|
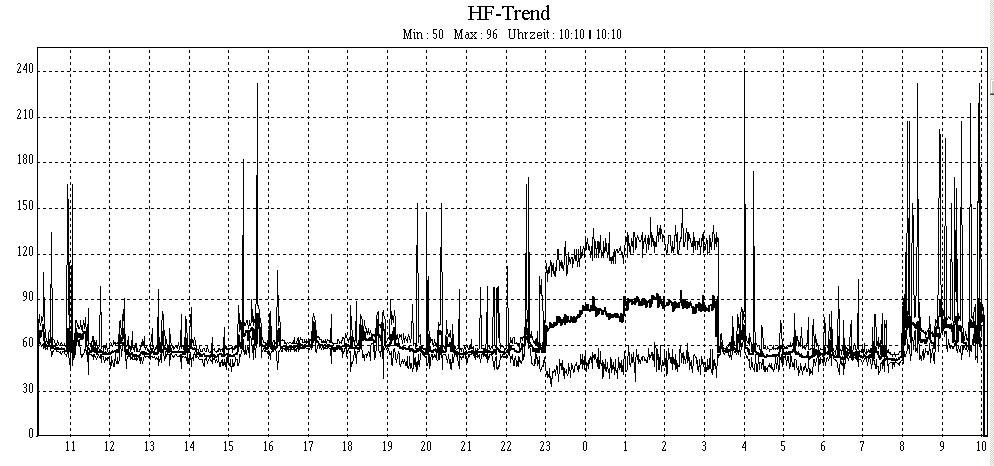
Ballistocardiography
The ballistocardiograph (BCG) is a measure of ballistic forces generated by the heart. The downward movement of blood through the descending aorta produces an upward recoil, moving the body upward with each heartbeat. As different parts of the aorta expand and contract, the body continues to move downward and upward in a repeating pattern. Ballistocardiography is a technique for producing a graphical representation of repetitive motions of the human body arising from the sudden ejection of blood into the great vessels with each heart beat. It is a vital sign in the 1–20 Hz frequency range which is caused by the mechanical movement of the heart and can be recorded by noninvasive methods from the surface of the body. It was shown for the first time, after an extensive research work by Dr. Isaac Starr, that the effect of main heart malfunctions can be identified by observing and analyzing the BCG signal. Recent work also validates BCG could be monitored using camera in a non-cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Starr
Isaac "Jack" Starr (March 6, 1895 – June 22, 1989), known as the father of ballistocardiography, was an American physician, heart disease specialist, and clinical epidemiologist notable for developing the first practical ballistocardiograph. His early academic positions included being an assistant professor in pharmacology and later the first Hartzell Professor of Research Therapeutics at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania as well as dean of the school from 1945 to 1948. Education Starr attended primary and secondary school in Philadelphia, graduating from the Chestnut Hill Academy in 1912. From there he went to Princeton University where he received his Bachelor of Science degree, graduating ''magna cum laude'' in 1916. He received his Doctor of Medicine degree from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in 1920. After receiving his M.D., Starr went to Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston where he completed his int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistics
Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially ranged weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets or the like; the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance. A ballistic body is a free-moving body with momentum which can be subject to forces such as the forces exerted by pressurized gases from a gun barrel or a propelling nozzle, normal force by rifling, and gravity and air drag during flight. A ballistic missile is a missile that is guided only during the relatively brief initial phase of powered flight and the trajectory is subsequently governed by the laws of classical mechanics; in contrast to (for example) a cruise missile which is aerodynamically guided in powered flight like a fixed-wing aircraft. History and prehistory The earliest known ballistic projectiles were stones and spears, and the throwing stick. The oldes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possibly defibrillation are needed until further treatment can be provided. Cardiac arrest results in a rapid loss of consciousness, and breathing may be abnormal or absent. While cardiac arrest may be caused by heart attack or heart failure, these are not the same, and in 15 to 25% of cases, there is a non-cardiac cause. Some individuals may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, an elevated heart rate, and a light-headed feeling immediately before entering cardiac arrest. The most common cause of cardiac arrest is an underlying heart problem like coronary artery disease that decreases the amount of oxygenated blood supplying the heart muscle. This, in turn, damages the structure of the muscle, which can alter its function. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Tests
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, the most common of which are diagnosis, screening and evaluation. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Testing Equipment
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCP-ECG
SCP-ECG, which stands for ''Standard communications protocol for computer assisted electrocardiography'', is a standard for ECG traces, annotations, and metadata, that specifies the interchange format and a messaging procedure for ECG cart-to-host communication and for retrieval of SCP-ECG records from the host to the ECG cart. It is defined in the joint ANSI/AAMI standard EC71:2001 and in the CEN standard EN 1064:2005. History The SCP Standard was first developed between 1989 and 1991 during a European AIM R&D project. Other ECG data formats DICOM, HL7 aECG, MFER (ISO 22077) References External links * OpenECG Software Tools Repository(WebArchive)'' — ThOpenECGGroup supports SCP-ECG by providing and supporting open source Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized sof ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holter Monitor
In medicine, a Holter monitor (often simply Holter) is a type of ambulatory electrocardiography device, a portable device for cardiac monitoring (the monitoring of the electrical activity of the cardiovascular system) for at least 24 hours. The Holter's most common use is for monitoring ECG heart activity (electrocardiography or ECG). Its extended recording period is sometimes useful for observing occasional cardiac arrhythmias which would be difficult to identify in a shorter period. For patients having more transient symptoms, a cardiac event monitor which can be worn for a month or more can be used. The Holter monitor was developed at the Holter Research Laboratory in Helena, Montana, US by experimental physicists Norman J. Holter and Bill Glasscock, who started work on radio telemetry in 1949. Inspired by a suggestion from cardiologist Paul Dudley White in the early 1950s, they redirected their efforts toward development of a wearable cardiac monitoring device. The Holter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate Monitor
A heart rate monitor (HRM) is a personal monitoring device that allows one to measure/display heart rate in real time or record the heart rate for later study. It is largely used to gather heart rate data while performing various types of physical exercise. Measuring electrical heart information is referred to as electrocardiography (ECG or EKG). Medical heart rate monitoring used in hospitals is usually wired and usually multiple sensors are used. Portable medical units are referred to as a Holter monitor. Consumer heart rate monitors are designed for everyday use and do not use wires to connect. History Early models consisted of a monitoring box with a set of electrode leads which attached to the chest. The first wireless EKG heart rate monitor was invented in 1977 by Polar Electro as a training aid for the Finnish National Cross Country Ski team. As "intensity training" became a popular concept in athletic circles in the mid-80s, retail sales of wireless personal heart mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Monitoring
Cardiac monitoring generally refers to continuous or intermittent monitoring of heart activity to assess a patient's condition relative to their cardiac rhythm. Cardiac monitoring is usually carried out using electrocardiography, which is a noninvasive process that records the heart's electrical activity and displays it in an electrocardiogram. It is different from hemodynamic monitoring, which monitors the pressure and flow of blood within the cardiovascular system. The two may be performed simultaneously on critical heart patients. Cardiac monitoring for ambulatory patients (those well enough to walk around) is known as ambulatory electrocardiography and uses a small, wearable device, such as a Holter monitor, wireless ambulatory ECG, or an implantable loop recorder. Data from a cardiac monitor can be transmitted to a distant monitoring station in a process known as telemetry or biotelemetry. Cardiac monitoring in an emergency department setting focuses primarily on the monitori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EKG Tech
Cardiovascular technologists (also known as a cardiovascular technicians or vascular technicians) are health professionals that deal with the circulatory system. Cardiac sonographer Technologists who use ultrasound to examine the heart chambers, valves, and vessels are referred to as cardiac sonographers. They use ultrasound instrumentation to create images called echocardiograms. An echocardiogram may be performed while the patient is either resting or physically active. Technologists may administer medication to physically active patients to assess their heart function. Cardiac sonographers also may assist physicians who perform transesophageal echocardiography, which involves placing a tube in the patient's esophagus to obtain ultrasound images. Vascular technologist Those who assist physicians in the diagnosis of disorders affecting the circulation are known as vascular technologists, vascular specialists or vascular sonographers. They obtain a medical history, evaluate p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, called systole. After emptying, the heart immediately relaxes and expands to receive another influx of blood returning from the lungs and other systems of the body, before again contracting to pump blood to the lungs and those systems. A normally performing heart must be fully expanded before it can efficiently pump again. Assuming a healthy heart and a typical rate of 70 to 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle, or heartbeat, takes about 0.8 second to complete the cycle. There are two atrial and two ventricle chambers of the heart; they are paired as the left heart and the right heart—that is, the left atrium with the left ventricle, the right atrium with the right ventricle—and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |