|
Battle Of Pont Du Feneau
The Battle of Pont du Feneau was the last battle of the siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré by the English forces that had come to help the Huguenot rebellions of La Rochelle. It took place on 8 November 1627. The English lost the battle, and this final failure forced them to withdraw back to England. Before the battle English side The English forces, having been defeated earlier that day at the siege of Saint-Martin, pulled back to the village of Loix, where their ships were anchored. Because of bad food, many soldiers in their army were sick. The army was commanded by George Villiers, the first duke of Buckingham, and was composed of 12 infantry regiments and 4 cannons, as well as several volunteer rochelais protestants, all covered by the cavalry, consisting of about 68 horses. Not having seen the French forces since their retreat from Saint-Martin, Buckingham's troops thought the French would not attack and, growing reckless, were neither walking in closed or open ranks. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenot Rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted against royal authority. The uprising occurred a decade after the death of Henry IV who, himself originally a Huguenot before converting to Catholicism, had protected Protestants through the Edict of Nantes. His successor Louis XIII, under the regency of his Italian Catholic mother Marie de' Medici, became more intolerant of Protestantism. The Huguenots tried to respond by defending themselves, establishing independent political and military structures, establishing diplomatic contacts with foreign powers, and openly revolting against central power. The Huguenot rebellions came after two decades of internal peace under Henry IV, following the intermittent French Wars of Religion of 1562–1598. First Huguenot rebellion (1620–1622) The fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
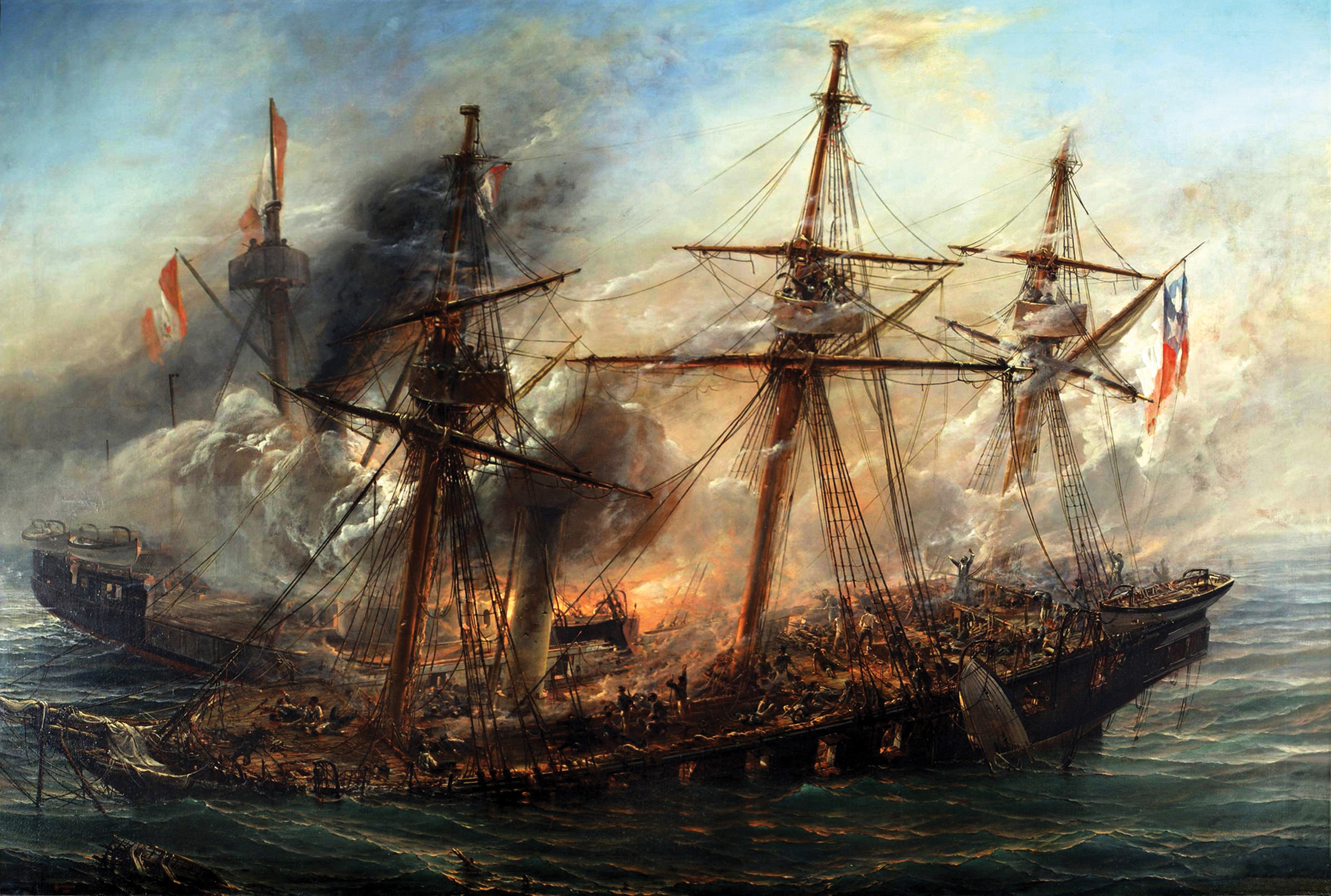
Combat Et Victoire Obtenue Sur Les Anglois Michel De La Mathoniere 1627
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or can be used as a tool to impose one's will on others. An instance of combat can be a stand-alone confrontation or a small part of a much larger violent conflict. Instances of combat may also be benign and recreational, as in the cases of combat sports and mock combat. Combat may comply with, or be in violation of local or international laws regarding conflict. Examples of rules include the Geneva Conventions (covering the treatment of people in war), medieval chivalry, the Marquess of Queensberry rules (covering boxing) and several forms of combat sports. Hand-to-hand combat Hand-to-hand combat (melee) is combat at very close range, attacking the opponent with the body ( striking, kicking, strangling, etc.) and/or with a melee weap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of France
The military history of France encompasses an immense panorama of conflicts and struggles extending for more than 2,000 years across areas including modern France, Europe, and a variety of regions throughout the world. According to historian Niall Ferguson, France is the most successful military power in history. It participated in 50 of the 125 major European wars that have been fought since 1495; more than any other European state. The first major recorded wars in the territory of modern-day France itself revolved around the Gallo-Roman conflict that predominated from 60 BC to 50 BC. The Romans eventually emerged victorious through the campaigns of Julius Caesar. After the decline of the Roman Empire, a Germanic tribe known as the Franks took control of Gaul by defeating competing tribes. The "land of Francia", from which France gets its name, had high points of expansion under kings Clovis I and Charlemagne, who established the nucleus of the future French state. In the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four million people died from violence, famine or diseases which were directly caused by the conflict; additionally, the conflict severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. The fighting ended in 1598 when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, the Catholics continued to have a hostile opinion of Protestants in general and they also continued to have a hostile opinion of him as a person, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée De L'Armée
The Musée de l'Armée (; "Army Museum") is a national military museum of France located at Les Invalides in the 7th arrondissement of Paris. It is served by Paris Métro stations Invalides (Paris Métro and RER), Invalides, Varenne (Paris Métro), Varenne and La Tour-Maubourg (Paris Métro), La Tour-Maubourg The Musée de l'Armée was created in 1905 with the merger of the Musée d'Artillerie and the Musée Historique de l'Armée. The museum's seven main spaces and departments contain collections that span the period from antiquity through the 20th century. History The Musée de l'Armée was created in 1905 with the merger of the Musée d'Artillerie and the Musée Historique de l'Armée. The ''Musée de l'artillerie'' (Museum of Artillery - "''artillerie''" meaning all things related to weapons) was founded in 1795 in the aftermath of the French Revolution, and expanded under Napoleon. It was moved into the Hôtel des Invalides in 1871, immediately following the Franco-Prussian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council. Portsmouth is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom, with a population last recorded at 208,100. Portsmouth is located south-west of London and south-east of Southampton. Portsmouth is mostly located on Portsea Island; the only English city not on the mainland of Great Britain. Portsea Island has the third highest population in the British Isles after the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. Portsmouth also forms part of the regional South Hampshire conurbation, which includes the city of Southampton and the boroughs of Eastleigh, Fareham, Gosport, Havant and Waterlooville. Portsmouth is one of the world's best known ports, its history can be traced to Roman times and has been a significant Royal Navy dockyard and base for centuries. Portsm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyhound Pub
The ''Greyhound'' was a public house (popularly known as "The Spotted Dog"), in High Street, Old Portsmouth, England. It is famous as the site of the murder of George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham in 1628. It is now a hotel. Architecture and conservation The building is timber-framed, but this is not evident from outside as it has been refronted. It became a private building called Buckingham House and was listed under that name in 1953. In letters The murder site was toured by the famous diarist and Royal Navy administrator Samuel Pepys in 1662. Pepys was accompanied by his wife Elisabeth, along with his Republican clerk Tom Hayter and wife, and the Earl of Sandwich Earl of Sandwich is a noble title in the Peerage of England, held since its creation by the House of Montagu. It is nominally associated with Sandwich, Kent. It was created in 1660 for the prominent naval commander Admiral Sir Edward Montagu. ...'s Puritan secretary John Creed ( Pepys' ''Diary'', 3 June ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Felton (assassin)
John Felton ( – 29 November 1628) was a lieutenant in the English Army who stabbed George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham to death in the Greyhound Pub of Portsmouth on 23 August 1628. King Charles I trusted Buckingham, who made himself rich in the process but proved a failure at foreign and military policy. Charles gave him command of the military expedition against Spain in 1625. It was a total fiasco with many dying from disease and starvation. He led another disastrous military campaign in 1627. Buckingham was hated and the damage to the king's reputation was irreparable. England rejoiced when he was assassinated by Felton. Early life John Felton was born around 1595, possibly in Suffolk, to a family related to the Feltons of Playford in Suffolk and distantly related to Thomas Howard, 21st Earl of Arundel. His father, Thomas Felton, prospered as a pursuivant, one appointed to the task of hunting down those who refused to attend Anglican church services (''see recusancy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri, Duke Of Rohan
Henri (II) de Rohan (21 August 157913 April 1638), Duke of Rohan and Prince of Léon, was a Breton-French soldier, writer and leader of the Huguenots. Early life Rohan was born at the Château de Blain (now a part of Blain, Loire-Atlantique), in Brittany. His father was René II, viscount of Rohan (1550–1586), and head of one of the oldest and most distinguished families in France, which was connected with many of the reigning houses of Europe.''Louis XIV, and the Court of France in the Seventeenth Century: In Three Volumes (Volume 1)'' by Julia Pardoe (Bentley, 1847) He was educated by his mother, Catherine de Parthenay< ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin, Duke Of Soubise
Benjamin de Rohan, duc de Soubise (1580–1642), was a French Huguenot leader. Son of René II, Viscount of Rohan, and younger brother of Henri de Rohan, he inherited the lordship of Soubise through his mother Catherine de Parthenay. He served his apprenticeship as a soldier under Maurice of Nassau in the Low Countries. In the religious wars from 1621 onwards his elder brother chiefly commanded on land and in the south, Soubise in the west and along the sea-coast. His exploits in the conflict have been sympathetically related by his brother, one of the most highly regarded military critics of the time. Soubise's chief exploit was a singularly bold and well-conducted attack (in 1625) on the Royalist fleet in the river Blavet (which included the cutting of a boom in the face of superior numbers) and the occupation of the islands of Ré and Oléron in 1625, leading to the Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1625) in which Louis XIII recovered the island of Ré. He commanded at La Roche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notre-Dame De Paris
Notre-Dame de Paris (; meaning "Our Lady of Paris"), referred to simply as Notre-Dame, is a medieval Catholic cathedral on the Île de la Cité (an island in the Seine River), in the 4th arrondissement of Paris. The cathedral, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, is considered one of the finest examples of French Gothic architecture. Several of its attributes set it apart from the earlier Romanesque style, particularly its pioneering use of the rib vault and flying buttress, its enormous and colourful rose windows, and the naturalism and abundance of its sculptural decoration. Notre Dame also stands out for its musical components, notably its three pipe organs (one of which is historic) and its immense church bells. Construction of the cathedral began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and was largely completed by 1260, though it was modified frequently in the centuries that followed. In the 1790s, during the French Revolution, Notre-Dame suffered extensive desecration; much of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


2009.jpg)

