|
Bare Machine Computing
Bare Machine Computing (BMC) is a computer architecture based on bare machines. In the BMC paradigm, applications run without the support of any operating system (OS) or centralized kernel i.e., no intermediary software is loaded on the bare machine prior to running applications. The applications, which are called bare machine applications or simply BMC applications, do not use any persistent storage or a hard disk, and instead are stored on detachable mass storage such as a USB flash drive. A BMC program consists of a single application or a small set of applications (application suite) that runs as a single executable within one address space. BMC applications have direct access to the necessary hardware resources. They are self-contained, self-managed and self-controlled entities that boot, load and run without using any other software components or external software. BMC applications have inherent security due to their design. There are no OS-related vulnerabilities, and each ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bare Machine
In information technology, bare machine (or bare-metal computer) is a computer which has no operating system. The software executed by a bare machine, commonly called a "bare metal program" or "bare metal application", is designed to interact directly with hardware. Bare machines are widely used in embedded systems, particularly in cases where resources are limited or high performance is required. Advantages Typically, a bare-metal application will run faster, use less memory and be more power efficient than an equivalent program that relies on an operating system, due to the inherent overhead imposed by system calls. For example, hardware inputs and outputs are directly accessible to bare metal software, whereas they must be accessed through system calls when using an OS. Disadvantages Bare metal applications typically require more effort to develop because operating system services such as memory management and task scheduling are not available. Debugging a bare-metal pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
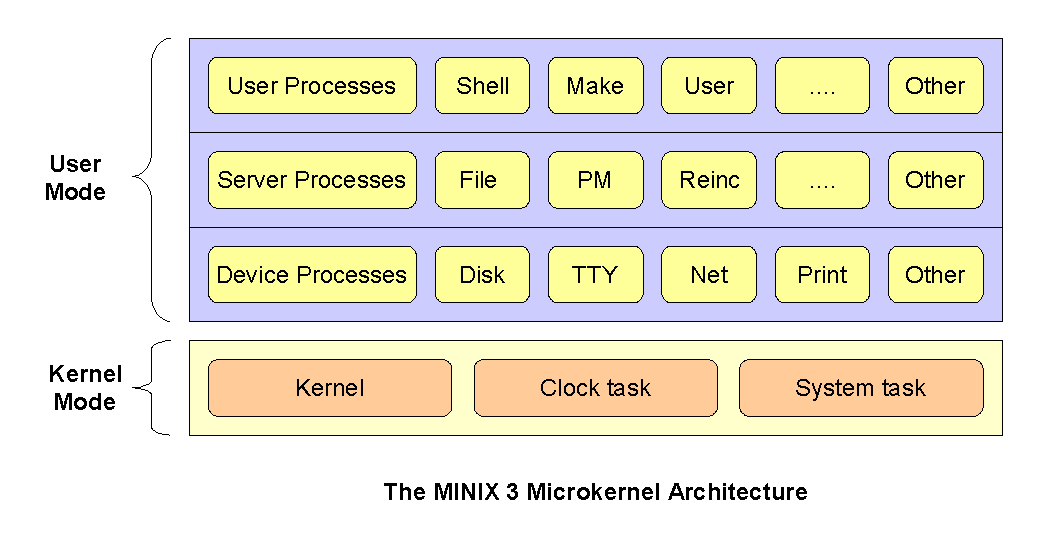
Microkernel
In computer science, a microkernel (often abbreviated as μ-kernel) is the near-minimum amount of software that can provide the mechanisms needed to implement an operating system (OS). These mechanisms include low-level address space management, thread (computing), thread management, and inter-process communication (IPC). If the hardware provides multiple Protection ring, rings or CPU modes, the microkernel may be the only software executing at the most privileged level, which is generally referred to as kernel mode, supervisor or kernel mode. Traditional operating system functions, such as device drivers, protocol stacks and file systems, are typically removed from the microkernel itself and are instead run in user space. In terms of the source code size, microkernels are often smaller than monolithic kernels. The MINIX 3 microkernel, for example, has only approximately 12,000 lines of code. History Microkernels trace their roots back to Danish computer pioneer Per Brinch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exokernel
Exokernel is an operating system kernel developed by the MIT Parallel and Distributed Operating Systems group, and also a class of similar operating systems. Operating systems generally present hardware resources to applications through high-level abstractions such as (virtual) file systems. The idea behind exokernels is to force as few abstractions as possible on application developers, enabling them to make as many decisions as possible about hardware abstractions. Exokernels are tiny, since functionality is limited to ensuring protection and multiplexing In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource� ... of resources, which is considerably simpler than conventional microkernels' implementation of message passing and monolithic kernels' implementation of high-level abstractions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TinyOS
TinyOS is an embedded, component-based operating system and platform for low-power wireless devices, such as those used in wireless sensor networks (WSNs), smartdust, ubiquitous computing, personal area networks, building automation, and smart meters. It is written in the programming language A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ... nesC, as a set of cooperating tasks and processes. It began as a collaboration between the University of California, Berkeley, Intel Research, and Crossbow Technology, was released as free and open-source software under a BSD licenses, BSD license, and has since grown into an international consortium, the TinyOS Alliance. TinyOS has been used in space, being implemented in ESTCube-1. Implementation TinyOS applications are written in the prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Type-III Library
The IBM Type-III Library (also: Type-III software, Type-III product) was software provided by IBM to its customers, available without charge, liability, or support, and typically (perhaps always) in source-code format. The best known examples are for mainframe software, but IBM also used this same classification on smaller systems. IBM also distributed other systems in source code form. Most early operating systems were shipped in this way. Source distribution of the VM family of operating systems continued for several decades after it supplanted CP/CMS from the Type-III Library, and TPF was always distributed in source form, apparently continued today with z/TPF. Unlike Type-III software, such systems ''were'' supported by IBM. Scope of the IBM Program Libraries During the mainframe era, IBM made a wide variety of programs available to its customers. Programs were offered in two broad categories. The first category of programs were IBM developed and supported. These were terme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded Systems
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System On A Chip
A system on a chip (SoC) is an integrated circuit that combines most or all key components of a computer or Electronics, electronic system onto a single microchip. Typically, an SoC includes a central processing unit (CPU) with computer memory, memory, input/output, and computer data storage#Secondary storage, data storage control functions, along with optional features like a graphics processing unit (GPU), Wi-Fi connectivity, and radio frequency processing. This high level of integration minimizes the need for separate, discrete components, thereby enhancing Performance per watt, power efficiency and simplifying device design. High-performance SoCs are often paired with dedicated memory, such as LPDDR, and flash storage chips, such as Universal Flash Storage, eUFS or eMMC, which may be stacked directly on top of the SoC in a Package on a package, package-on-package (PoP) configuration or placed nearby on the motherboard. Some SoCs also operate alongside specialized chips, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Bonding
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods. Link aggregation increases total throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and provides redundancy where all but one of the physical links may fail without losing connectivity. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports. Other umbrella terms used to describe the concept include trunking, bundling, bonding, channeling or teaming. Implementation may follow vendor-independent standards such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet, defined in IEEE 802.1AX or the previous IEEE 802.3ad, but also proprietary protocols. Motivation Link aggregation increases the bandwidth and resilience of Ethernet connections. Bandwidth requirements do not scale linearly. Ethernet bandwidths historically have increased tenfold each generation: , , , . If one started to bump into bandwidth c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |