|
Battle Of Veracruz (other)
{{disambiguation ...
The Battle of Veracruz may refer to: * Attack on Veracruz (1683) pirate attack on Veracruz in Spanish Colonial Mexico * Battle of Veracruz (1838), a French attack on Veracruz during the Pastry War * Siege of Veracruz (1847), an American siege on the Mexican city of Veracruz during the Mexican-American War * Siege of Veracruz, either of two rebel attacks on Veracruz during the Mexican Reform War of 1857–1861 * Battle of Veracruz (1914), an American attack on Veracruz during the United States occupation of Veracruz The United States occupation of Veracruz (April 21 to November 23, 1914) began with the Battle of Veracruz and lasted for seven months. The incident came in the midst of poor diplomatic relations between Mexico and the United States, and was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Veracruz
The attack on Veracruz was a 1683 raid against the port of Veracruz, in the Viceroyalty of New Spain (colonial Mexico). It was led by the Dutch pirates Laurens de Graaf, Nicholas van Hoorn and Michel de Grammont. History On 17 May 1683 the pirates arrived off the coast of Veracruz with a small fleet which included five large vessels, eight smaller vessels and around 1300 pirates. At the head of the fleet sailed two Spanish warships, previously captured by van Hoorn, designed to confuse the townsfolk into thinking the fleet was Spanish.''Piracy: The Complete History'' by Angus Konstam (, 2008) While the fleet was anchored offshore, de Graaf and |
Battle Of Veracruz (1838)
The Battle of Veracruz, also known as the Battle of San Juan de Ulúa, was a naval engagement that pitted a French frigate squadron under Rear Admiral Charles Baudin against the Mexican citadel of San Juan de Ulúa, which defended the city of Veracruz, from 27 November to 5 December 1838. Having crossed the Atlantic to settle a dispute between France and Mexico, the squadron anchored off Veracruz and negotiated until all diplomatic means to resolve the dispute appeared exhausted. After announcing that hostilities would begin, Baudin had his squadron bombard the fort. French fire, particularly heavy mortars mounted on bomb vessels and Paixhans guns on frigates, silenced the citadel and forced it to surrender on 28 November, a remarkable feat for the time. Mexican authorities, however, refused to cave in to French demands, forcing Baudin to mount a raid against the city itself on 5 December. Despite its limited ground forces, the French squadron succeeded in capturing Gen. Mariano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Veracruz
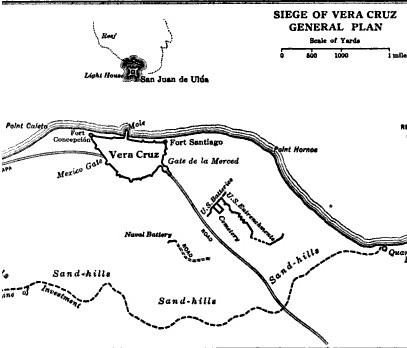
The Battle of Veracruz was a 20-day siege of the key Mexican beachhead seaport of Veracruz during the Mexican–American War. Lasting from March 9–29, 1847, it began with the first large-scale amphibious assault conducted by United States military forces, and ended with the surrender and occupation of the city. U.S. forces then marched inland to Mexico City. Background After the battles of Monterrey and Buena Vista, much of Zachary Taylor's Army of Occupation was transferred to the command of Major General Winfield Scott in support of the upcoming campaign. That campaign, determined by Scott and other Washington officials, would be a Veracruz landing and an advance inland.Bauer, K.J., 1974, ''The Mexican War, 1846–1848'', New York: Macmillan, Mexican military intelligence knew in advance of U.S. plans to attack Veracruz, but internal government turmoil left them powerless to send crucial reinforcements before the American assault commenced. Opposing forces Mexican de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform War
The Reform War, or War of Reform ( es, Guerra de Reforma), also known as the Three Years' War ( es, Guerra de los Tres Años), was a civil war in Mexico lasting from January 11, 1858 to January 11, 1861, fought between liberals and conservatives, over the promulgation of Constitution of 1857, which had been drafted and published under the presidency of Ignacio Comonfort. The constitution had codified a liberal program intended to limit the political, economic, and cultural power of the Catholic Church; separate church and state; reduce the power of the Mexican Army by elimination of the ''fuero''; strengthen the secular state through public education; and economically develop the nation. The constitution had been promulgated on February 5, 1857 with the intention of coming into power on September 16, only to be confronted with extreme opposition from Conservatives and the Catholic Church over its anti-clerical provisions, most notably the Lerdo law, which forced the sale of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |