|
Battle Of Carentan
The Battle of Carentan was an engagement in World War II between airborne forces of the United States Army and the German Wehrmacht during the Operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy. The battle took place between 6 and 13 June 1944, on the approaches to and within the town of Carentan, France. The objective of the attacking American forces was consolidation of the U.S. beachheads (Utah Beach and Omaha Beach) and establishment of a continuous defensive line against expected German counterattacks. The defending German force attempted to hold the town long enough to allow reinforcements en route from the south to arrive, prevent or delay the merging of the lodgments, and keep the First Army (United States), U.S. First Army from launching an attack towards Lessay-Périers that would cut off the Cotentin Peninsula. Carentan was defended by two battalions of Fallschirmjäger-Regiment 6 (6th Parachute Regiment) of the 2nd Parachute Division (Germany), 2nd Fallschirmjäger-Division. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Normandy landings. A 1,200-plane Airborne forces, airborne assault preceded an amphibious warfare, amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake a cross-channel invasion in 1944 was taken at the Washington Conference (1943), Trident Conference in Washington, D.C., Washington in May 1943. General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, which comprised all the land forces involved in the invasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panzergrenadier
''Panzergrenadier'' (), abbreviated as ''PzG'' (WWII) or ''PzGren'' (modern), meaning '' "Armour"-ed fighting vehicle "Grenadier"'', is a German term for mechanized infantry units of armoured forces who specialize in fighting from and in conjunction with infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) – that is, armoured troop carriers designed to carry a mechanized squad of six to eight soldiers into combat while providing direct fire support for those troops. Panzergrenadier combat is conducted in close cooperation with IFVs. Each Panzergrenadier squad has its own designated IFV during battle. Combat can be conducted either from within the vehicle (so-called ''"mounted combat"'') using portholes in the walls or hatches on the roof, etc, or from outside the vehicle in its vicinity (so-called ''"dismounted combat"'') using dismount-hatches at the back of the vehicle. Combat missions consist of ambushing, fire support, reconnaissance, spearhead attacks, etc. Depending on the armament, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibious Warfare
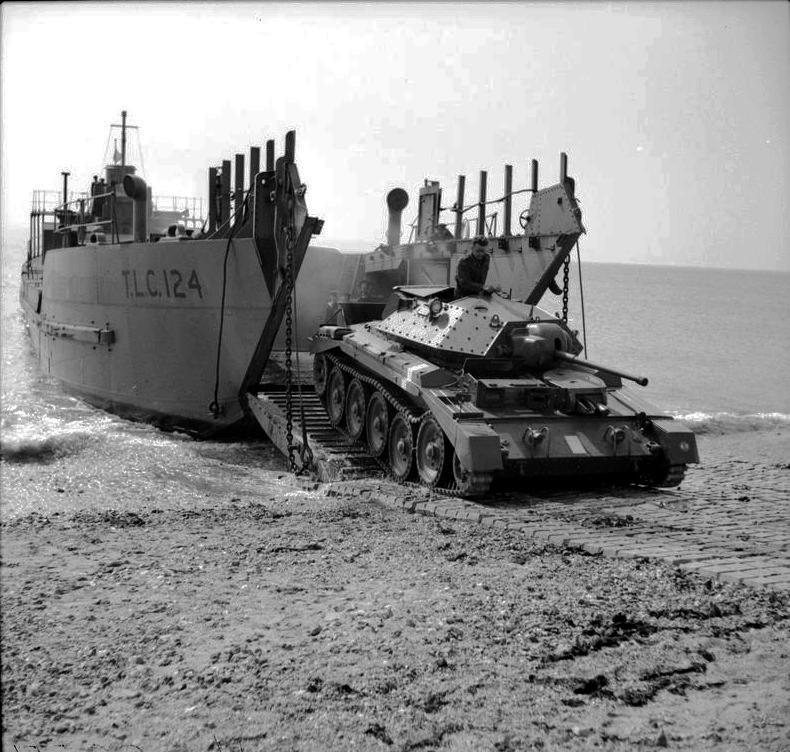
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted using ship's boats as the primary method of delivering troops to shore. Since the Gallipoli Campaign, specialised watercraft were increasingly designed for landing troops, material and vehicles, including by landing craft and for insertion of commandos, by fast patrol boats, zodiacs (rigid inflatable boats) and from mini-submersibles. The term ''amphibious'' first emerged in the United Kingdom and the United States during the 1930s with introduction of vehicles such as Vickers-Carden-Loyd Light Amphibious Tank or the Landing Vehicle Tracked.The first LVT prototypes were named ''Alligator'' and '' Crocodile'', though neither species is actual amphibian Amphibious warfare includes operations defined by their type, purpose, scale an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Airborne Landings In Normandy
The U.S. airborne landings in Normandy were the first U.S. combat operations during Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy by the Western Allies on June 6, 1944, during World War II. Around 13,100 American paratroopers of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Divisions made night parachute drops early on D-Day, June 6, followed by 3,937 glider troops flown in by day. Includes pathfinders. All statistics, except where otherwise noted, are derived from this source, which referenced Warren. As the opening maneuver of Operation Neptune (the assault operation for Overlord) the two American airborne divisions were delivered to the continent in two parachute and six glider missions. The divisions were part of the U.S. VII Corps and provided it with support in its mission of capturing Cherbourg as soon as possible to provide the Allies with a port of supply. The specific missions of the two airborne divisions were to block approaches into the vicinity of the amphibious landing at Utah Beac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China. Membership in the Allies varied during the course of the war. When the conflict broke out on 1 September 1939, the Allied coalition consisted of the United Kingdom, France, and Poland, as well as their respective dependencies, such as British India. They were soon joined by the independent dominions of the British Commonwealth: Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Consequently, the initial alliance resembled that of the First World War. As Axis forces began invading northern Europe and the Balkans, the Allies added the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Greece, and Yugoslavia. The Soviet Union, which initially had a nonaggression pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th SS Panzergrenadier Division Götz Von Berlichingen
The 17th SS Panzergrenadier Division "Götz von Berlichingen" (german: 17. SS-Panzergrenadier-Division "Götz von Berlichingen") was a German Waffen-SS division that saw action on the Western Front during World War II. Formation and training The division was raised near Poitiers, France, as the ''Panzer-Grenadier-Division "Götz von Berlichingen"'' in October 1943. It was formed from scratch, with the majority of its original cadre coming from replacement units and conscripts, many of whom were Romanian Germans and French volunteers. After September 8, 1943, around five hundred Italian volunteers, coming from units deployed in France were enlisted in "Götz von Berlichingen". The division was granted the honour-title ''Götz von Berlichingen''. Obersturmbannführer Otto Binge oversaw the formation of the division, with the newly promoted Brigadeführer Werner Ostendorff taking command in January 1944. The ''Götz von Berlichingen'' was placed under the LXXX Army Corps, a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotentin Peninsula
The Cotentin Peninsula (, ; nrf, Cotentîn ), also known as the Cherbourg Peninsula, is a peninsula in Normandy that forms part of the northwest coast of France. It extends north-westward into the English Channel, towards Great Britain. To its west lie the Gulf of Saint-Malo and the Channel Islands, and to the southwest lies the peninsula of Brittany. The peninsula lies wholly within the department of Manche, in the region of Normandy. Geography The Cotentin peninsula is part of the Armorican Massif (with the exception of the Plain lying in the Paris Basin) and lies between the estuary of the Vire river and Mont Saint-Michel Bay. It is divided into three areas: the headland of Cap de la Hague, the Cotentin Pass (the Plain), and the valley of the Saire River (Val de Saire). It forms the bulk of the department of Manche. Its southern part, known as "le Marais" (the Marshlands), crosses from east to west from just north west of Saint Lo and east of Lessay and marks a natural bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Army (United States)
First Army is the oldest and longest-established field army of the United States Army. It served as a theater army, having seen service in both World War I and World War II, and supplied the US army with soldiers and equipment during the Korean War and the Vietnam war under some of the most famous and distinguished officers of the U.S. Army. It now serves as a mobilization, readiness and training command. History Establishment and World War I The First Army was established on 10 August 1918 as a field army when sufficient American military manpower had arrived on the Western Front during the final months of World War I. The large number of troops assigned to the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) required the activation of subordinate commands. To fill this need, First Army was the first of three field armies established under the AEF. The first commander was General John J. Pershing, who also served as Commander-in-Chief (C-in-C) of the AEF. The headquarters planned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
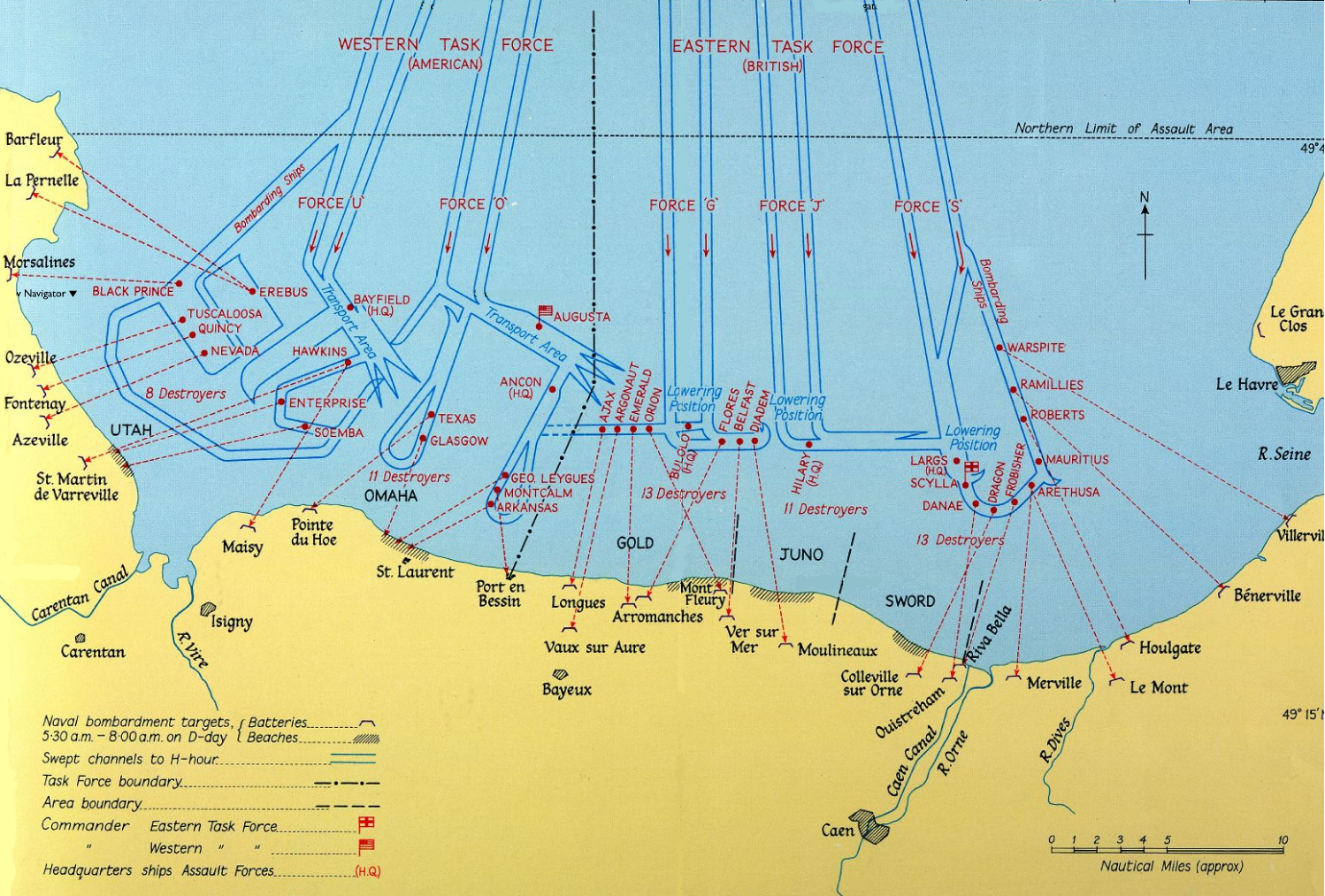
Omaha Beach
Omaha Beach was one of five beach landing sectors designated for the amphibious assault component of operation Overlord during the Second World War. On June 6, 1944, the Allies invaded German-occupied France with the Normandy landings. "Omaha" refers to an section of the coast of Normandy, France, facing the English Channel, from east of Sainte-Honorine-des-Pertes to west of Vierville-sur-Mer on the right bank of the Douve River estuary. Landings here were necessary to link the British landings to the east at Gold with the American landing to the west at Utah, thus providing a continuous lodgement on the Normandy coast of the Bay of the Seine. Taking Omaha was to be the responsibility of United States Army troops, with sea transport, mine sweeping, and a naval bombardment force provided predominantly by the United States Navy and Coast Guard, with contributions from the British, Canadian and Free French navies. The primary objective at Omaha was to secure a beachhead deep, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah Beach
Utah, commonly known as Utah Beach, was the code name for one of the five sectors of the Allied invasion of German-occupied France in the Normandy landings on June 6, 1944 (D-Day), during World War II. The westernmost of the five code-named landing beaches in Normandy, Utah is on the Cotentin Peninsula, west of the mouths of the Douve and Vire rivers. Amphibious landings at Utah were undertaken by United States Army troops, with sea transport, mine sweeping, and a naval bombardment force provided by the United States Navy and Coast Guard as well as elements from the British, Dutch and other Allied navies. The objective at Utah was to secure a beachhead on the Cotentin Peninsula, the location of important port facilities at Cherbourg. The amphibious assault, primarily by the US 4th Infantry Division and 70th Tank Battalion, was supported by airborne landings of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Division. The intention was to rapidly seal off the Cotentin Peninsula, prevent the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beachhead
A beachhead is a temporary line created when a military unit reaches a landing beach by sea and begins to defend the area as other reinforcements arrive. Once a large enough unit is assembled, the invading force can begin advancing inland. The term is sometimes used interchangeably (both correctly and incorrectly) with ''bridgehead'' and ''lodgement''. Beachheads were important in many military actions; examples include operations such as ''Operation Neptune'' during World War II, the Korean War (especially at Inchon), and the Vietnam War. Although many references state that ''Operation Neptune'' refers to the naval operations in support of ''Operation Overlord'', the most reliable references make it clear that ''Overlord'' referred to the establishment of a large-scale ''lodgement'' in Normandy, and that ''Neptune'' referred to the landing phase which created the beachhead; ''Neptune'' was therefore the first part of ''Overlord''. According to the D-Day Museum: Once an amph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close-cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |