|
Balancing And Deranking
In linguistics, balancing and deranking are terms used to describe the form of verbs used in various types of subordinate clauses and also sometimes in co-ordinate constructions. * A verb form is said to be balanced if it is identical to forms used in independent declarative clauses * A subordinate verb form is said to be deranked if it cannot be used in independent declarative clauses Deranked verb forms Verb forms that occur in subordinate clauses of various languages that cannot occur in independent clauses are of various types, but there do exist some typical patterns that differentiate these forms from main-clause verb forms in the same language. # There are verb forms that possess the same type of person and tense marking as the verb forms used in independent declarative clauses, but differ in mood. Typical examples include such forms as subjunctives and irrealis moods. In the Eskimo–Aleut languages, there are special "dependent moods" used only in subordinate clauses. # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salishan Languages
The Salishan (also Salish) languages are a family of languages of the Pacific Northwest in North America (the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana). They are characterised by agglutinativity and syllabic consonants. For instance the Nuxalk word ''clhp’xwlhtlhplhhskwts’'' (), meaning "he had had n his possessiona bunchberry plant", has thirteen obstruent consonants in a row with no phonetic or phonemic vowels. The Salishan languages are a geographically contiguous block, with the exception of the Nuxalk (Bella Coola), in the Central Coast of British Columbia, and the extinct Tillamook language, to the south on the central coast of Oregon. The terms ''Salish'' and ''Salishan'' are used interchangeably by linguists and anthropologists studying Salishan, but this is confusing in regular English usage. The name ''Salish'' or ''Selisch'' is the endonym of the Flathead Nation. Linguists later applied the name S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Clause
In linguistics, a small clause consists of a subject and its predicate, but lacks an overt expression of tense. Small clauses have the semantic subject-predicate characteristics of a clause, and have some, but not all, the properties of a constituent. Structural analyses of small clauses vary according to whether a flat or layered analysis is pursued. The small clause is related to the phenomena of raising-to-object, exceptional case-marking, accusativus cum infinitivo, and object control. History The two main analyses of small clauses originate with Edwin Williams (1975, 1980) and Timothy Stowell (1981). Williams' analysis follows the Theory of Predication, where the "subject" is the "external argument of a maximal projection". In contrast, Stowell's theory follows the Theory of Small Clauses, supported by linguists such as Chomsky, Aarts, and Kitagawa. This theory uses X-bar theory to treat small clauses as constituents. Linguists debate which analysis to pursue, as there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergative Case
In grammar, the ergative case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that identifies the noun as the agent of a transitive verb in ergative–absolutive languages. Characteristics In such languages, the ergative case is typically marked (most salient), while the absolutive case is unmarked. Recent work in case theory has vigorously supported the idea that the ergative case identifies the agent (the intentful performer of an action) of a verb (Woolford 2004). In Kalaallisut (Greenlandic) for example, the ergative case is used to mark subjects of transitive verbs and possessors of nouns. This syncretism with the genitive is commonly referred to as the ''relative'' case. Nez Perce has a three-way nominal case system with both ergative (''-nim'') and accusative (''-ne'') plus an absolute (unmarked) case for intransitive subjects: ''hipáayna qíiwn'' ‘the old man arrived’; ''hipáayna wewúkiye'' ‘the elk arrived’; ''wewúkiyene péexne qíiwnim'' ‘the old man saw an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accusative Case
The accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb. In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: 'me,' 'him,' 'her,' 'us,' and ‘them’. The spelling of those words will change depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example, the pronoun ''they'', as the subject of a sentence, is in the nominative case ("They wrote a book"); but if the pronoun is instead the object, it is in the accusative case and ''they'' becomes ''them'' ("The book was written by them"). The accusative case is used in many languages for the objects of (some or all) prepositions. It is usually combined with the nominative case (for example in Latin). The English term, "accusative", derives from the Latin , which, in turn, is a translation of the Greek . The word may also mean "causative", and this may have been the Greeks' intention in this name, but the sense of the Roman translation has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Clause
A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phraseRodney D. Huddleston, Geoffrey K. Pullum, ''A Student's Introduction to English Grammar'', CUP 2005, p. 183ff. and uses some grammatical device to indicate that one of the arguments in the relative clause refers to the noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence ''I met a man who wasn't too sure of himself'', the Dependent clause, subordinate clause ''who wasn't too sure of himself'' is a relative clause since it modifies the noun ''man'' and uses the pronoun ''who'' to indicate that the same "man" is referred to in the subordinate clause (in this case as its subject (grammar), subject). In many European languages, relative clauses are introduced by a special class of pronouns called ''relative pronouns'', such as ''who'' in the example just given. In other languages, relative clauses may be marked in different ways: they may be introduced by a special class of conjunctions called ''relativizers'', the main verb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolutive Case
In grammar, the absolutive case (abbreviated ) is the case of nouns in ergative–absolutive languages that would generally be the subjects of intransitive verbs or the objects of transitive verbs in the translational equivalents of nominative–accusative languages such as English. In ergative–absolutive languages In languages with ergative–absolutive alignment, the absolutive is the case used to mark both the subject of an intransitive verb and the object of a transitive verb in addition to being used for the citation form of a noun. It contrasts with the marked ergative case, which marks the subject of a transitive verb. For example, in Basque the noun ''mutil'' ("boy") takes the bare singular article ''-a'' both as the subject of the intransitive clause ''mutila etorri da'' ("the boy came") and as the object of the transitive clause ''Irakasleak mutila ikusi du'' ("the teacher has seen the boy") in which the subject bears the ergative ending ''-a-k''. In very few cases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Case
In grammar, the nominative case (abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of English) the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''cāsus nominātīvus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ὀνομαστικὴ πτῶσις, ''onomastikḗ ptôsis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onomázō'' "call by name", from ''ónoma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orthḗ'' or ''eutheîa'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''least marked'') of ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
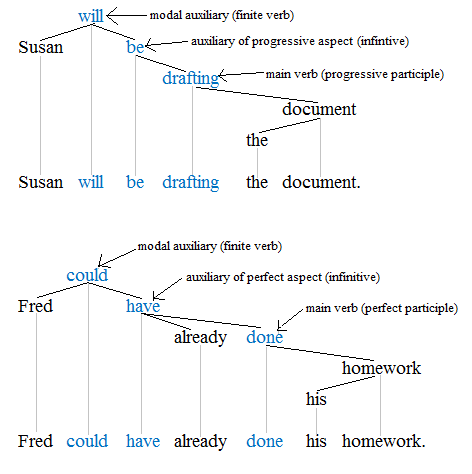
Modal Verb
A modal verb is a type of verb that contextually indicates a modality such as a ''likelihood'', ''ability'', ''permission'', ''request'', ''capacity'', ''suggestion'', ''order'', ''obligation'', or ''advice''. Modal verbs generally accompany the base (infinitive) form of another verb having semantic content. In English, the modal verbs commonly used are ''can'', ''could'', ''may'', ''might'', ''shall'', ''should'', ''will'', ''would'', ''ought to'', ''used to'', ''dare'' and ''must.'' Function A modal auxiliary verb gives information about the function of the main verb that it governs. Modals have a wide variety of communicative functions, but these functions can generally be related to a scale ranging from possibility ("may") to necessity ("must"), in terms of one of the following types of modality: *epistemic modality, concerned with the theoretical ''possibility of propositions being true or not true'' (including likelihood and certainty) *deontic modality, concerned with ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakota Language
Lakota ( ), also referred to as Lakhota, Teton or Teton Sioux, is a Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. Lakota is mutually intelligible with the two dialects of the Dakota language, especially Western Dakota, and is one of the three major varieties of the Sioux language. Speakers of the Lakota language make up one of the largest Native American language speech communities in the United States, with approximately 2,000 speakers, who live mostly in the northern plains states of North Dakota and South Dakota. Many communities have immersion programs for both children and adults. The language was first put into written form by European-American missionaries around 1840. The orthography has since evolved to reflect contemporary needs and usage. History and origin The Lakota people's creation stories say that language originated from the creation of the tribe. Other creation stories say language was invented by Iktomi. Phonology Vowels Lakota has fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu Language
Ainu (, ), or more precisely Hokkaido Ainu, is a language spoken by a few elderly members of the Ainu people on the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido. It is a member of the Ainu language family, itself considered a language family isolate with no academic consensus of origin. It is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger. Until the 20th century, the Ainu languages – Hokkaido Ainu and the now-extinct Kuril Ainu and Sakhalin Ainu – were spoken throughout Hokkaido, the southern half of the island of Sakhalin and by small numbers of people in the Kuril Islands. Due to the colonization policy employed by the Japanese government, the number of Hokkaido Ainu speakers decreased through the 20th century, and it is now moribund. A very few elderly people still speak the language fluently, though attempts are being made to revive it. According to P. Elmer, the Ainu languages are a contact language, having strong influences from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
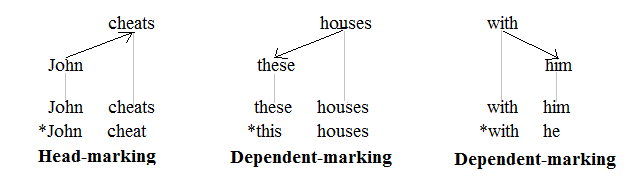
Head-marking Language
A language is head-marking if the grammatical marks showing agreement between different words of a phrase tend to be placed on the heads (or nuclei) of phrases, rather than on the modifiers or dependents. Many languages employ both head-marking and dependent-marking, and some languages double up and are thus double-marking. The concept of head/dependent-marking was proposed by Johanna Nichols in 1986 and has come to be widely used as a basic category in linguistic typology. In English The concepts of head-marking and dependent-marking are commonly applied to languages that have richer inflectional morphology than English. There are, however, a few types of agreement in English that can be used to illustrate these notions. The following graphic representations of a clause, a noun phrase, and a prepositional phrase involve agreement. The three tree structures shown are those of a dependency grammar (as opposed to those of a phrase structure grammar): :: Heads and dependents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |