|
Baden Army
The Baden Army (german: Badische Armee) was the military organisation of the German state Baden until 1871. The origins of the army were a combination of units that the Baden margraviates of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden had set up in the Baroque era, and the standing army of the Swabian Circle, to which both territories had to contribute troops. The reunification of the two small states to form the Margraviate of Baden in 1771 and its subsequent enlargement and elevation by Napoleon to become the Grand Duchy of Baden in 1806 created both the opportunity and obligation to maintain a larger army, which Napoleon used in his campaigns against Austria, Prussia and Spain and, above all, Russia. After the end of Napoleon's rule, the Grand Duchy of Baden contributed a division to the German Federal Army. In 1848, Baden troops helped to suppress the Hecker uprising, but a year later a large number sided with the Baden revolutionaries. After the violent suppression of the revolution by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden (state)
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918. It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subsequently split into the states of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden, which were reunified in 1771. It then became the much-enlarged Grand Duchy of Baden after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire from 1803 to 1806 and was a sovereign country until it joined the German Empire in 1871. In 1918, it became part of the Weimar Republic as the Republic of Baden. Baden was bordered to the north by the Kingdom of Bavaria and the Grand Duchy of Hessen-Darmstadt; to the west, along most of its length, by the river Rhine, which separated Baden from the Bavarian Rhenish Palatinate and Alsace in modern France; to the south by Switzerland; and to the east by the Kingdom of Württemberg, the Principality of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and Bavaria. After Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupation Of Upper Baden
The occupation of Upper Baden refers to the occupation of the upper part of the Margraviate of Baden-Baden by troops of Margrave Ernest Frederick of Baden-Durlach under Wolf Dietrich von Gemmingen (1550–1601) on 21 November 1594, and its subsequent administration which lasted until 1622. Occupied territories The main towns – Ettlingen, Baden-Baden, Kuppenheim, Stollhofen and Rastatt – were immediately occupied. The Lordship of Gräfenstein as well as the further and anterior regions of the County of Sponheim were not occupied; the dominions of Rodemachern, Useldingen and Hesperingen formed the separate Margraviate of Baden-Rodemachern at that time and were ruled by Philip III, a brother of Eduard Fortunat. An attempt by Ernest Frederick to take over the Lordship of Gräfenstein was fended off. The Badenian portion of the County of Eberstein had been enfeoffed by Eduard Fortunat in the spring of 1595 to Philip III of Eberstein, for which he was to receive over 20,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like other artillery equipment, are usually organized in a group called a battery. Howitzers, together with long-barreled guns, mortars, and rocket artillery, are the four basic types of modern artillery. Mortars fire at angles of elevation greater than 45°, and are useful for mountain warfare because the projectile could go over obstacles. Cannons fire at low angles of elevation (<45°), and the projectile lands much faster at its target than it would in the case of a mortar. But the cannon is not useful if there is an obstacle like a hill/wall in front of its target. Etymology The English word ''howitzer'' comes from the Czech word , from , 'crowd', and is in turn a borrowing from the Middle High German word or (mode ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic League (1609)
The Catholic League ( la, Liga Catholica, german: Katholische Liga) was a coalition of Catholic Church, Catholic List of states in the Holy Roman Empire, states of the Holy Roman Empire formed 10 July 1609. While initially formed as a confederation to act politically to negotiate issues vis-à-vis the Protestant Union (formed 1608), modelled on the more intransigent ultra-Catholic French Catholic League (1576), it was subsequently concluded as a military alliance "for the defence of the Catholic religion and peace within the Empire". Notwithstanding the league's founding, as had the founding of the Protestant Union, it further exacerbated long standing tensions between the Protestant Protestant Reformation, reformers and the adherents of the Catholic Church which thereafter began to get worse with ever more frequent episodes of civil disobedience, Political repression, repression, and retaliation that would eventually ignite into the first phase of the Thirty Years' War roughly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Baden Occupation
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage ''The Upper Footage'' (also known as ''Upper'') is a 2013 found footage film written and directed by Justin Cole. First released on January 31, 2013 to a limited run of midnight theatrical screenings at Landmark’s Sunshine Cinema in New York Cit ...'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
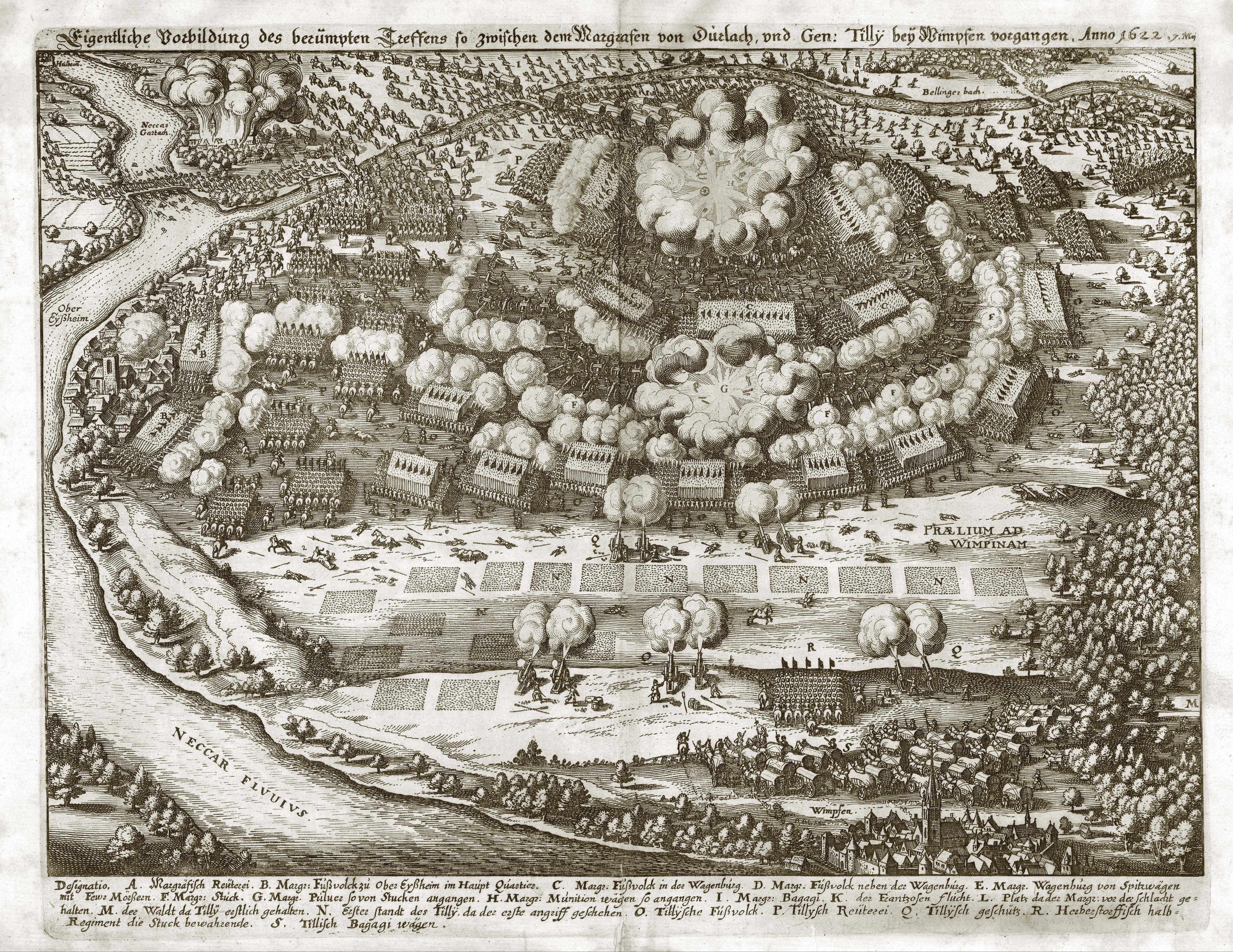
Battle Of Wimpfen
The Battle of Wimpfen was a battle in the Palatinate campaign period of the Thirty Years' War on 6 May 1622 near Wimpfen. The combined forces of the Catholic League and the Spanish Empire under Marshal Tilly and Gonzalo de Córdoba defeated the Protestant forces of Georg Friedrich, Margrave of Baden. Background Bohemian revolt In the ''Bohemian revolt'' phase of the Thirty Years' War, the Protestant Bohemian nobility refused to confirm Catholic Ferdinand II as their king and had offered Count Frederick V of the Palatinate the crown of Bohemia. Frederick was crowned in 1619 but lost the kingdom to Catholic League troops under General Tilly at the Battle of the White Mountain in 1620. Due to disunity among Protestant princes the Protestant Union was forced to declare its neutrality in the conflict in the Treaty of Ulm in 1620 and dissolved the following year. Palatinate campaign Count Georg Friedrich, Margrave of Baden had been one of the Protestant Union's gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann T'Serclaes Von Tilly
Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly ( nl, Johan t'Serclaes Graaf van Tilly; german: Johann t'Serclaes Graf von Tilly; french: Jean t'Serclaes de Tilly ; February 1559 – 30 April 1632) was a field marshal who commanded the Catholic League's forces in the Thirty Years' War. From 1620–31, he had an unmatched and demoralizing string of important victories against the Protestants, including White Mountain, Wimpfen, Höchst, Stadtlohn and the Conquest of the Palatinate. He destroyed a Danish army at Lutter and sacked the Protestant city of Magdeburg, which caused the death of some 20,000 of the city's inhabitants, both defenders and non-combatants, out of a total population of 25,000. Tilly was then crushed at Breitenfeld in 1631 by the Swedish army of King Gustavus Adolphus. A Swedish arquebus bullet wounded him severely at the Battle of Rain, and he died two weeks later in Ingolstadt. Along with Duke Albrecht von Wallenstein of Friedland and Mecklenburg, he was one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Von Mansfeld
Peter Ernst, Graf von Mansfeld (german: Peter Ernst Graf von Mansfeld; c. 158029 November 1626), or simply Ernst von Mansfeld, was a German military commander who, despite being a Catholic, fought for the Protestants during the early years of the Thirty Years' War. He was one of the leading mercenary generals of the war. Biography Mansfeld was an illegitimate son of Count Peter Ernst von Mansfeld (1517–1604), a member of the comital House of Mansfeld and royal Spanish stadtholder. He was raised in the Catholic faith at his father's palace in Luxembourg. He gained his earliest military experiences during the Long War in Hungary, where his elder half-brother Charles (1543–1595), also a soldier of renown, held a high command in the imperial army. While his brother succumbed to an epidemic within short time, young Ernst stayed at the theatre of war for several years. In the War of the Jülich Succession he served under Archduke Leopold V of Austria, until that prince's ingra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick V Of The Palatinate
Frederick V (german: link=no, Friedrich; 26 August 1596 – 29 November 1632) was the Elector Palatine of the Rhine in the Holy Roman Empire from 1610 to 1623, and reigned as King of Bohemia from 1619 to 1620. He was forced to abdicate both roles, and the brevity of his reign in Bohemia earned him the derisive sobriquet "the Winter King" (Czech: ''Zimní král''; German: ''Winterkönig''). Frederick was born at the hunting lodge (german: Jagdschloss) in Deinschwang, Palatinate (present-day Lauterhofen, Germany). He was the son of Frederick IV and of Louise Juliana of Orange-Nassau, the daughter of William the Silent and Charlotte de Bourbon-Montpensier. An intellectual, a mystic, and a Calvinist, he succeeded his father as Prince-Elector of the Rhenish Palatinate in 1610. He was responsible for the construction of the famous ''Hortus Palatinus'' gardens in Heidelberg. In 1618 the largely Protestant Czech nobility of Bohemia rebelled against their Catholic King Ferdinand, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500). The first early ..., lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegen
Siegen () is a city in Germany, in the south Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a States of Germany, state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more tha .... It is located in the district of Siegen-Wittgenstein in the Arnsberg (region), Arnsberg region. The university town (nearly 20,000 students in the 2018–2019 winter semester) is the district seat, and is ranked as a "higher centre" in the South Westphalian urban agglomeration. In 1975, municipal reforms and amalgamations lifted Siegen's population above the 100,000 mark. Geography Location The city of Siegen lies in the basin of the upper reaches of the river Sieg (river), Sieg. From there, lateral valleys branch off in many directions. The heights of the surrounding mountains, wherever they are not actually settled, are covered in Coppic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John VII, Count Of Nassau-Siegen
Count John VII ‘the Middle’ of Nassau-Siegen (7 June 1561 – 27 September 1623), german: Johann VII. ‘der Mittlere’ Graf von Nassau-Siegen, official titles: ''Graf zu Nassau, Katzenelnbogen, Vianden und Diez, Herr zu Beilstein'', was since 1606 Count of Nassau-Siegen, a part of the County of Nassau, and the progenitor of the House of Nassau-Siegen, a cadet branch of the Ottonian Line of the House of Nassau. He was one of the most important military theorists of his time, who introduced many innovations and inventions. His ''Kriegsbuch'' contained all the military knowledge of his time, but also many new ideas, which made an essential contribution to the reform of the Dutch States Army by his cousin Maurice. John served in the Dutch States Army, was colonel general of the Palatinate and commander-in-chief of the Swedish army. His reputation reached far beyond the borders of the Holy Roman Empire. Biography John was born at Menk (2004), p. 193. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)




