|
Baw Baw Frog
The Baw Baw frog (''Philoria frosti'') is a critically endangered species of Australian frog as categorised on the IUCN Red List and listed under the ''Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act (1988)''. It has suffered a decline in population, mostly due to infection caused by chytrid fungus. Zoos Victoria has undertaken a breeding program to ensure survival of the species which commenced in 2010, and in October 2018 successfully collected the first eggs laid in captivity. Taxonomy and etymology The species was described as ''Philoria frosti'' by Walter Baldwin Spencer in 1901, honouring Charles Frost, an Australian naturalist. The specimens used in the species description (type series) were provided by Frost, an amateur herpetologist, who recovered five individuals that had been regurgitated by a tiger snake '' Notechis scutatus''. Description Adult length is between . Adults are dark brown and often have brown to dark brown, yellow flecked bellies. These frogs have a promin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Baldwin Spencer
Sir Walter Baldwin Spencer (23 June 1860 – 14 July 1929), commonly referred to as Baldwin Spencer, was a British-Australian evolutionary biologist, anthropologist and ethnologist. He is known for his fieldwork with Aboriginal peoples in Central Australia, contributions to the study of ethnography, and academic collaborations with Frank Gillen. Spencer introduced the study of zoology at the University of Melbourne and held the title of Emeritus Professor until his death in 1929. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1900 and knighted in 1916. Early life and education Spencer was born on 23 June 1860 in Stretford, Lancashire, England to Martha (née Circuit) and Rueben Spencer. He was educated at Old Trafford school and Manchester School of Art, where he received training in drawing. In 1879, Spencer began study at Owens College (University of Manchester), where he first developed an interest in evolutionary biology. In 1884, he obtained a BA in biology from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolk Sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development. In humans The yolk sac is the first element seen within the gestational sac during pregnancy, usually at 3 days gestation. The yolk sac is situated on the front (ventral) part of the embryo; it is lined by extra-embryonic endoderm, outside of which is a layer of extra-embryonic mesenchyme, derived from the epiblast. Blood is conveyed to the wall of the yolk sac by the primitive aorta and after circulating through a wide-meshed capillary plexus, is returned by the vitelline veins to the tubular heart of the embryo. This constitutes the vitell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of Victoria (Australia)
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frogs Of Australia
Amphibians of Australia are limited to members of the order Anura, commonly known as frogs. All Australian frogs are in the suborder Neobatrachia, also known as the modern frogs, which make up the largest proportion of extant frog species. About 230 of the 5,280 species of frog are native to Australia with 93% of them endemic. Compared with other continents, species diversity is low, and may be related to the climate of most of the Australian continent. There are two known invasive amphibians, the cane toad and the smooth newt. Origins The Australian continent once formed part of the supercontinent Pangaea, which split into Gondwana and Laurasia approximately 180 million years ago. The earliest true frog fossil, ''Vieraella herbsti'', is dated between 188 and 213 million years old. This predates the splitting of Gondwana, and has resulted in frogs present on all continents. The first two continents to split from Australia were South America and Africa. The amphibian fauna of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philoria
''Philoria'' is a genus of frogs native to eastern and southern Australia. These frogs are all confined to mountain areas, with 7 species occurring in the mountains of northern New South Wales and southern Queensland. One species occurs in Victoria. All species are listed as endangered, except the Baw Baw frog, which is listed as critically endangered. They are small to medium-sized frogs that live in water saturated sites, such as sphagnum bogs and seepages on rocky slopes. The eggs are laid in foam nests hidden from light. The tadpoles remain within the nest and live entirely on the yolk.Altig, R., & Johnston, G. (1989). Guilds of Anuran Larvae: Relationships among Developmental Modes, Morphologies, and Habitats. Herpetological Monographs, 3, 81-109. doi:10.2307/1466987 Some taxonomists class only the Baw Baw frog (''Philoria frosti'') in the genus ''Philoria'' and class the other 5 species in the genus ''Kyarranus'' because of osteological features, size differences (''Philori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Rylah Institute For Environmental Research
The Arthur Rylah Institute for Environmental Research (ARI) is the biodiversity research organisation for the government of Victoria, Australia. It provides advice on ecologically sustainable land and water management issues and with regard to threatened native flora and fauna. It is named after Sir Arthur Rylah, a long-serving Victorian politician and deputy state premier between 1955 and 1971. History Arthur Rylah Institute for Environmental Research (ARI) was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth on 8 April 1970 as part of the Fisheries and Wildlife Division. The foundation Director was Alfred Dunbavin Butcher who also had an association with Melbourne Zoo and Healesville Sanctuary. He had a keen interest in art and this attracted a large collection of wildlife art and the commissioning of a large mural at the institute. The institute was subsequently incorporated into various Victorian Government Departments since then including the Ministry for Conservation, the Departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
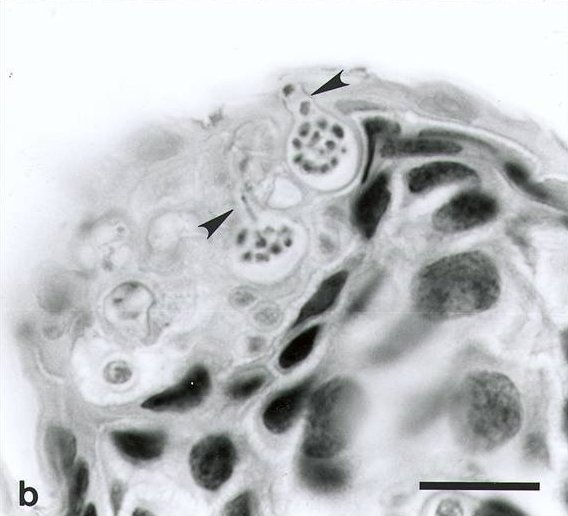
Chytridiomycosis
Chytridiomycosis ( ) is an infectious disease in amphibians, caused by the chytrid fungi ''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and ''Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans''. Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or extinctions of amphibian species in western North America, Central America, South America, eastern Australia, east Africa (Tanzania), and Dominica and Montserrat in the Caribbean. Much of the New World is also at risk of the disease arriving within the coming years. The fungus is capable of causing sporadic deaths in some amphibian populations and 100% mortality in others. No effective measure is known for control of the disease in wild populations. Various clinical signs are seen by individuals affected by the disease. A number of options are possible for controlling this disease-causing fungus, though none has proved to be feasible on a large scale. The disease has been proposed as a contributing factor to a global decline in amphibian populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Broadcasting Corporation
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is the national broadcaster of Australia. It is principally funded by direct grants from the Australian Government and is administered by a government-appointed board. The ABC is a publicly-owned body that is politically independent and fully accountable, with its charter enshrined in legislation, the ''Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983''. ABC Commercial, a profit-making division of the corporation, also helps to generate funding for content provision. The ABC was established as the Australian Broadcasting Commission on 1 July 1932 by an act of federal parliament. It effectively replaced the Australian Broadcasting Company, a private company established in 1924 to provide programming for A-class radio stations. The ABC was given statutory powers that reinforced its independence from the government and enhanced its news-gathering role. Modelled after the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), which is funded by a tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio, such as radio and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radio waves for heating or industrial purposes, such as microwave ovens or diathermy equipment, are not usually called transmitters, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytridiomycosis
Chytridiomycosis ( ) is an infectious disease in amphibians, caused by the chytrid fungi ''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and ''Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans''. Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or extinctions of amphibian species in western North America, Central America, South America, eastern Australia, east Africa (Tanzania), and Dominica and Montserrat in the Caribbean. Much of the New World is also at risk of the disease arriving within the coming years. The fungus is capable of causing sporadic deaths in some amphibian populations and 100% mortality in others. No effective measure is known for control of the disease in wild populations. Various clinical signs are seen by individuals affected by the disease. A number of options are possible for controlling this disease-causing fungus, though none has proved to be feasible on a large scale. The disease has been proposed as a contributing factor to a global decline in amphibian populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some insects, fish, amphibians, mollusks, crustaceans, cnidarians, echinoderms, and tunicates undergo metamorphosis, which is often accompanied by a change of nutrition source or behavior. Animals can be divided into species that undergo complete metamorphosis (" holometaboly"), incomplete metamorphosis ("hemimetaboly"), or no metamorphosis (" ametaboly"). Scientific usage of the term is technically precise, and it is not applied to general aspects of cell growth, including rapid growth spurts. Generally organisms with a larva stage undergo metamorphosis, and during metamorphosis the organism loses larval characteristics. References to "metamorphosis" in mammals are imprecise and only colloquial, but historically idealist ideas of transformation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)