|
Battle Of Wola Cyrusowa
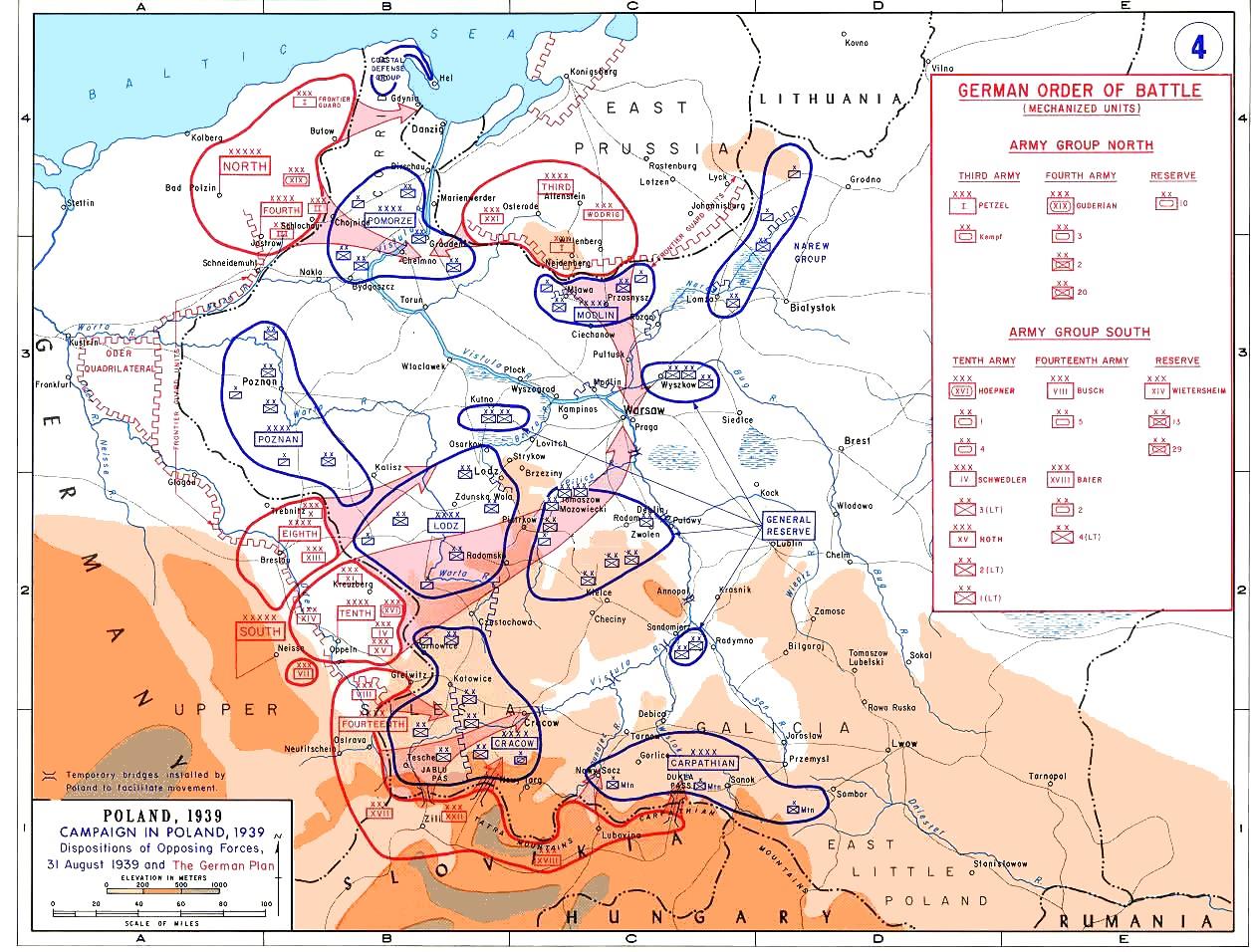
The Battle of Wola Cyrusowa took place on 8 September 1939 near the village of Wola Cyrusowa near Stryków in Poland, during the September Campaign. It was fought between the forces of the Polish Piotrków Operational Group under Gen. Wiktor Thommée and the German 10th Infantry Division. In the effect of a successive delaying action, the Polish forces managed to regroup and withdraw eastwards while at the same time inflicting heavy losses on the opposing unit. However, their victory was only a temporary setback for the Nazi invasion of Poland. Prelude Due to the strategic errors made by Gen. Juliusz Rómmel, the commander of the Łódź Army, the Polish units that were to form a defensive wedge against the German assault towards Warsaw were dislocated too close to the German border. Because of that, the Piotrków Operational Group, along with the rest of that army's units, entered contact with enemy forces already on September 1 and lost the chance to successfully support the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Poland (1939)
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stryków
Stryków (german: 1943-45 Strickau) is a town in central Poland, in Łódź Voivodeship, in Zgierz County. It has 3,428 inhabitants (2020). History Early history The first mention of Stryków was in 1387. Stryków was a village situated on the route from Zgierz to Lowicz. Stryków received city rights in 1394 from King Wladyslaw Jagiello, at the request of the heir of the town founder, Strykowskiego Deresława. In the middle of the eighteenth century, the city had 45 artisans (13 clothiers, 5 merchants and shopkeepers, and 5 others) and was a local center of commerce and crafts. It was also a center of aristocratic wealth. In 1744 the town received the privilege of organizing eight fairs a year. Stryków belonged to medium-sized cities. Textile manufacturing was attempted by the then owner Felix Czarnecki but without success. The town economy remained centered on crafts and agriculture. Contemporary activities have left traces of the old town in the form of an existing semi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Military Equipment Of World War II
The following is a list of German military equipment of World War II which includes artillery, vehicles and vessels. World War II was a global war that was under way by 1939 and ended in 1945. Following political instability build-up in Europe from 1930, the Germans, which aimed to dominate Europe, attacked Poland on 1 September 1939, marking the start of World War II. The war in Europe ended 8 May 1945 with the unconditional surrender of Germany to the Allied forces. The Germans used a number of type designations for their weapons. In some cases the type designation and series number (i.e. FlaK 30) are sufficient to identify a system, but occasionally multiple systems of the same type are developed at the same time and share a partial designation. Personal arms Knives and bayonets Small arms Pistols (manual and semi-automatic) Automatic pistols and submachine guns Rifles Grenades and grenade launchers * Blendkörper 1H * Blendkörper 2H * Gewehr-Granatpatrone 40 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of World War II Military Equipment Of Poland
Polish Armament in 1939–45 article is a list of equipment used by Polish army before and during the Invasion of Poland, foreign service in British Commonwealth forces and last campaign to Germany with the Red Army in 1945. Aircraft Local designs *Lublin R-VIIIbis *Lublin R-VIIID *Lublin R-XIIIE (prototype) *Lublin R-XIIIF (prototype) *Lublin R-XIIIG (prototype) *Lublin R-XVIB * Lublin R-XXII (project) * Lublin R-XXIII (R-XIIIDr.)(project) *LWS-3 Mewa * LWS-7 Mewa II (project) *PWS-16 *PWS-18 *PWS-26 * PWS-27 (project) * PWS-28 (project) * PWS-29 (project) *PWS-24bis * PWS-35 Ogar *PZL P.7a *PZL P.11c *PZL P.11g Kobuz (prototype) * PZL.50 Jastrząb (prototype) * PZL.23A Karaś A * PZL.23B Karaś B / Karaś II * PZL.37B Łoś B * PZL.38 Wilk (prototypes) * PZL.43 Karaś * PZL.46 Sum (prototype) * PZL.48 Lampart (project) * PZL.49 Miś (project) * PZL.54 Ryś (project) *RWD-8 * RWD-13 * RWD-13S *RWD-14 Czapla *RWD-17 *RWD-17W (prototype) *Bartel BM-4a *Bartel BM-4c *Bartel BM-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 8th Army (German: ''8. Armee Oberkommando'') was a World War II field army. It existed twice during the war, in the invasion of Poland in 1939, and on the Eastern Front from 1943 onwards. The 8th Army was activated on 1 August 1939 with General Johannes Blaskowitz in command. In 1939 it was part of Gerd von Rundstedt's Army Group South for the Invasion of Poland. It consisted of two corps, X. Armeekorps and XIII. Armeekorps, and was responsible for the northern part of Army Group South's front. The army saw heavy combat during the Battle of the Bzura. After the conclusion of the Polish campaign, it was reorganized into the 2nd Army which took part in the Battle of France in 1940. In 1943 it was reformed after the Battle of Kursk from Army Detachment Kempf. After fierce defensive battles throughout 1943, 1944 and the first months of 1945, it finally surrendered in Austria Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish 28th Infantry Division
The 28 Dywizja Piechoty was a Polish Army infantry division which saw action against the invading Germans during the Invasion of Poland of World War II. The division suffered heavy casualties in battles near Łódź and the remnants retreated to Warsaw, where they surrendered. The history of the division dates back to the autumn of 1921, when Polish Army changed its structure, after the victorious Polish–Soviet War. New unit was formed in Warsaw, out of three previously existing infantry regiments, and one light artillery regiment. The 15th Infantry Regiment, which had belonged to the 9th Infantry Division, was on August 19–21 transported by rail to Dęblin, which became its peacetime garrison. The 36th Infantry Regiment, previously of the 8th Infantry Division, remained in Warsaw, and the 72nd Infantry Regiment (previously of the 18th Infantry Division) was on October 7–8, 1921, transported from Brzesc nad Bugiem to Warsaw. Furthermore, the 28th Light Artillery Regiment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish 2nd Legions Infantry Division
Polish 2nd Legions Infantry Division (''2. Dywizja Piechoty Legionów'') was a tactical unit of the Polish Army between the World Wars. Formed on February 21, 1919, in the towns of Zegrze and Jablonna near Warsaw, and composed mostly of veterans of the Polish Legions in World War I, the unit saw extensive action during the Polish-Bolshevik War and the Invasion of Poland. During the Polish-Bolshevik War the division was commanded by Henryk Minkiewicz and Michal Zymierski. In a later stage, it took part in the Battle of Niemen as part of the Third Army. In the Second Polish Republic, the unit's headquarters were stationed in Kielce, with some regiments in the garrisons of Sandomierz and Jarosław. During that time its commanders included General Aleksander Narbutt-Łuczyński (1921 - 1930), General Juliusz Zulauf (1930 - 1938) and Colonel Edward Dojan-Surówka (1938 - Sept. 8 1939). In 1921 - 1939, the division's headquarters was garrisoned in Kielce. Its 2nd Legions' Infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Głowno
Głowno is a town and community in Poland, in Łódź Voivodeship, in Zgierz County, about 25 km northeast of Łódź. The town administratively belonged to the Łódź Voivodeship from 1975 to 1998. According to data from 2020, the city had 13,961 inhabitants. History Although the first settlement at the site of present-day Głowno is thought to have appeared in the 11th century, the first town was organized in the early 15th century near a trade route from the Duchy of Masovia, a Polish fief, to the Polish Kingdom. Rawa Mazowiecka feudal lord and Sochaczew podczaszy (deputy cup-bearer) Jakub Głowiński founded Głowno's first Roman Catholic church, which was consecrated on March 11, 1420 as the Church of St. Jacob. On Jakub's request, Duke Siemowit V of Masovia granted city rights under Kulm law. The city rights have been maintained until the modern day, with an interruption between the years 1870–1925. Upon incorporation of the Duchy of Rawa into the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poznań Army
Army Poznań ( pl, Armia Poznań) led by Major General Tadeusz Kutrzeba was one of the Polish Armies during the Invasion of Poland in 1939. Tasks Flanked by Armia Pomorze to the north and Łódź Army to the south, the Army was to provide flanking operations in Grand Poland region, defend it and withdraw towards lines of defence along the Warta river. Operational history During the Invasion of Poland, in the battle of the Border the German Army Group South struck between Poznań and Łódź Armies, penetrating Polish defenses and forcing Polish armies to retreat. The Poznań Army itself was not heavily engaged during those early days but was forced to retreat due to danger of being flanked. Later the Poznań Army strengthened by the remains of the Pomorze Army took part in the Polish counteroffensive Battle of Bzura; finally remaining units withdrew towards Warsaw and took part in its defense. Organization The Army was commanded by gen. Tadeusz Kutrzeba; its chief of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków Army
Kraków Army ( pl, Armia Kraków) was one of the List of Polish armies, Polish armies which took part in the Invasion of Poland (1939), Polish Defensive War of 1939. It was officially created on March 23, 1939 as the main pivot of Polish defence. It was commanded by Gen. Antoni Szylling. Originally, Kraków Army was to be made of seven infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one mountain brigade. On September 1, 1939, General Szylling had the force which consisted of five infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one brigade of mountain infantry. Altogether, the army was made of 59 battalions, 29 squadrons, 352 cannons, 90 tanks, two armoured trains and 44 planes. These forces were not enough to halt German advance, especially in the area north of Częstochowa, where Kraków Army connected with Łódź Army. Main thrust of Wehrmacht panzer units was directed there, and this area was defended only by the Polish 7th I.D., which was destroyed in the early days of September 1939, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łódź Army
Łódź Army ( pl, Armia Łódź) was one of the Polish armies that took part in the Invasion of Poland of 1939. It was officially created on 23 March 1939 with the task of filling the gap between Poznań Army in the north and Kraków Army in the south. Commanded by Juliusz Rómmel, it consisted of five infantry divisions and two cavalry brigades with support from the air force. Tasks The army's task was to fill the gap between Army Poznań in the north (defending Greater Poland under general Tadeusz Kutrzeba) and Army Kraków in the south (operating in Silesia and Lesser Poland under general Antoni Szylling), prevent enemy attacks in the direction of Łódź and Piotrków Trybunalski and if possible, advance towards Sieradz. It was also to cover the mobilization of a reserve Prusy Army behind the Polish lines. Because of that, the main strategic purpose of the army was to gain time and offer delaying actions and harsh resistance on the expected main German offensive lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juliusz Rómmel
Juliusz Karol Wilhelm Józef Rómmel (german: Julius Karl Wilhelm Josef Freiherr von Rummel; 3 June 1881 – 8 September 1967) was a Polish military commander, a general of the Polish Armed Forces. He graduated from the Corps of Cadets in Pskov and the Military School of St. Petersburg. During World War I he served as a Tsarist army officer and fought in the 1st Artillery Brigade of the Russian Army. In 1917 he joined the Polish Army. During the Polish–Soviet War, he gained great fame for achieving a decisive victory in the Battle of Komarów, the largest cavalry engagement of the 20th century. A commander of two Polish armies during the Polish Defensive War of 1939, Rómmel was one of the most controversial of the generals to serve during that conflict. After the invasion he was captured by German troops and interned in a POW camp in Murnau. After liberation by the Americans he returned to Poland to serve as Commander in Chief. After 1956 Rómmel worked in the Association o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |