|
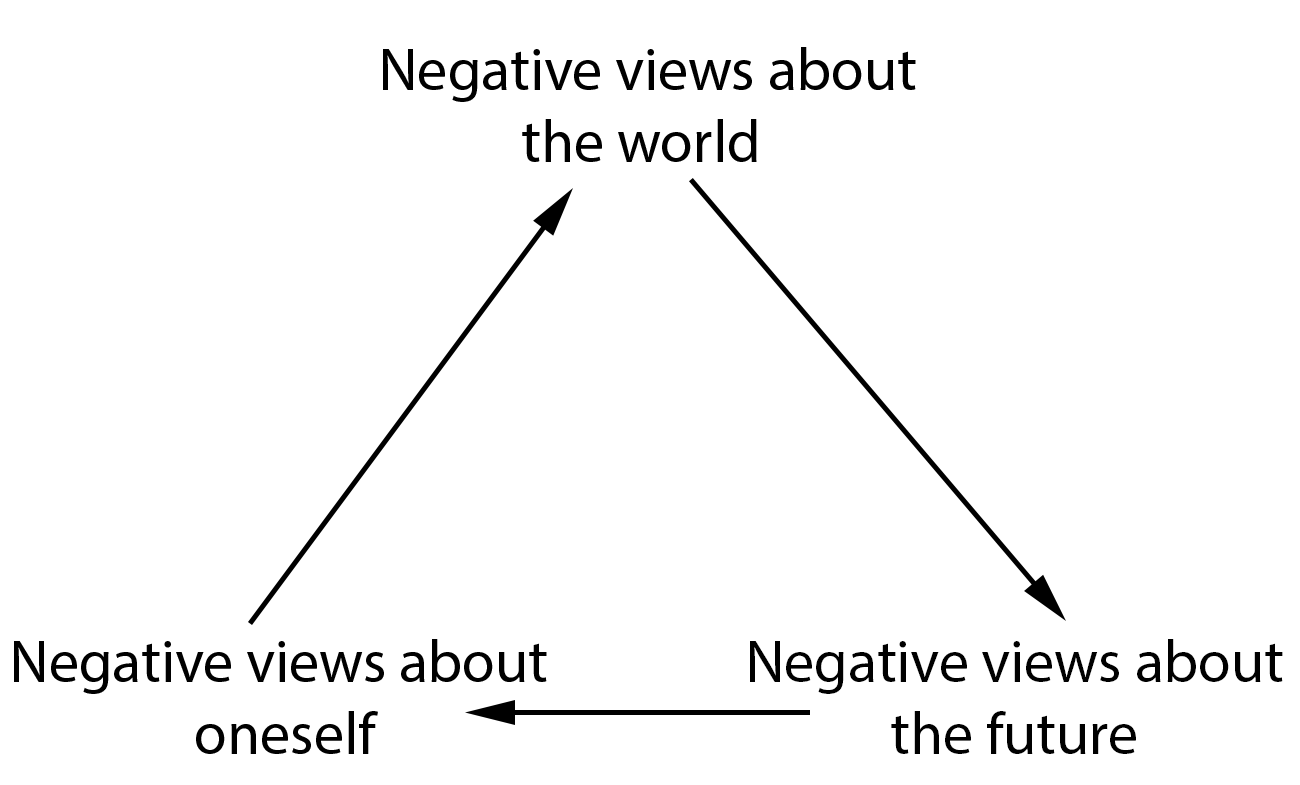
Beck's Cognitive Triad
Beck's cognitive triad, also known as the negative triad, is a cognitive-therapeutic view of the three key elements of a person's belief system present in depression. It was proposed by Aaron Beck in 1967. The triad forms part of his cognitive theory of depression and the concept is used as part of CBT, particularly in Beck's " Treatment of Negative Automatic Thoughts" (TNAT) approach. The triad involves "automatic, spontaneous and seemingly uncontrollable negative thoughts" about: * The ''self'' * The '' world or environment'' * The ''future'' Examples of this negative thinking include: *The self – "I'm worthless and ugly" or "I wish I was different" *The world – "No one values me" or "people ignore me all the time" *The future – "I'm hopeless because things will never change" or "things can only get worse!" Beck's cognitive model of depression From a cognitive perspective, depressive disorders are characterized by people's dysfunctional negative views of themselves, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Abstraction
In clinical psychology, selective abstraction is a type of cognitive bias or cognitive distortion in which a detail is taken out of context and believed whilst everything else in the context is ignored. It commonly appears in Aaron T. Beck's work in cognitive therapy. Another definition is: "focusing on only the negative aspects of an event, such as, 'I ruined the whole recital because of that one mistake.Weems, C. F., Berman, S. L., Silverman, W. K., & Saavedra, L. M. (2001). "Cognitive errors in youth with anxiety disorders: The linkages between negative cognitive errors and anxious symptoms". ''Cognitive Therapy and Research'', ''25''(5), 559-575. Effects A team of researchers analyzed the association between cognitive errors in youths with anxiety disorders by using the Children's Negative Cognitive Error Questionnaire (CNCEQ) and "several other self-reporting measures" (Children's Depression Inventory, Childhood Anxiety Sensitivity Index, Revised Children's Manifest Anxiety S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subjective Well-being
Subjective well-being (SWB) is a self-reported measure of well-being, typically obtained by questionnaire. Ed Diener developed a tripartite model of subjective well-being in 1984, which describes how people experience the quality of their lives and includes both emotional reactions and cognitive judgments. It posits "three distinct but often related components of wellbeing: frequent positive affect, infrequent negative affect, and cognitive evaluations such as life satisfaction." Subjective well-being is an overarching ideology that encompasses such things as "high levels of pleasant emotions and moods, low levels of negative emotions and moods, and high life-satisfaction." SWB therefore encompasses moods and emotions as well as evaluations of one's satisfaction with general and specific areas of one's life. SWB is one definition of happiness. Although SWB tends to be stable over the time and is strongly related to personality traits, the emotional component of SWB can be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-image
Self-image is the mental picture, generally of a kind that is quite resistant to change, that depicts not only details that are potentially available to an objective investigation by others (height, weight, hair color, etc.), but also items that have been learned by persons about themselves, either from personal experiences or by internalizing the judgments of others. Self-image may consist of six types: # Self-image resulting from how an individual sees oneself. # Self-image resulting from how others see the individual. # Self-image resulting from how the individual perceives the individual sees oneself. # Self-image resulting from how the individual perceives how others see the individual. # Self-image resulting from how others perceive how the individual sees oneself. # Self-image resulting from how others perceive how others see the individual. These six types may or may not be an accurate representation of the person. All, some, or none of them may be true. A more technical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosis
Neurosis is a class of functional mental disorders involving chronic distress, but neither delusions nor hallucinations. The term is no longer used by the professional psychiatric community in the United States, having been eliminated from the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) in 1980 with the publication of DSM III. However, it is still used in the ICD-10 Chapter V F40–48. Neurosis should not be mistaken for ''psychosis'', which refers to a loss of touch with reality. Nor should it be mistaken for ''neuroticism'', a fundamental personality trait proposed in the Big Five personality traits theory. Etymology The term is derived from the Greek word ''neuron'' (νεῦρον, 'nerve') and the suffix ''-osis'' (-ωσις, 'diseased' or 'abnormal condition'). The term ''neurosis'' was coined by Scottish doctor William Cullen in 1769 to refer to "disorders of sense and motion" caused by a "general affection of the nervous system." Cullen used the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explanatory Style
Explanatory style is a psychological attribute that indicates how people explain to themselves why they experience a particular event, either positive or negative. Aspects Personal This aspect covers the degree to which a person attributes the cause of an event to internal or external sources. An optimist might attribute a bad experience to a stroke of bad luck whereas a pessimist might unreasonably assume it is their fault or punishment. A person might also attribute the responsibility of their actions to external forces in a maladaptive, unhealthy way (e.g. "I had no choice but to get violent.") Permanent This aspect covers characteristics considered stable versus unstable (across time). An optimist would tend to define his or her failures as unstable (I just didn't study enough for this particular test) whereas a pessimist might think, for example, "I'm never good at tests". Pervasive This distinction covers global versus local and/or specific and the extent of the effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-schema
The self-schema refers to a long lasting and stable set of memories that summarize a person's beliefs, experiences and generalizations about the self, in specific behavioral domains. A person may have a self-schema based on any aspect of themselves as a person, including physical characteristics (body image), personality traits and interests, as long as they consider that aspect of their self to be important to their own self-definition. When someone has a schema about themselves they hyper focus on a trait about themselves and believe what they say to themselves about that specific trait. A self schema can be good or bad depending on what that person talks to themselves about and what kind of tone they talk to themselves with. For example, someone will have a self-schema of extroversion if they think of themselves as extroverted and also believe that their extroversion is central to who they are. Their self-schema for extroversion may include general self-categorizations ("I am s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and substance abuse (including alcoholism and the use of and withdrawal from benzodiazepines) are risk factors. Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; and improving economic conditions. Although crisis hotlines are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. The most commonly adopted metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pessimism
Pessimism is a negative mental attitude in which an undesirable outcome is anticipated from a given situation. Pessimists tend to focus on the negatives of life in general. A common question asked to test for pessimism is "Is the glass half empty or half full?"; in this situation, a pessimist is said to see the glass as half empty, while an optimist is said to see the glass as half full. Throughout history, the pessimistic disposition has had effects on all major areas of thinking. Etymology The term pessimism derives from the Latin word ''pessimus'' meaning 'the worst'. It was first used by Jesuit critics of Voltaire's 1759 novel ''Candide, ou l'Optimisme''. Voltaire was satirizing the philosophy of Leibniz who maintained that this was the 'best (optimum) of all possible worlds'. In their attacks on Voltaire, the Jesuits of the ''Revue de Trévoux'' accused him of ''pessimisme''. As a psychological disposition In the ancient world, psychological pessimism was associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhedonia
Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure. While earlier definitions emphasized the inability to experience pleasure, anhedonia is currently used by researchers to refer to reduced motivation, reduced anticipatory pleasure (wanting), reduced consummatory pleasure (liking), and deficits in reinforcement learning. In the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), anhedonia is a component of depressive disorders, substance-related disorders, psychotic disorders, and personality disorders, where it is defined by either a reduced ability to experience pleasure, or a diminished interest in engaging in pleasurable activities. While the ''International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision'' (ICD-10) does not explicitly mention anhedonia, the depressive symptom analogous to anhedonia as described in the DSM-5 is a loss of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Distortion
A cognitive distortion is an exaggerated or irrational thought pattern involved in the onset or perpetuation of psychopathological states, such as depression and anxiety. Cognitive distortions are thoughts that cause individuals to perceive reality inaccurately. According to Aaron Beck's cognitive model, a negative outlook on reality, sometimes called ''negative schemas'' (or ''schemata''), is a factor in symptoms of emotional dysfunction and poorer subjective well-being. Specifically, negative thinking patterns reinforce negative emotions and thoughts. During difficult circumstances, these distorted thoughts can contribute to an overall negative outlook on the world and a depressive or anxious mental state. According to hopelessness theory and Beck's theory, the meaning or interpretation that people give to their experience importantly influences whether they will become depressed and whether they will experience severe, repeated, or long-duration episodes of depression. Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Model_of_Attributional_Style.png)
.jpg)

