|
Battle Of Polygon Wood
The Battle of Polygon Wood took place from 26 September to 3 October 1917, during the second phase of the Third Battle of Ypres in the First World War. The battle was fought near Ypres in Belgium, in the area from the Menin road to Polygon Wood and thence north, to the area beyond St Julien. Much of the woodland had been destroyed by the huge quantity of shellfire from both sides since 16 July and the area had changed hands several times. General Herbert Plumer continued the series of British general attacks with limited objectives. The attacks were led by lines of skirmishers, followed by small infantry columns organised in depth (a formation which had been adopted by the Fifth Army in August) with a vastly increased amount of artillery support, the infantry advancing behind five layers of creeping barrage on the Second Army front. The advance was planned to cover and stop on reverse slopes, which were easier to defend, enclosing ground which gave observation of German reinf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Passchendaele
The Third Battle of Ypres (german: link=no, Dritte Flandernschlacht; french: link=no, Troisième Bataille des Flandres; nl, Derde Slag om Ieper), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele (), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Allies at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere ( Koekelare). Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport ( Nieuwpoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
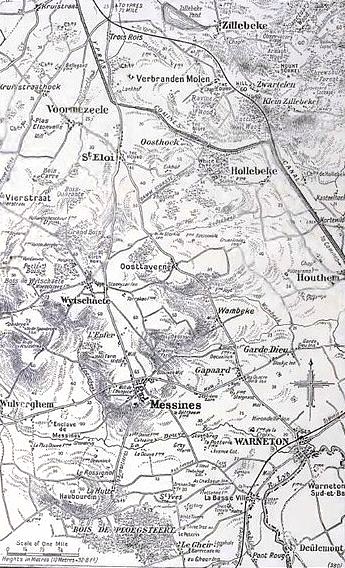
Battle Of Messines (1917)
The Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917) was an attack by the British Second Army (General Sir Herbert Plumer), on the Western Front, near the village of Messines (now Mesen) in West Flanders, Belgium, during the First World War. The Nivelle Offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more grandiose aims, had led to the demoralisation of French troops and confounded the Anglo-French strategy for 1917. The attack forced the Germans to move reserves to Flanders from the Arras and Aisne fronts, relieving pressure on the French. The British tactical objective was to capture the German defences on the ridge, which ran from Ploegsteert Wood (Plugstreet to the British) in the south, through Messines and Wytschaete to Mt Sorrel, depriving the German 4th Army of the high ground. The ridge gave commanding views of the British defences and back areas of Ypres to the north, from which the British intended to conduct the Northern Operation, an advance to Passchendaele Ridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 4
QF may stand for: * Qantas, an airline of Australia (IATA code QF) * Qatar Foundation, a private, chartered, non-profit organization in the state of Qatar * Quality factor, in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system * Quick-firing gun, a sort of artillery piece * Quiverfull, a movement of Christians who eschew all forms of birth control * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges (see British ordnance terms#QF) * Quds Force The Quds Force ( fa, نیروی قدس, niru-ye qods, Jerusalem Force) is one of five branches of Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) specializing in unconventional warfare and military intelligence operations. U.S. Army's Iraq War ... an expeditionary warfare unit of IRGC {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance QF 18-pounder
The Ordnance QF 18-pounder,British military traditionally denoted smaller ordnance by the weight of its standard projectile, in this case approximately or simply 18-pounder gun, was the standard British Empire field gun of the First World War-era. It formed the backbone of the Royal Field Artillery during the war, and was produced in large numbers. It was used by British Forces in all the main theatres, and by British troops in Russia in 1919. Its calibre (84 mm) and shell weight were greater than those of the equivalent field guns in French (75 mm) and German (77 mm) service. It was generally horse drawn until mechanisation in the 1930s. The first versions were introduced in 1904. Later versions remained in service with British forces until early 1942. During the interwar period, the 18-pounder was developed into the early versions of the equally famous Ordnance QF 25-pounder, which would form the basis of the British artillery forces during and after the Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Hush
Operation Hush was a British plan to make amphibious landings on the Belgian coast in 1917 during the First World War, supported by an attack from Nieuwpoort and the Yser bridgehead, positions which were a legacy of the Battle of the Yser in 1914. Several plans were considered in 1915 and 1916, then shelved due to operations elsewhere. Operation Hush was intended to begin when the Third Battle of Ypres, the main offensive at Ypres had advanced to Roulers, Koekelare and Thourout, linked by advances by the French and Belgian armies in between. (Operation Beach Party) was a German spoiling attack, conducted on 10 July by , in anticipation of an Allied coastal operation. The Germans used mustard gas for the first time, supported by a mass of heavy artillery, captured part of the bridgehead over the Yser and annihilated two British infantry battalions. After several postponements, Operation Hush was cancelled on 14 October 1917, as the advance at Ypres did not meet the objective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Hamilton-Gordon (British Army Officer, Born 1859)
Lieutenant General Sir Alexander Hamilton-Gordon KCB (6 July 1859 – 13 February 1939) was a British general during World War I. Early life Hamilton-Gordon was one of ten children of General Sir Alexander Hamilton-Gordon, K.C.B. and Caroline Herschel. His paternal grandfather was George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1852 until 1855. His maternal grandfather was John Herschel. Military career Educated at Winchester College, Hamilton-Gordon was commissioned into the Royal Artillery in 1880. His first military service was in the Second Anglo-Afghan War in 1880. Hamilton-Gordon later served in the Boer War taking part in actions at Ladysmith, Spion Kop, Vaal Kranz and Tugela Heights. He became Deputy Assistant Adjutant General for Intelligence in South Africa in early 1901. Arriving back in the United Kingdom, he briefly became an instructor at the School of Gunnery before he was appointed a Deputy Assistant Quarter-Master-Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IX Corps (United Kingdom)
IX Corps was a corps-sized formation of the British Army that existed during the First and the Second World Wars. First World War The IX Corps was originally formed in England in 1915 in readiness to make a new landing at Suvla during the Battle of Gallipoli. Headquarters was formed at the Tower of LondonBecke, pp. 185–91. Command of the corps was given to Lieutenant-General Sir Frederick Stopford. His handling of the corps during the August Offensive warranted his replacement after only 9 days with Lieutenant-General Julian Byng. During the Gallipoli campaign the corps comprised the following divisions: * 10th (Irish) Division * 11th (Northern) Division * 13th (Western) Division * 53rd (Welsh) Division * 54th (East Anglian) Division * 2nd Mounted Division * IX Corps Signals was provided by London District Signals, Royal Engineers Following the British evacuation of Gallipoli, the corps was moved to France in 1916, where it was commanded by Alexander Hamilton-Gordon unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aylmer Hunter-Weston
Lieutenant General Sir Aylmer Gould Hunter-Weston (23 September 1864 – 18 March 1940) was a British Army officer who served in World War I at Gallipoli in 1915 and in the very early stages of the Somme Offensive in 1916. He was also a Scottish Unionist MP. Nicknamed "Hunter-Bunter", Hunter-Weston has been seen as a classic example of a "donkey" general; he was described by his superior, Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig, as a "rank amateur", and has been referred to by one modern writer as "one of the Great War's spectacular incompetents". However, another historian writes that although his poor performance at the battles of Krithia earned his reputation "as one of the most brutal and incompetent commanders of the First World War" "in his later battles (at Gallipoli) he seemed to hit upon a formula for success ...(but) these small achievements were largely forgotten". Early life Hunter-Weston was born at Hunterston, West Kilbride, on 23 September 1864, the son of Lieutenant-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIII Corps (United Kingdom)
VIII Corps was a British Army corps formation that existed during the First and Second World Wars. In the latter, it took part in the Normandy Campaign in 1944, where it was involved in Operation Epsom and Operation Goodwood. It would later play a supporting role in Operation Market Garden and finish the war by advancing from the Rhine to the Baltic Sea. Prior to the First World War In 1876, a Mobilisation Scheme was published for the forces in Great Britain and Ireland, which included eight army corps of the 'Active Army'. The '8th Corps' was to be headquartered at Edinburgh and was primarily militia formation. In 1880, its order of battle was as follows: *1st Division (Edinburgh) **1st Brigade (Edinburgh) ***Kerry Militia (Tralee), Northumberland Militia (Alnwick), Fermanagh Militia (Enniskillen) **2nd Brigade ***Antrim Militia (Belfast), Cavan Militia (Cavan), Donegal Militia (Lifford) **Divisional Troops ***50th Foot (Edinburgh), Ayrshire Yeomanry (Ayr) **Artillery *** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Birdwood
Field Marshal William Riddell Birdwood, 1st Baron Birdwood, (13 September 1865 – 17 May 1951) was a British Army officer. He saw active service in the Second Boer War on the staff of Lord Kitchener. He saw action again in the First World War as Commander of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during the Gallipoli Campaign in 1915, leading the landings on the peninsula and then the evacuation later in the year, before becoming commander-in-chief of the Fifth Army on the Western Front during the closing stages of the war. He went on to be general officer commanding the Northern Army in India in 1920 and Commander-in-Chief, India, in 1925. Early life William Riddell Birdwood was born on 13 September 1865 in Kirkee, India. His father, Herbert Mills Birdwood, born in Bombay and educated in the UK, had returned to India in 1859 after passing the Indian Civil Service examination. In 1861, Herbert Birdwood married Edith Marion Sidonie, the eldest daughter of Surgeon-Major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I Anzac Corps
The I ANZAC Corps (First Anzac Corps) was a combined Australian and New Zealand army corps that served during World War I. It was formed in Egypt in February 1916 as part of the reorganisation and expansion of the Australian Imperial Force and the New Zealand Expeditionary Force (NZEF) following the evacuation of Gallipoli in December 1915. Along with the II ANZAC Corps, it replaced the original Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC). The corps initially participated in the defence of the Suez Canal before being transferred to the Western Front in France and Belgium in late March 1916. Later in 1916 the New Zealand Division was removed from I ANZAC's order of battle, swapping with II ANZAC's Australian 4th Division. In November 1917, I ANZAC ceased to exist when the Australian infantry divisions in France were grouped together as the Australian Corps and the New Zealand Division, then part of II ANZAC Corps, was allocated to a British corps. History Formation Follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Army (United Kingdom)
The British Second Army was a field army active during the First and Second World Wars. During the First World War the army was active on the Western Front throughout most of the war and later active in Italy. During the Second World War the army was the main British contribution to the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944 and advance across Europe. First World War The Second Army was part of the British Army formed on 26 December 1914, when the British Expeditionary Force was split in two due to becoming too big to control its subordinate formations. The army controlled both III Corps and IV Corps. Second Army spent most of the war positioned around the Ypres salient, but was redeployed to Italy as part of the Italian Expeditionary Force between November 1917 and March 1918. In 1919 it was reconstituted as the British Army of the Rhine.Edmonds (1987) Commanders * 1914–1915 General Sir Horace Smith-Dorrien * 1915–1917 General Sir Herbert Plumer * 1917–1918 General Sir Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)