|
Battle Of Estrelleta
The Battle of Estrelleta was a major battle of the Dominican War of Independence and was fought on September 17, 1845, at the site of Estrelleta, near Las Matas de Farfán, San Juan Province (Dominican Republic), San Juan Province. A force of Dominican troops, a portion of the Army of the South, led by General Antonio Duvergé, defeated an outnumbering force of the Haitian Army led by General Jean-Louis Pierrot. Prelude Campaign of 1845 On June 17, 1845, the Dominicans, under the command of General Antonio Duvergé, invaded Haiti in retaliation for Haitian border raids. The invaders captured two towns on the Plateau du Centre and established a bastion at Cachimán. Haitian President Jean-Louis Pierrot quickly mobilized his army and counter-attacked on July 22, driving the invaders from Cachimán and back across the frontier. On August 6, Pierrot ordered his army to invade the Dominican Republic. Battle On September 17, 1845, the Dominicans defeated the Haitian vanguard near the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican War Of Independence
The Dominican War of Independence made the Dominican Republic a sovereign state on February 27, 1844. Before the war, the island of Hispaniola had been united for 22 years when the newly independent nation, previously known as the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, was unified with the Republic of Haiti in 1822. The criollo class within the country overthrew the Spanish crown in 1821 before unifying with Haiti a year later. After the struggles that were made by Dominican patriots to free the country from Haitian control, they had to withstand and fight against a series of incursions that served to consolidate their independence (1844–56). Haitian soldiers would make incessant attacks to try to gain back control of the nation, but these efforts were to no avail, as the Dominicans would go on to win every battle. Background At the beginning of the 1800s, the colony of Santo Domingo, which had once been the headquarters of Spanish power in the New World, was in its worst decli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
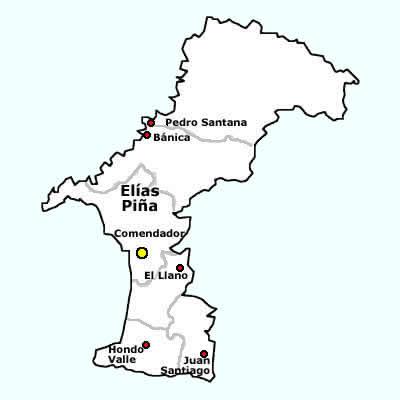
Comendador, Dominican Republic
Comendador is the capital of the Elías Piña province of the Dominican Republic. It has a border crossing to the Haitian town Belladère. Population The municipality had, in 2012, a total population of 43,894. In this numbers are included the population of the municipal district Sabana Larga. History The city was named after its founder, the "Comendador of Lares" (''Comendador'' was the chief of a military or religious order) but on 29 November 1930 it was changed to Elías Piña. By the Law 342 of 29 May 1972 the city was named again ''Comendador''. Economy The main economic activity of the municipality is agriculture Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to .... References Populated places in Elías Piña Province Municipalities of the Dominican Republic Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elías Piña Province
Elías Piña () is a westernmost province which composing one of the 32 Provinces of the Dominican Republic, provinces of the Dominican Republic. It is divided into 6 municipalities and its capital city is Comendador, Elías Piña, Comendador. It is bordered by the provinces of Dajabón Province, Dajabón to the north-west, Santiago Rodríguez Province, Santiago Rodríguez to the north-east, San Juan Province (Dominican Republic), San Juan to the east, Independencia Province, Independencia to the south and the Nord-Est (department), Nord-Est department of Haiti to the west. It was created on 1942 with the name ''San Rafael''. In 1965, its name was changed to ''Estrelleta'' and, finally, in 1972 it got its current name. It was a ''municipio'' of the San Juan province before being elevated to the category of province. Location The Elías Piña province has the Dajabón Province, Dajabón and Santiago Rodríguez Province, Santiago Rodríguez provinces to the north, the San Juan Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Dominican Republic (up To 1844)
The flag of the Dominican Republic represents the Dominican Republic and, together with the coat of arms and the national anthem, has the status of a national symbol. The blue on the flag stands for liberty, the white for salvation, and the red for the blood of heroes. The civil flag follows the same design, but without the charge in the center. The flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte. Description As described by Article 21 of the Dominican Constitution, the flag features a centered white cross that extends to the edges and divides the flag into four rectangles; the top ones are blue (hoist side) and red, and the bottom ones are red (hoist side) and blue. The national coat of arms, featuring a shield with the flag design and supported by a bay laurel branch (left) and a palm frond (right), is at the center of the cross. Above the shield, a blue ribbon displays the national motto ''Dios, Patria, Libertad'' (English: God, Homeland, Liberty). Below the shield, the words ''R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands, along with Saint Martin, that is shared by two sovereign states. The Dominican Republic is the second-largest nation in the Antilles by area (after Cuba) at , and third-largest by population, with approximately 10.7 million people (2022 est.), down from 10.8 million in 2020, of whom approximately 3.3 million live in the metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The official language of the country is Spanish. The native Taíno people had inhabited Hispaniola before the arrival of Europeans, dividing it into five chiefdoms. They had constructed an advanced farming and hunting society, and were in the process of becoming an organized civilization. The Taínos also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration."Haiti" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Haiti is in size, the third largest country in the Caribbean by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the most populous country in the Caribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Duvergé
Antonio Duvergé Duval (1807–April 11, 1855), a Dominican general of French origin and one of the most legendary military figures in the history of the Dominican Republic, served in the Dominican War of Independence. He was a hero and martyr who proclaimed the birth of the new Republic on February 28, 1844, in Bani and days later in Azua. Origins Antonio Duvergé Duval was born in Mayagüez, Puerto Rico to French-Dominican Joseph Duverger and Maria Duval. His grandfather Alexander was born Nantes. A member of De la Rochejacquelein family, he left France during the Drownings at Nantes for being a royalist. Alexander fought for the French against Haitian General Toussaint Louverture. After the invasion of Santo Domingo by Jean-Jacques Dessalines, he was exiled to Puerto Rico with his son Joseph Duverger and his wife Maria Duval. In 1808, when Antonio Duvergé was one year old, the family returned to Santo Domingo, settling in San Cristobal and later in El Seibo. At that tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Joaquín Puello
José Joaquín Puello de Castro (Santo Domingo, 1805/1808–ibid., 23 December 1847) was a general and government minister from the Dominican Republic. He and his brothers, Gabino Puello, Gabino and Eusebio Puello, Eusebio, were the only prominent Afro-Dominican (Dominican Republic), black Dominicans in the Dominican War of Independence. Biography Puello was former colonel in the Armed Forces of Haiti, Haitian Army; when the Independence was proclaimed on 27 February 1844 he was made part of the Central Independent Government (CIG) since he was very popular among mulattoes and blacks in order to allay fears and rumors regarding an alleged restoration of slavery by the independence plotters. Before the involvement of Puello and his African diaspora, afro-descendant brothers with the secret society of La Trinitaria (Dominican Republic), La Trinitaria organized by Juan Pablo Duarte to attain its independence from Haiti, the majority of the population of African descent consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Louis Pierrot
Prince Jean-Louis Michel Paul Pierrot, Baron of Haïti (19 December 1761 - 18 February 1857) was a career officer general in the Haitian Army who also served as President of Haiti from 16 April 1845 to 1 March 1846. Revolution During the Haitian Revolution Pierrot led a black battalion at the Battle of Vertieres in 1803. During the period of the Kingdom of Haiti, Henri Christophe (Henry I) promoted Pierrot to the rank of Lieutenant General in the Army and granted him the hereditary title of Baron and Prince of Hayti. During the period of the Second Empire of Haiti, Faustin Soulouque (Faustin I) promoted Pierrot to the rank of the Grand Marshal of the Empire. President Pierrot was elected president of Haiti by the Council of State on 16 April 1845, the day after the death of Philippe Guerrier. As President of Haiti, he was intended to be a figurehead for the mulatto ruling class. Pierrot's most pressing duty as the new president was to check the incursions of the Dominicans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan Province (Dominican Republic)
San Juan () is a province of the Dominican Republic. Before 1961 it was known as ''Benefactor''. San Juan is the Republic's largest province, bearing a size of 3,569 square kilometers (1,378 miles), and it is landlocked. Geography It comprises a total area of 3,569.39 km², being the largest province in the Dominican Republic, and according to the 2002 census it had a population of 241,105 inhabitants. It is crossed by numerous rivers, among which the San Juan River, the Yaque del Sur River, the Sabaneta River, the Macasías and the Mijo stand out. It has three hydroelectric dams, Sabaneta, Sabana Yegua and Palomino, the latter inaugurated in 2013. Within the provincial territory there are three parks or protected areas, including the Juan Ulises García Bonelly Park, and the José Armando Bermúdez and José del Carmen Ramírez National Parks. In the area of Las Matas de Farfán there is a sulphurous spring, La Zurza, which is highly visited by regional tourism. The San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap-Haïtien
Cap-Haïtien (; ht, Kap Ayisyen; "Haitian Cape"), typically spelled Cape Haitien in English and often locally referred to as or , is a commune of about 190,000 people on the north coast of Haiti and capital of the department of Nord. Previously named ''Cap‑Français'' ( ht, Kap-Fransè; initially ''Cap-François'' ht, Kap-Franswa) and ''Cap‑Henri'' ( ht, Kap-Enri) during the rule of Henri I, it was historically nicknamed the ''Paris of the Antilles'', because of its wealth and sophistication, expressed through its architecture and artistic life. It was an important city during the colonial period, serving as the capital of the French Colony of Saint-Domingue from the city's formal foundation in 1711 until 1770 when the capital was moved to Port-au-Prince. After the Haitian Revolution, it became the capital of the Kingdom of Haiti under King Henri I until 1820. Cap-Haïtien's long history of independent thought was formed in part by its relative distance from Port-au-Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1845
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |