-hour days. Eventually, she suffered a spinal cord injury. She began an affair with the commander at her camp, a woman named Yin, although she attributes the affair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goal was to preserve Chinese communism by purging remnants of capitalist and traditional elements from Chinese society. The Revolution marked the effective commanding return of Mao –who was still the Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP)– to the centre of power, after a period of self-abstention and ceding to less radical leadership in the aftermath of the Mao-led Great Leap Forward debacle and the Great Chinese Famine (1959–1961). The Revolution failed to achieve its main goals. Launching the movement in May 1966 with the help of the Cultural Revolution Group, Mao charged that bourgeois elements had infiltrated the government and society with the aim of restoring capitalism. Mao called on young people to "bombard the headqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novels Set In China
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself from the la, novella, a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ''novellus'', diminutive of ''novus'', meaning "new". Some novelists, including Nathaniel Hawthorne, Herman Melville, Ann Radcliffe, John Cowper Powys, preferred the term "romance" to describe their novels. According to Margaret Doody, the novel has "a continuous and comprehensive history of about two thousand years", with its origins in the Ancient Greek and Roman novel, in Chivalric romance, and in the tradition of the Italian renaissance novella.Margaret Anne Doody''The True Story of the Novel'' New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1996, rept. 1997, p. 1. Retrieved 25 April 2014. The ancient romance form was revived by Romanticism, especially the historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books About Maoist China
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many page (paper), pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bookbinding, bound together and protected by a book cover, cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is ''codex'' (plural, ''codices''). In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a Recto, leaf and each side of a leaf is a page (paper), page. As an intellectual object, a book is prototypically a composition of such great length that it takes a considerable investment of time to compose and still considered as an investment of time to read. In a restricted sense, a book is a self-sufficient section or part of a longer composition, a usage reflecting that, in antiquity, long works had to be written on several scrolls and each scroll had to be identified by the book it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novels By Anchee Min
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself from the la, novella, a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ''novellus'', diminutive of ''novus'', meaning "new". Some novelists, including Nathaniel Hawthorne, Herman Melville, Ann Radcliffe, John Cowper Powys, preferred the term "romance" to describe their novels. According to Margaret Doody, the novel has "a continuous and comprehensive history of about two thousand years", with its origins in the Ancient Greek and Roman novel, in Chivalric romance, and in the tradition of the Italian renaissance novella.Margaret Anne Doody''The True Story of the Novel'' New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1996, rept. 1997, p. 1. Retrieved 25 April 2014. The ancient romance form was revived by Romanticism, especially the historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Depictions Of Mao Zedong
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typical be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Historical Novels
Chinese can refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Han Chinese, the largest ethnic group in the world and the majority ethnic group in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Singapore ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
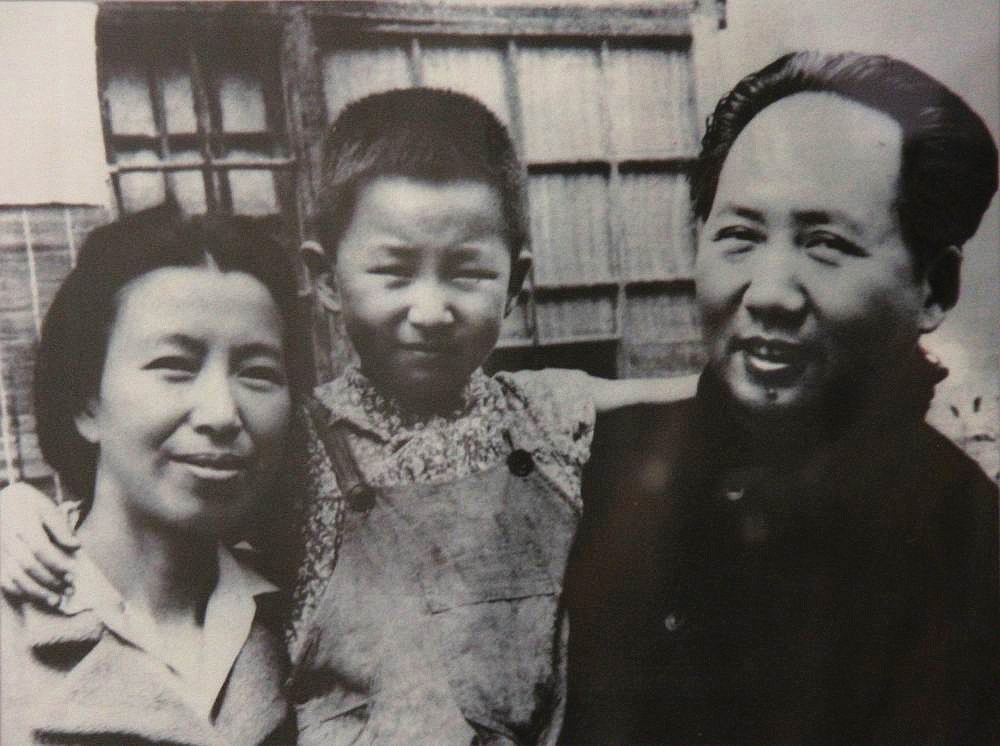
Li Na (daughter Of Mao Zedong)
Li Na ( or Li Ne, born 3 August 1940), is the daughter of Mao Zedong and his fourth wife Jiang Qing, and their only child together. Her surname is Li rather than Mao, because her father used the pseudonym "Li Desheng" () for a period of time during the Chinese Civil War. The names of Li Na and her sister Li Min come from Book 4 of the ''Analects'' of Confucius: "''ne'' yu yan er ''min'' yu xing" (, meaning ''slow'' in speech and ''earnest'' in conduct). Early life Li Na was born at Central Hospital in Yan'an on 3 August 1940. In her childhood, she was fascinated by Russian as well as Classical Chinese literature. In 1949, Li moved to Beijing with her parents, and started third grade at Yuying Primary School. Four years later, in 1953, she was admitted to the Beijing Normal University Girls' High School (北京师范大学附属女子中学, now known as Experimental High School Attached to Beijing Normal University). Cultural Revolution Excelling in her studies, she major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hua Guofeng
Hua Guofeng (; born Su Zhu; 16 February 1921 – 20 August 2008), alternatively spelled as Hua Kuo-feng, was a Chinese politician who served as Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party and Premier of the People's Republic of China. The designated successor of Mao Zedong, Hua held the top offices of the government, party, and the military after the deaths of Mao and Premier Zhou Enlai, but was gradually forced out of supreme power by a coalition of party leaders between December 1978 and June 1981, and subsequently retreated from the political limelight, though still remaining a member of the Central Committee until 2002. Born and raised in Jiaocheng, Shanxi, Hua was educated at the Jiaocheng County Commercial School and joined the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in 1938, seeing action in both the Second Sino–Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War as a guerrilla fighter.Ye Yonglie, 邓小平改变中国——1978:中国命运大转折 (Deng Xiaoping Changed China-1978: China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yao Wenyuan
Yao Wenyuan (January 12, 1931 – December 23, 2005) was a Chinese literary critic, a politician, and a member of the Gang of Four during China's Cultural Revolution. Biography Yao Wenyuan was born in Zhuji, Zhejiang, to an intellectual family. His father, Yao Pengzi () was a writer, translator and art critic. He began his career in Shanghai as a literary critic, where he became known for his sharp attacks against colleagues, such as in June 1957 against the newspaper '' Wenhuibao''. Since that time, he began to closely collaborate with leftist Shanghai politicians, including the head of the city's Propaganda Department, Zhang Chunqiao. His article "On the New Historical Beijing Opera 'Hai Rui Dismissed from Office, published in ''Wenhuibao'' on November 10, 1965, launched the Cultural Revolution. The article was about a popular opera by Wu Han, who was deputy mayor of Beijing. Zhang Chunqiao and Jiang Qing feared the play could be counter-revolutionary because parallels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Hongwen
Wang Hongwen (December 1935 – 3 August 1992) was a Chinese labour activist and politician who spent most of his career in Shanghai. He was an important political figure during the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976). He was the youngest member of the political clique called the "Gang of Four." During the Cultural Revolution, Wang rose from a member of the working class to become one of the foremost members of national leadership of the Chinese Communist Party. At the pinnacle of his power he was the second Vice Chairman of the CCP, and ranked third in the Communist Party's hierarchy. Following Mao's death in 1976, Wang was arrested and charged with "counterrevolutionary activity," then sentenced to life imprisonment in 1981. Biography Wang was born in a village in the outskirts of Changchun, Jilin province. In the early 1950s he took part in the Korean War. He joined the Chinese Communist Party in 1953. After the war, he was sent to Shanghai to work in Shanghai No. 17 Cotton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)