|
Baháʼí Faith In The Marshall Islands
The Baháʼí Faith in the Marshall Islands begins after 1916 with a mention by ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, then head of the religion, that Baháʼís should take the religion there. The first Baháʼí to pioneer there arrived in August 1954 however she could only stay until March 1955. Nevertheless, with successive pioneers and converts the first Baháʼí Local Spiritual Assembly in 1967 in Majuro. The community continued to grow and in 1977 elected its first National Spiritual Assembly. Before 1992 the Baháʼís began to operate state schools under contract with the government. Middle estimates of the Baháʼí population are just over 1,000, or 1.50% in 2000. Early days ʻAbdu'l-Bahá's Tablets of the Divine Plan ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, head of the Bahá’í Faith from 1892 to 1921, mentioned the Marshall Islands among the places Baháʼís should take the religion to. He wrote a series of letters, or Tablets, to the followers of the religion in the United States in 1916–1917; these l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Of Baháʼu'lláh
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Greek '' hippeis'' and ''hoplite'' (ἱππεῖς) and Roman ''eques'' and ''centurion'' of classical antiquity. In the Early Middle Ages in Europe, knighthood was conferred upon mounted warriors. During the High Middle Ages, knighthood was considered a class of lower nobility. By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior. Often, a knight was a vassal who served as an elite fighter or a bodyguard for a lord, with payment in the form of land holdings. The lords trusted the knights, who were skilled in battle on horseback. Knighthood in the Middle Ages was closely linked with horsemanship (and especially the joust) from its origins in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lae Atoll
Lae Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 20 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is only , but it encloses a lagoon with an area of . It is located approximately east of Ujae Atoll. The population of Lae Atoll was 347 in 2011. Its islands include Lae, Looj (Lotj), Bilalalon, Riblong (Ribon) and Lweijab (Lejab). History In early 1884, Japanese explorer and agent Suzuki Tsunenori was dispatched to Lae Atoll to investigate the murder of a Japanese sailor. When he arrived, he raised the national flag and claimed the island for Japan. However, he was ordered to return to the island to take down the flag, and the government made no formal gestures towards annexation of the islands. Lae Atoll was claimed by the Empire of Germany along with the rest of the Marshall Islands later that year, and the Germans established a trading outpost. After World War I, the island came under the South Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mili Atoll
Mili Atoll (Marshallese language, Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 92 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. It is located approximately southeast of Arno Atoll, Arno. Its total land area is making it the second largest of the Marshall Islands after Kwajalein. It encloses a much smaller lagoon than Kwajalein, with an area of . The atoll is separated by a Channel (geography), water channel called the Klee Passage from the Knox Atoll which is considerably smaller. The population of Mili Atoll was 738 as of 2011. The main village is also called Mili. Other villages include Nallu, Enejet, Lukonor, Tokewa, and Wau, Mili. Nallu, Enejet and Lukonwor are only accessible from Mili by land during lowtide. Only Mili and Enejet have runways for small aircraft. Mili Airport and Enejit Airport are served by Air Marshall Islands when its aircraft are operational. History The British merchant vessel ''Rolla (1800 ship), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujelang Atoll
Ujelang Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 30 islands in the Pacific Ocean, in the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is , and it encloses a lagoon of . It is the westernmost island in the Marshall Islands, approximately southeast of Enewetak, and approximately west of the main Ralik Chain. History Ujelang's first European visitor was Álvaro de Saavedra on 21 September 1529 shortly before his death, in his second attempt to return from Tidore to New Spain. Sighting of Ujelang was again recorded by the Spanish expeditions of Ruy López de Villalobos on 6 January 1543; of Miguel López de Legazpi on 15 January 1565; and by the mutineers of the ''San Jeronimo'' led by the pilot Lope Martín in 1566. In 1811, the British merchant vessel ''Providence'' rediscovered the Atoll, and named Ujelang Island Providence Island.Levesque & Leresque (2001), p.85. ''Providence'' had transported convicts from Britain to New South Wales and was on her way to China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baháʼí Administration
The Baháʼí administration or Baháʼí administrative order is the administrative system of the Baháʼí Faith. It has two arms, the #Elected institutions, elected and the #Appointed institutions, appointed. The supreme governing institution of the Baháʼí Faith is the Universal House of Justice, situated in Haifa, Israel. Some features set apart the Baháʼí administration from similar systems of human government: elected representatives should follow their conscience, rather than being responsible to the views of electors; political campaigning, nominations and parties are prohibited; and religious authority was passed down from its founder to the Universal House of Justice. The Baháʼí administration has four charter documents, the Kitáb-i-Aqdas, the Tablets of the Divine Plan, the Tablets of Baháʼu'lláh#Lawh-i-Karmil (Tablet of Carmel), Tablet of Carmel and the Will and Testament of ʻAbdu'l-Bahá. Character of Baháʼí administration Shoghi Effendi wrote tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebeye Island
Ebeye ( ; Marshallese: , or in older orthography, ; locally, , , after the English pronunciation) is the most populous island of Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands, as well as the center for Marshallese culture in the Ralik Chain of the archipelago. Settled on of land, it has a population of more than 15,000. Over 50% of the population is estimated to be under the age of 18. History Etymology When Christian missionaries first arrived in the Marshall Islands, they introduced Latin script writing and orthographized the Marshallese language. Originally, Ebeye was written ''Ebeje'' by Europeans (' in modern orthography, pronounced ), which (according to elders of the atoll) means "making something out of nothing." However, the colonial German administration mispronounced the J as if it were German language , and foreign observers recorded the resulting pronunciation as ''Ebeye''. During the Japanese period, though, the island's pronunciation in katakana, , re-approximated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwajalein Atoll
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilian personnel) often use the shortened name, Kwaj . The total land area of the atoll amounts to just over . It lies in the Ralik Chain, southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii. The US Navy has hosted a naval base on Kwajalein Island since World War II. It was the final resting place of the German cruiser '' Prinz Eugen'' after it survived the Operation Crossroads nuclear test in 1946. In the late 1950s, the US Army took over the base as part of their Nike Zeus anti-ballistic missile efforts, and since then the atoll has been widely used for missile tests of all sorts. Today it is part of the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site, with various radars, tracking cameras, missile launchers, and many support systems spread across many islands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pohnpei
Pohnpei "upon (''pohn'') a stone altar (''pei'')" (formerly known as Ponape or Ascension, Proto-Chuukic-Pohnpeic: ''*Fawo ni pei)'' is an island of the Senyavin Islands which are part of the larger Caroline Islands group. It belongs to Pohnpei State, one of the four states in the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). Major population centers on Pohnpei include Palikir, the FSM's capital, and Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State. Pohnpei Island is the largest with an area of , and a highest point of , the most populous with 36,832 people, and the most developed single island in the FSM. Pohnpei is home to the megaliths and ruined city of Nan Madol, built of artificial islands off the island's eastern shore beginning in the 8th or 9th century. An important archaeological site, it was declared a national historic site in 1985. Pohnpei contains a wealth of biodiversity. It is one of the wettest places on Earth with annual recorded rainfall exceeding each year in certain mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
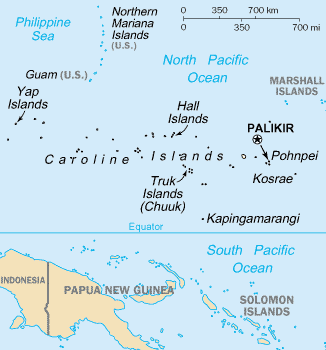
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the central and eastern parts of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end. Historically, this area was also called ''Nuevas Filipinas'' or New Philippines, because they were part of the Spanish East Indies and were governed from Manila in the Philippines. The Carolines are scattered across a distance of approximately 3,540 kilometers (2,200 miles), from the westernmost island, Tobi (island), Tobi, in Palau, to the easternmost island, Kosrae, a Administrative divisions of the Federated States of Micronesia, state of the FSM. Description The group consists of about 500 small coral islands, east of the Philippines, in the Pacific Ocean. The distance from Yap (one of the larger Caroline islands) to Manila is . Most of the islands are made up of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace Holley (Baháʼí)
Horace Holley (April 7, 1887 in Torrington, Connecticut – July 12, 1960 in Haifa, Israel) was a prominent follower of the Baháʼí Faith, having been elected to several Spiritual Assemblies, appointed by Shoghi Effendi in 1951 as a Hand of the Cause, and later elected as one of the nine Custodians who stewarded the religion from 1957–1963. Holley was born in Torrington, Connecticut in 1887. He was introduced to the Baháʼí Faith in 1909, and later served as a member and secretary to the Spiritual Assembly of the Baha'is of the United States and Canada, first being elected in 1923. He also became editor of ''World Unity Magazine''. He was elected by his fellow Hands of the Cause as a Custodian in 1959. This being announced on Christmas Day of 1959 in the New York Times: The National Spiritual Assembly of the Bahais announced today that Horace Holley had resigned as secretary as the chief steward of the faith at international headquarters in Haifa, Israel.'' New Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |