|
Battle Of Pavia (other)
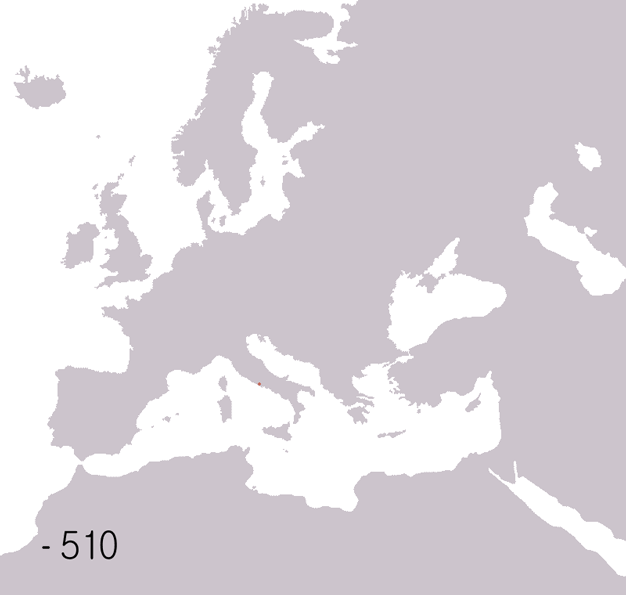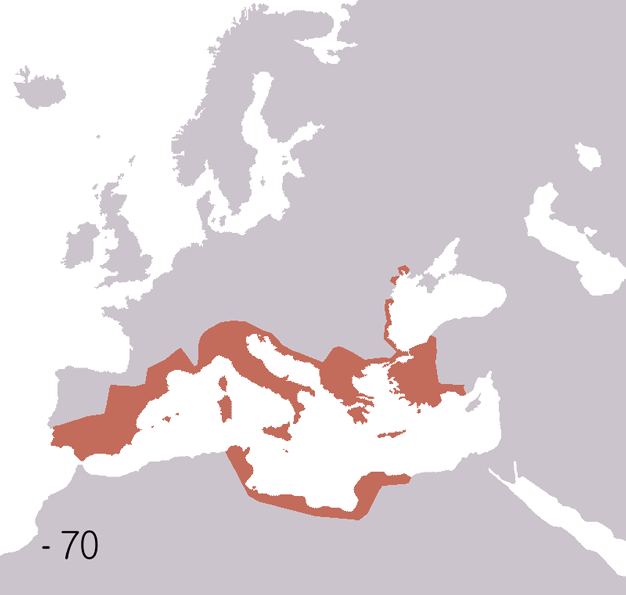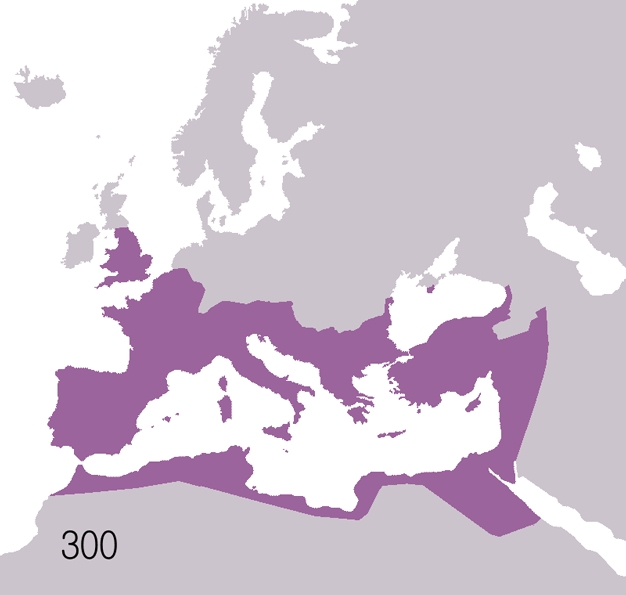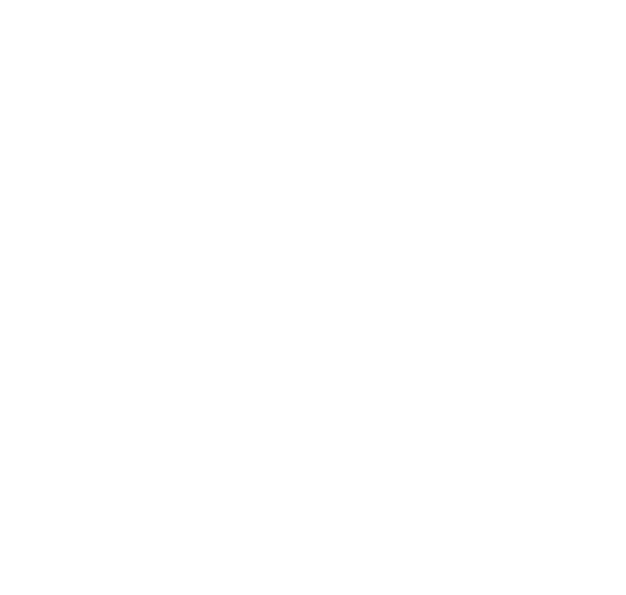
Battle of Pavia may refer to the following battles: * Battle of Pavia (271) ŌĆō Alamanni invasion of the Roman Empire * Battle of Pavia (476) ŌĆō Fall of the Western Roman Empire *Siege of Pavia (569ŌĆō572) ŌĆō Lombard invasion of Italy * Siege of Pavia (773ŌĆō774) ŌĆō Conquests of Charlemagne *Battle of Pavia (1431) ŌĆō Wars in Lombardy *Battle of Pavia (1525) The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521ŌĆō1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor as well as ruler of Spain, Au ... ŌĆō Italian War of 1521 See also * Siege of Pavia (other) {{disambig Pavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pavia (271)
The Battle of Ticinum, or Battle of Pavia, was fought in 271 near Ticinum (Pavia) in Italy, and resulted in the emperor Aurelian destroying the retreating Juthungi army. Background In 271, the Juthungi invaded Roman Italy. They defeated Aurelian's army at the Battle of Placentia but, on their way to attack the defenseless city of Rome, they were repulsed by the imperial army at the Battle of Fano. The Juthungi then asked for peace but Aurelian rejected their demand for safe passage. Trying to force their way back to their homelands, they headed north using the Via Aemilia. Aurelian wanted a decisive victory in order to restore his damaged reputation after the loss at Placentia as well as to recover the plunder the Juthungi were carrying. Therefore, he went in pursuit of the invaders, waiting for the best moment to attack. The battle Aurelian attacked the Juthungi while they were entering the open plains near Ticinum (Pavia). He was able to destroy their entire force, except f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pavia (476)
The Battle of Pavia was fought between the Western Roman Empire under Orestes and the Germanic warrior Odoacer. Odoacer was the leader of a group of Herulian and Scirian mercenaries serving in the Roman army The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500ŌĆō31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BCŌĆō395 AD), and its medieval continu .... Leading a mutiny of these troops, Odoacer defeated the Roman general Orestes near Pavia, executing Orestes. Odoacer thereafter marched on Ravenna, capturing the city and executing Orestes' son Paul. Odoacer overthrew the Roman emperor Romulus Augustus, also a son of Orestes, which marked the effective fall of the Western Roman Empire. Sources * 476 Pavia Pavia Pavia Military history of Italy Pavia {{Italy-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor Polity, polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western Roman province, provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the Late Roman army, army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the Roman economy, economy, the competence of the Roman emperor, emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climate variability and change, Climatic changes and both Endemic (epide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pavia (569ŌĆō572)
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774. The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) that the Lombards descended from a small tribe called the Winnili,: "From Proto-Germanic '' winna-'', meaning "to fight, win" who dwelt in southern Scandinavia (''Scadanan'') before migrating to seek new lands. By the time of the Roman-era - historians wrote of the Lombards in the 1st century AD, as being one of the Suebian peoples, in what is now northern Germany, near the Elbe river. They continued to migrate south. By the end of the fifth century, the Lombards had moved into the area roughly coinciding with modern Austria and Slovakia north of the Danube, where they subdued the Heruls and later fought frequent wars with the Gepids. The Lombard king Audoin defeated the Gepid leader Thurisind in 551 or 552, and his successo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pavia (773ŌĆō774)
The siege or battle of Pavia was fought in 773–774 in northern Italy, near Ticinum (modern Pavia), and resulted in the victory of the Franks under Charlemagne against the Lombards under King Desiderius. Background Charlemagne, ''rex Francorum'', had succeeded to the throne in 768 jointly with his brother Carloman. At the time there was antagonism between not only the two ruling brothers, but between the king of the Lombards, Desiderius, and the papacy. In 772, Pope Hadrian I expelled all the Lombard officials from the papal curia. In response, Desiderius invaded papal territory, even taking Otriculum (modern Otricoli), just a day's march from Rome.*. Hadrian called Charlemagne for assistance. Charles had produced an alliance with the Lombards by marrying one of Desiderius' daughters, Desiderata; within a year, however, he had changed his mind about the marriage and alliance, and divorced his wife, sending her back to her father. This was taken as an insult by the Lombard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pavia (1431)
The Battle on the Po was a battle of the Wars in Lombardy. It occurred in June 1431, on the Po River, near Cremona. The battle was fought between 85 Venetian galleys, sent towards Cremona to support Count of Carmagnola's army, and a somewhat superior number of Milanese galleys. The Venetians were commanded by Niccol├▓ Trevisani. The battle resulted in the defeat of the Venetians, who could not be helped by Carmagnola's field army, with a loss of c. 2,500 men, 28 galleys, and 42 transport ships. See also *Battle of Soncino The Battle of Soncino was a battle of the Wars in Lombardy, fought in March 1431. It was fought between the armies of the Republic of Venice, under Count of Carmagnola, and of the Duchy of Milan, under Francesco I Sforza Francesco I Sforza ... Sources 1431 in Europe 1430s in the Holy Roman Empire 15th century in the Republic of Venice Pavia 1431 Pavia 1431 Pavia 1431 Battles in Lombardy Conflicts in 1431 Riverine warfare Po (river) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pavia (1525)
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521ŌĆō1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor as well as ruler of Spain, Austria, the Low Countries, and the Two Sicilies. The French army was led by King Francis I of France, who laid siege to the city of Pavia (then part of the Duchy of Milan within the Holy Roman Empire) in October 1524 with 26,200 troops. The French infantry consisted of 6,000 French foot soldiers and 17,000 foreign mercenaries: 8,000 Swiss, 5,000 Germans and 4,000 Italians ( black bands). The French cavalry consisted of 2,000 ''gendarmes'' and 1,200 lances fournies. Charles V, intending to break the siege, sent a relief force of 22,300 troops to Pavia (where the Imperial garrison stationed consisted of 5000 Germans and 1000 Spaniards) under the command of the Fleming Charles de Lannoy, Imperial lieutenant and viceroy of Naples, and of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pavia (other)
Siege of Pavia can refer to one of the following sieges of the city of Pavia (ancient Ticinum) in Italy: * Siege of Pavia (476), by Odoacer * , by Tufa * Siege of Pavia (569ŌĆō572), by the Lombards * , by Pippin the Short * Siege of Pavia (773ŌĆō774), by Charlemagne * during the Hungarian invasions of Europe * , by the Visconti * , by the Visconti * , by the Visconti * , by the Visconti * during the Italian War of 1521ŌĆō1526 * Siege of Pavia (1524ŌĆō1525) during the Italian campaign of 1524ŌĆō1525 * Siege of Pavia (1527), by the League of Cognac * during the War of the League of Cognac * during the War of the League of Cognac * during the Franco-Spanish War (1635-1659) * during the War of the Spanish Succession See also * Battle of Pavia (other) Battle of Pavia may refer to the following battles: * Battle of Pavia (271) ŌĆō Alamanni invasion of the Roman Empire * Battle of Pavia (476) ŌĆō Fall of the Western Roman Empire *Siege of Pavia (569ŌĆ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |