|
Batusangkar Inscription
Saruaso II inscription, also previously known as Batusangkar inscription, is one of the inscriptions from the King Adityawarman era (14th century CE). It is currently located at the Fort van der Capellen area, in the courtyard of the old office of the Monuments Preservation Department (BPCB, the old Balai Adat hall), in Batusangkar city, West Sumatra, Indonesia. The inscription was previously displayed across in front of the Indo Jalito Building, which was the residence of the Regent of Tanah Datar during the Dutch colonial period (researcher L.C. Westenenk once lived there). The inscription is written in Old Javanese script and Sanskrit language. The inscription is carved into a brown quartz sandstone and slightly yellowish color on both sides. The inscription shape is rectangular, measuring 110 cm high, 75 cm wide, and 17 cm thick. There is writing on both sides (side A and side B), which are basically the same content but in slightly different sentence structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ananggawarman
Ananggawarman was a crown prince (''yuvaraja'') of the Malayapura kingdom, which ruled at the end of the 14th century. The Malayapura kingdom was centered on the Minangkabau Highlands and its territory covers much of central Sumatra. The name Ananggawarman is inscribed on Saruaso II inscription as the son of King Adityawarman (r. 1347–1375). It is not clear when Ananggawarman began to reign in place of his father, but it was written in the ''History of Ming'' that the kingdom sent a messenger again to China in 1376. Ananggawarman is mentioned in the inscription with the title ''Hevajra nityasmrti'', which indicated that he professed the same belief as his father, the Tantric Buddhism. This means that the rulers of Sumatra embraced esoteric Buddhism at least until the 14th century. In those days it was also thought that trade between Sumatra and South India was going well and there were quite a number of South Indian merchants settled in Minangkabau, as there is also found an inscri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Inscriptions
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 ( MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagaruyung Kingdom
Pagaruyung (ڤاڬارويوڠ; also Pagarruyung, Pagar Ruyung and, Malayapura or Malayupura) was the seat of the Minangkabau kings of Western Sumatra, though little is known about it. Modern Pagaruyung is a village in ''Tanjung Emas'' subdistrict, Tanah Datar regency, located near the town of Batusangkar, Indonesia. History Beginnings Adityawarman is believed to have founded the kingdom and presided over the central Sumatra region between 1347 and 1375, most likely to control the local gold trade. The few artefacts recovered from Adityawarman's reign include a number of stones containing inscriptions, and statues. Some of these items were found at ''Bukit Gombak'', a hill near modern Pagarruyung, and it is believed a royal palace was located there. There is a major gap in the historical picture in the Minangkabau highlands between the last date of Adityawarman's inscription in 1375 and Tomé Pires ''Suma Oriental'', written some time between 1513 and 1515. By the 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Gijsbertus De Casparis
Johannes Gijsbertus de Casparis (31 May 1916, Eemnes – 19 June 2002, Wassenaar) was a Dutch orientalist and indologist. Early years After attending Barlaeus Gymnasium in Amsterdam, De Casparis started piano study at the conservatory of Amsterdam. However, a year later, in 1934, he turned to classical languages with Russian as a minor at the University of Amsterdam. Barend Faddegon was teaching Sanskrit in Amsterdam and under his influence, de Casparis switched to Sanskrit. In 1935, the archaeologist Willem Frederik Stutterheim of the Oudheidkundige Dienst in Nederlandsch-Indië (Archaeological Service in the Netherlands Indies) gave a lecture at the University of Amsterdam at which time he advised de Casparis to transfer to Leiden to continue his studies because the Oudheidkundige Dienst was looking for an epigrapher to replace Roelof Goris. Accordingly, de Casparis registered for Indology at the University of Leiden in 1936. He excelled as a student and quickly passed his exami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantric Buddhism
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring to Buddhist traditions associated with Tantra and "Secret Mantra", which developed in the medieval Indian subcontinent and spread to Tibet, Nepal, other Himalayan states, East Asia, and Mongolia. Vajrayāna practices are connected to specific lineages in Buddhism, through the teachings of lineage holders. Others might generally refer to texts as the Buddhist Tantras. It includes practices that make use of mantras, dharanis, mudras, mandalas and the visualization of deities and Buddhas. Traditional Vajrayāna sources say that the tantras and the lineage of Vajrayāna were taught by Śākyamuni Buddha and other figures such as the bodhisattva Vajrapani and Padmasambhava. Contemporary historians of Buddhist studies meanwhile argue that this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hevajra
Hevajra (Tibetan: kye'i rdo rje / kye rdo rje; Chinese: 喜金剛 Xǐ jīngāng / 呼金剛 Hū jīngāng;) is one of the main yidams (enlightened beings) in Tantric, or Vajrayana Buddhism. Hevajra's consort is Nairātmyā (Tibetan: bdag med ma). History India The Hevajra Tantra, a yoginītantra of the ''anuttarayogatantra'' class, is believed to have originated between the late 8th (Snellgrove), and the late 9th or early 10th centuries (Davidson), in Eastern India, possibly Kamarupa. Tāranātha lists Saroruha and Kampala (also known as "Lva-va-pā", "Kambhalī", and "Śrī-prabhada") as its "bringers": .. the foremost yogi Virupa meditated on the path of Yamāri and attained siddhi under the blessings of Vajravārāhi,...His disciple Dombi Heruka..understood the essence of the Hevajra Tantra, and composed many śāstras like the ''Nairātmā-devi-sādhana'' and the ''Sahaja-siddhi''. He also conferred abhiṣeka on his own disciples. After this, two ācāryas Lva-v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuvraj
Yuv(a)raj(a) (Sanskrit: युवराज) is an Indian title for the crown prince, and the heir apparent to the throne of an Indian (notably Hindu) kingdom or (notably in the Mughal Empire or British Raj) princely state. It is usually applied to the eldest son of a Raja (King) or Maharaja (Great King), a kshatriya chief ruling one of the former kingdoms or vassal-rank princely states. Individuals * Yuvraj Singh (politician), was an Indian Politician and a MLA from Hamirpur constituency from Uttar Pradesh. * Yuvaraj Dhayalan, Tamil film assistant director * Yuvraj Hans, a Punjabi actor and singer * Yuvraj Singh, an Indian cricketer * Yuvraj Walmiki, an Indian professional field hockey player *Yuvraj Khanal, a professional student Other uses * ''Yuvvraaj'', a Bollywood movie by Subhash Ghai featuring Salman Khan Abdul Rashid Salim Salman Khan (; 27 December 1965) is an Indian actor, film producer, and television personality who works in Hindi films. In a film career sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is a primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Language
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Javanese
Old Javanese or Kawi is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the islands of Madura, Bali and Lombok. It had a sizable vocabulary of Sanskrit loanwords but had not yet developed the formal ''krama'' language register, to be used with one's social superiors that is characteristic of modern Javanese. History While evidence of writing in Java dates to the Sanskrit '' Tarumanegara inscription'' of 450, the oldest example written entirely in Javanese, called the Sukabumi inscription, is dated 25 March 804. This inscription, located in the district of Pare in the Kediri Regency of East Java, is actually a copy of the original, dated some 120 years earlier; only this copy has been preserved. Its contents concern the construction of a dam for an irrigation canal near the river Śrī Hariñjing (now shortened to Srinj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
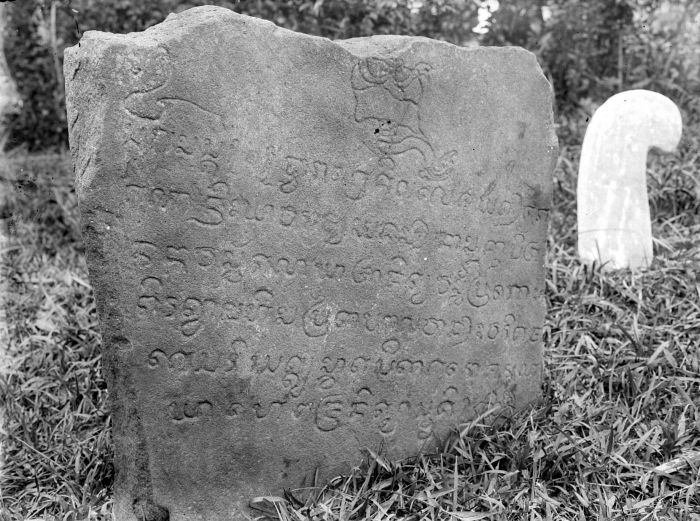


_(8697431158).jpg)


