|
Baada
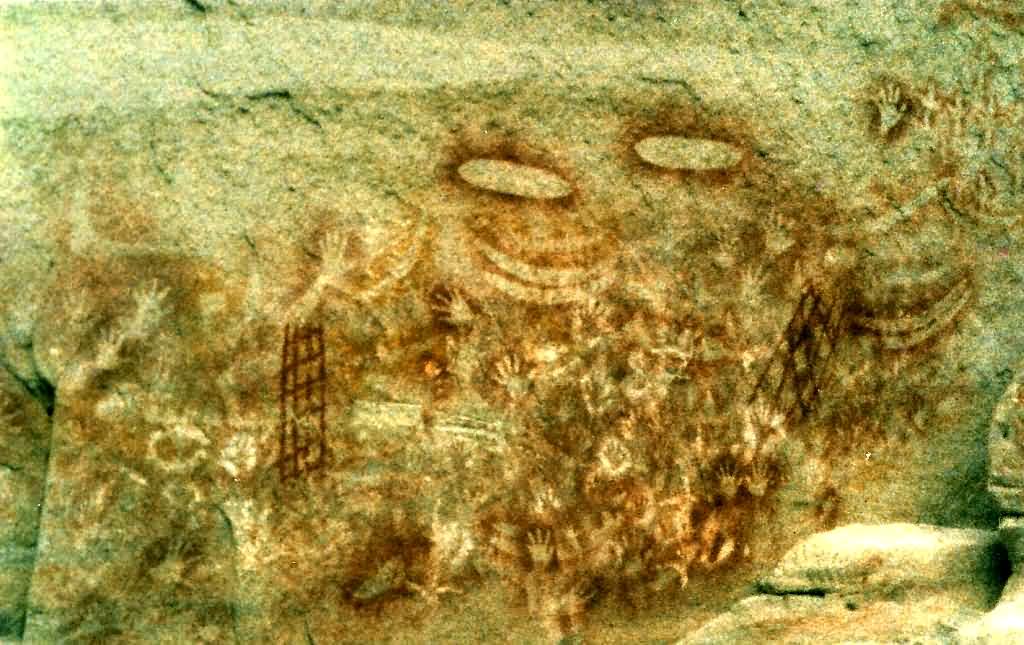
The Bardi people, also spelt Baada or Baardi and other variations, are an Aboriginal Australian people, living north of Broome and inhabiting parts of the Dampier Peninsula in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. They are ethnically close to the Jawi people, and several organisations refer to the Bardi Jawi grouping, such as the Bardi Jawi Niimidiman Aboriginal Corporation Registered Native Title Body (RNTBC) and the Bardi Jawi Rangers. Language The Bardi language is a non-Pama-Nyungan tongue, the most northerly variety of the Nyulnyulan language family. It is mutually intelligible with Jawi. It is the best known Nyulnyulan language, and a detailed grammar of the language exists, written by Claire Bowern. The Pallotine priest and linguist, Father Hermann Nekes, who worked with Ernst Alfred Worms in compiling dictionaries of Baardi and related languages, found his informants to be extremely linguistically astute. In an interview in 1938, a journalist writes of him an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
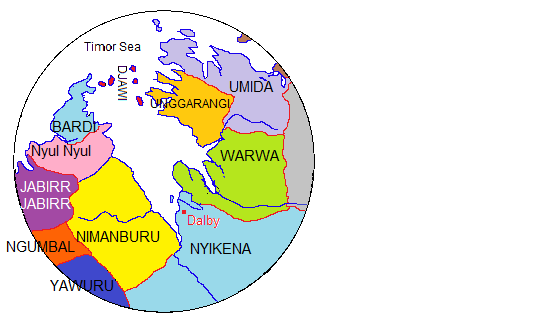
Traditional Lands Of Australian Aboriginal Tribes Around Derby
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years—the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is commonly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose, whether that be political or cultural, over short periods of time. Various academic disciplines also use the word in a variety of ways. The phrase "according to tradition", or "by tradition", usually means that whatever information follows is known only by oral t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Tindale
Norman Barnett Tindale AO (12 October 1900 – 19 November 1993) was an Australian anthropologist, archaeologist, entomologist and ethnologist. Life Tindale was born in Perth, Western Australia in 1900. His family moved to Tokyo and lived there from 1907 to 1915, where his father worked as an accountant at the Salvation Army mission in Japan. Norman attended the American School in Japan, where his closest friend was Gordon Bowles, a Quaker who, like him, later became an anthropologist. The family returned to Perth in August 1917, and soon after moved to Adelaide where Tindale took up a position as a library cadet at the Adelaide Public Library, together with another cadet, the future physicist, Mark Oliphant. In 1919 he began work as an entomologist at the South Australian Museum. From his early years, he had acquired the habit of taking notes on everything he observed, and cross-indexing them before going to sleep, a practice which he continued throughout his life, and which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilic Vein
The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. It originates on the medial (ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm, where its course is generally visible through the skin as it travels in the subcutaneous fat and fascia lying superficial to the muscles. The basilic vein terminates by uniting with the brachial veins to form the axillary vein. Anatomy Course As it ascends the medial side of the biceps in the arm proper (between the elbow and shoulder), the basilic vein normally perforates the brachial fascia (deep fascia) superior to the medial epicondyle, or even as high as mid-arm. Tributaries and anastomoses Near the region anterior to the cubital fossa (in the bend of the elbow joint), the basilic vein usually communicates with the cephalic vein (the other large superficial vein of the upper extremity) via the median cubital vein. The layout of superfic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djarindjin
Djarindjin is a medium-sized Aboriginal community located north of Broome in the Kimberley region of Western Australia, within the Shire of Broome. It is within the traditional lands of the Bardi and Jawi peoples. Location Djarindjin is located on the west coast of the northern Dampier Peninsula sub-region, north of Broome. Djarindjin is part of a single urban area that incorporates the Lombadina Aboriginal community and the Lombadina Mission. At the 2016 Census, this single urban area had a total population of 397, including 312 Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. The township is approximately due west of Cape Leveque Road The Cape Leveque Road is a regional Western Australian road that runs through pindan woodland for between Broome and Cape Leveque on the Dampier Peninsula. The southernmost section was narrow-sealed, the northernmost section (between south .... Djarindjin Aboriginal Corporation maintains a very large land holding surrounding the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjuringa
A Tjurunga, also spelt Churinga and Tjuringa, is an object considered to be of religious significance by Central Australian Aboriginal people of the Arrernte (Aranda, Arunta) groups. Tjurunga often had a wide and indeterminate native significance. They may be used variously in sacred ceremonies, as bullroarers, in sacred ground paintings, in ceremonial poles, in ceremonial headgear, in sacred chants and in sacred earth mounds. Meaning Generally speaking, tjurunga denote sacred stone or wooden objects possessed by private or group owners together with the legends, chants, and ceremonies associated with them. They were present among the Arrernte, the Luritja, the Kaitish, the Unmatjera, and the Illpirra. These items are most commonly oblong pieces of polished stone or wood. Some of these items have hair or string strung through them and were named "bull roarers" by Europeans. Upon each tjurunga is a totem of the group to which it belongs. Tjurunga are highly sacred, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus ''Eucalyptus'' have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard or stringy, leaves with oil glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut". Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are native to Australia, and every state and territory has representative species. About three-quarters of Australian forests are eucalypt forests. Wildfire is a feature of the Australian landscape and many eucalypt species are adapted to fire, and resprout after fire or have seeds which survive fire. A few species are native to islands north of Australia and a smaller number are only found outside the continent. Eucalypts have been grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullroarer
The bullroarer, ''rhombus'', or ''turndun'', is an ancient ritual musical instrument and a device historically used for communicating over great distances. It consists of a piece of wood attached to a string, which when swung in a large circle produces a roaring vibrato sound. It dates to the Paleolithic period, being found in Ukraine dating from 18,000 BC. Anthropologist Michael Boyd, a bullroarer expert, documents a number found in Europe, Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Australia. In ancient Greece it was a sacred instrument used in the Dionysian Mysteries and is still used in rituals worldwide. It was a prominent musical technology among the Australian Aboriginal people, used in ceremonies and to communicate with different people groups across the continent. Many different cultures believe that the sounds they make have the power to ward off evil influences. Design, use, and sound A bullroarer consists of a weighted airfoil (a rectangular thin slat of wood about lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paperbark
''Melaleuca'' () is a genus of nearly 300 species of plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae, commonly known as paperbarks, honey-myrtles or tea-trees (although the last name is also applied to species of ''Leptospermum''). They range in size from small shrubs that rarely grow to more than high, to trees up to . Their flowers generally occur in groups, forming a "head" or "spike" resembling a brush used for cleaning bottles, containing up to 80 individual flowers. Melaleucas are an important food source for nectarivorous insects, birds, and mammals. Many are popular garden plants, either for their attractive flowers or as dense screens and a few have economic value for producing fencing and oils such as "tea tree" oil. Most melaleucas are endemic to Australia, with a few also occurring in Malesia. Seven are endemic to New Caledonia, and one is found only on (Australia's) Lord Howe Island. Melaleucas are found in a wide variety of habitats. Many are adapted for life in swamps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Hero
A culture hero is a mythological hero specific to some group ( cultural, ethnic, religious, etc.) who changes the world through invention or discovery. Although many culture heroes help with the creation of the world, most culture heroes are important because of their effect on the world after creation. A typical culture hero might be credited as the discoverer of fire, agriculture, songs, tradition, law, or religion, and is usually the most important legendary figure of a people, sometimes as the founder of its ruling dynasty. Culture heroes in mythology History of a culture hero The term "culture hero" was originated by historian Kurt Breysig, who used the German word ''heilbringer,'' which translates to ''savior''. Over the years, "culture hero" has been interpreted in many ways. Older interpretations by Breysig, Paul Ehrenreich, and Wilhelm Schmidt thought that the journeys of culture heroes were ways in which humans could attempt to understand things in nature, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreamtime
The Dreaming, also referred to as Dreamtime, is a term devised by early anthropologists to refer to a religio-cultural worldview attributed to Australian Aboriginal mythology, Australian Aboriginal beliefs. It was originally used by Francis James Gillen, Francis Gillen, quickly adopted by his colleague Walter Baldwin Spencer, Baldwin Spencer and thereafter popularised by A. P. Elkin, who, however, later revised his views. The Dreaming is used to represent Aboriginal concepts of ''Everywhen'', during which the land was inhabited by ancestral figures, often of heroic proportions or with supernatural abilities. These figures were often distinct from gods, as they did not control the material world and were not worshipped but only reverence (emotion), revered. The concept of the Dreamtime has subsequently become widely adopted beyond its original Australian context and is now part of global popular culture. The term is based on a rendition of the Arandic languages, Arandic word '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syzygium Suborbiculare
''Syzygium suborbiculare'', the red bush apple, is a shrub or small understorey tree native to northern Australia and New Guinea. Description This tree or shrub typically grows to a height of . It blooms between June and November producing white flowers. The leaves are smooth, thick, leathery, broad oval 7.2–19 cm long. Flowers are white with numerous stamens. The edible fruit is flattened-globular, fleshy, prominently ribbed, 3–7 cm long, with a large seed.Brock, J., ''Top End Native Plants'', 1988. Habitat It is found in open forests and woodland and on the flood plains and rocky sandstone hills of the Kimberley region of Western Australia where it grows in sandy soils. Uses The fruit is eaten raw by Aboriginal people. The tree is also used medicinally, as firewood and as a nectar source for bees Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stingray
Stingrays are a group of sea rays, which are cartilaginous fish related to sharks. They are classified in the suborder Myliobatoidei of the order Myliobatiformes and consist of eight families: Hexatrygonidae (sixgill stingray), Plesiobatidae (deepwater stingray), Urolophidae (stingarees), Urotrygonidae (round rays), Dasyatidae (whiptail stingrays), Potamotrygonidae (river stingrays), Gymnuridae (butterfly rays) and Myliobatidae (eagle rays). There are about 220 known stingray species organized into 29 genera. Stingrays are common in coastal tropical and subtropical marine waters throughout the world. Some species, such as the thorntail stingray (''Dasyatis thetidis''), are found in warmer temperate oceans and others, such as the deepwater stingray (''Plesiobatis daviesi''), are found in the deep ocean. The river stingrays and a number of whiptail stingrays (such as the Niger stingray (''Fontitrygon garouaensis'')) are restricted to fresh water. Most myliobatoids are demersa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)