|
Battle Of Lepanto (other)
The Battle of Lepanto was fought in 1571 and resulted in the Holy League's victory over the Ottoman fleet. There are many paintings titled ''The Battle of Lepanto'', including: * ''The Battle of Lepanto'' (Luna painting) (1887), by Filipino painter and revolutionary Juan Luna Other works: * "Lepanto," a 1911 poem by G. K. Chesterton See also Three earlier battles were fought in the vicinity of Naupactus (Lepanto): *Battle of Naupactus in 429 BC, an Athenian victory during the Peloponnesian War *Battle of Zonchio The naval Battle of Zonchio ( tr, Sapienza Deniz Muharebesi, also known as the Battle of Sapienza or the First Battle of Lepanto) took place on four separate days: 12, 20, 22, and 25 August 1499. It was a part of the Ottoman–Venetian War of ... in 1499, an Ottoman victory during the Ottoman-Venetian Wars * Battle of Modon (1500) in 1500, an Ottoman victory during the Ottoman-Venetian Wars {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lepanto
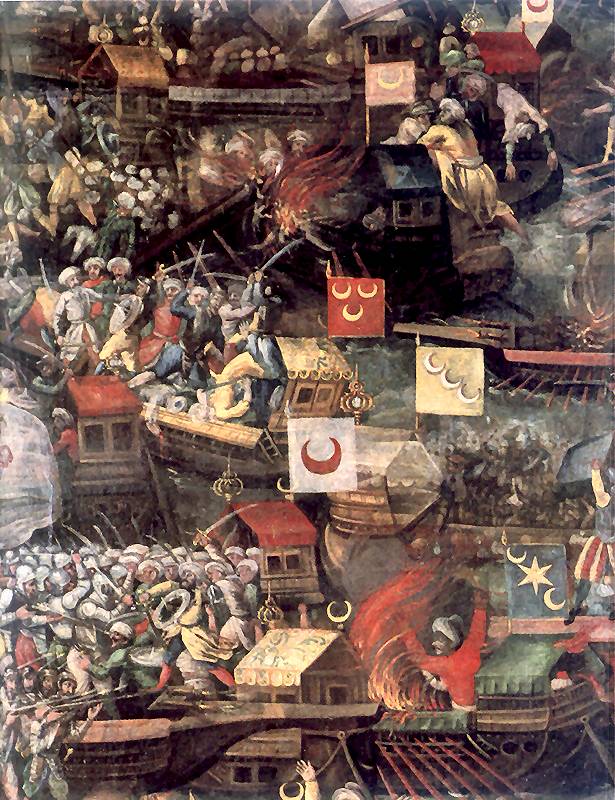
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states (comprising Spain and its Italian territories, several independent Italian states, and the Sovereign Military Order of Malta) arranged by Pope Pius V, inflicted a major defeat on the fleet of the Ottoman Empire in the Gulf of Patras. The Ottoman forces were sailing westward from their naval station in Lepanto (the Venetian name of ancient Naupactus – Greek , Ottoman ) when they met the fleet of the Holy League which was sailing east from Messina, Sicily. The Spanish Empire and the Venetian Republic were the main powers of the coalition, as the league was largely financed by Philip II of Spain, and Venice was the main contributor of ships. In the history of naval warfare, Lepanto marks the last major engagement in the Western world to be fought almost entirely between rowing vessels, namely the galleys and galleasses which were th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states (comprising Spain and its Italian territories, several independent Italian states, and the Sovereign Military Order of Malta) arranged by Pope Pius V, inflicted a major defeat on the fleet of the Ottoman Empire in the Gulf of Patras. The Ottoman forces were sailing westward from their naval station in Lepanto (the Venetian name of ancient Naupactus – Greek , Ottoman ) when they met the fleet of the Holy League which was sailing east from Messina, Sicily. The Spanish Empire and the Venetian Republic were the main powers of the coalition, as the league was largely financed by Philip II of Spain, and Venice was the main contributor of ships. In the history of naval warfare, Lepanto marks the last major engagement in the Western world to be fought almost entirely between rowing vessels, namely the galleys and galleasses which were th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Battle Of Lepanto (Luna Painting)
''The Battle of Lepanto'' (Spanish: ''La Batalla de Lepanto''"The Battle of Lepanto" by Juan Luna , worltourist.us) is a painting by painter and revolutionary activist . Along with , Luna is one of the first s to excel and ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepanto (poem)
"Lepanto" is a poem by G. K. Chesterton celebrating the victory of the Holy League in the Battle of Lepanto written in irregular stanzas of rhyming, roughly paeonic tetrameter couplets, often ending in a quatrain of four dimeter lines. The poem tells of the defeat of the Ottoman fleet of Ali Pasha by the Christian crusader, Don John of Austria. The poem was written in 1911 and published in Chesterton's 1915 collection ''Poems''. The poem's stirring verses helped inspire soldiers such as John Buchan during World War I. Context "Lepanto" was published in 1915, and is in line with the author's other works of early decades of the century as representing a spirited rejection of the ''fin de siècle'' Decadent Fatalism which was the dominating philosophy in his youth. As in the author's " The Ballad of the White Horse," the non-Christian forces are made representative of the determinist or fatalist philosophy that (in Chesterton's view) denied the value of human struggle an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naupactus
Nafpaktos ( el, Ναύπακτος) is a town and a former municipality in Aetolia-Acarnania, West Greece, situated on a bay on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, west of the mouth of the river Mornos. It is named for Naupaktos (, Latinized ''Naupactus''), an important Athenian naval station in the Peloponnesian war. As a strategically crucial possession controlling access to the Gulf of Corinth, Naupaktos changed hands many times during the Crusades and the Ottoman–Venetian Wars. It was under Venetian control in the 15th century, and came to be known by the Venetian form of its name, Lepanto. It fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1499 and was used as naval station by the Ottoman Navy in the 16th century, being the site of the decisive victory by the Holy League in the Battle of Lepanto in 1571. Except a brief period of Venetian control in 1687–1699, Lepanto remained under Ottoman control until Greek independence in 1829. The modern municipality was incorporated in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Naupactus
The Battle of Naupactus was a naval battle in the Peloponnesian War. The battle, which took place a week after the Athenian victory at Rhium, set an Athenian fleet of twenty ships, commanded by Phormio, against a Peloponnesian fleet of seventy-seven ships, commanded by Cnemus. In the battle, the Peloponnesians drew the Athenians out from their anchorage at Antirrhium by sailing into the Gulf of Corinth, moving as if to attack the vital Athenian base at Naupactus. The Athenians were forced to shadow their movements, sailing eastward along the northern shore of the gulf. Attacking suddenly, the Peloponnesians drove nine Athenian ships ashore and pursued the others towards Naupactus; victory seemed securely in their hands. At the entrance to the harbor of Naupactus, however, the last Athenian ship to reach the harbor turned the tide by circling around an anchored merchant ship to ram and sink its leading pursuer. Confusion set in among the Peloponnesians, and the newly embolden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zonchio
The naval Battle of Zonchio ( tr, Sapienza Deniz Muharebesi, also known as the Battle of Sapienza or the First Battle of Lepanto) took place on four separate days: 12, 20, 22, and 25 August 1499. It was a part of the Ottoman–Venetian War of 1499–1503. Preparations In January 1499 Kemal Reis set sail from Constantinople with a force of 10 galleys and 4 other types of ships, and in July met with the huge Ottoman fleet which was sent to him by Davud Pasha and took over its command in order to wage a large scale war against the Republic of Venice. The Ottoman fleet consisted of 67 galleys, 20 galliots, and about 200 smaller vessels. The Venetian fleet of 47 galleys, 17 galliots, and about 100 smaller vessels was under the command of Antonio Grimani. Grimani was 65 and although he was a proven captain in battle, he was not an experienced leader and had never commanded large battle fleets. He had only been given command because of a donation of 16,000 ducats to the state and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |