|
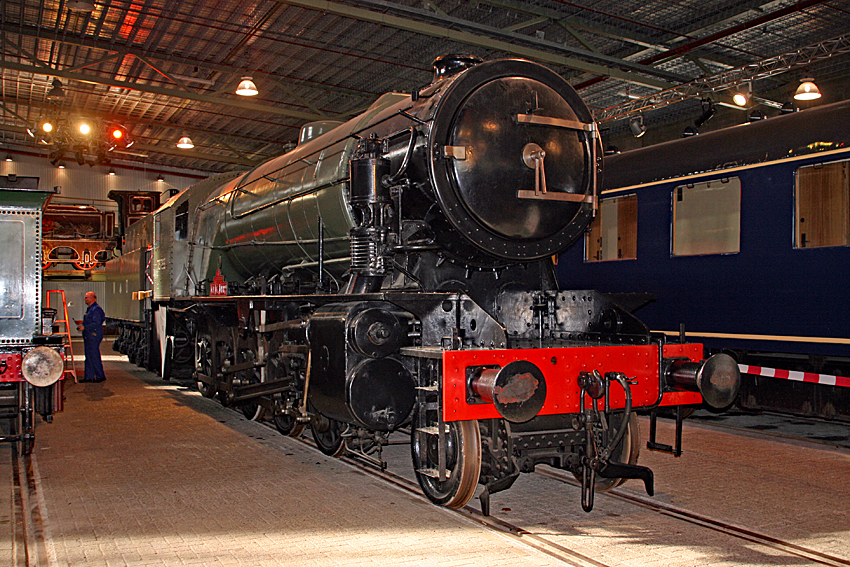
BR Standard Class 9F
The British Railways Standard Class 9F 2-10-0 is a class of steam locomotive designed for British Railways by Robert Riddles. The Class 9F was the last in a series of standardised locomotive classes designed for British Railways during the 1950s, and was intended for use on fast, heavy freight trains over long distances. It was one of the most powerful steam locomotive types ever built for British Railways, and successfully performed its intended duties. The class was given the nickname of 'Spaceships', due to its size and shape. At various times during the 1950s, the 9Fs worked passenger trains with great success, indicating the versatility of the design, sometimes considered to represent the ultimate in British steam development. Several experimental variants were constructed in an effort to reduce costs and maintenance, although these met with varying degrees of success. They were also capable of reaching speeds of up to 90 miles per hour (145 km/h). The total number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freight
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including transport by rail, van, truck, or intermodal container. The term cargo is also used in case of goods in the cold-chain, because the perishable inventory is always in transit towards a final end-use, even when it is held in cold storage or other similar climate-controlled facility. The term freight is commonly used to describe the movements of flows of goods being transported by any mode of transportation. Multi-modal container units, designed as reusable carriers to facilitate unit load handling of the goods contained, are also referred to as cargo, especially by shipping lines and logistics operators. Similarly, aircraft ULD boxes are also documented as cargo, with an associated packing list of the items contained within. When empty contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Railway Works
Brighton railway works (also known as Brighton locomotive works, or just the Brighton works) was one of the earliest railway-owned locomotive repair works, founded in 1840 by the London and Brighton Railway in Brighton, England, and thus pre-dating the more famous railway works at Crewe, Doncaster and Swindon. The works grew steadily between 1841 and 1900 but efficient operation was always hampered by the restricted site, and there were several plans to close it and move the facility elsewhere. Nevertheless, between 1852 and 1957 more than 1200 steam locomotives as well as prototype diesel electric and electric locomotives were constructed there, before the eventual closure of the facility in 1962. After use as a factory for constructing bubble cars, the facility was demolished and has since been redeveloped as part of the New England Quarter of Brighton. London and Brighton Railway The earliest locomotive servicing facility at Brighton was a small engine shed to the north-west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derby Works
The Derby Works comprised a number of British manufacturing facilities designing and building locomotives and rolling stock in Derby, England. The first of these was a group of three maintenance sheds opened around 1840 behind Derby station. This developed into a manufacturing facility called the Midland Railway Locomotive Works, known locally as "the loco" and in 1873 manufacturing was split into locomotive and rolling stock manufacture, with rolling stock work transferred to a new facility, Derby Carriage & Wagon Works. From its earliest days, it had carried out research and development in a number of areas, and in 1933 the London, Midland and Scottish Railway opened the LMS Scientific Research Laboratory. Around 1964, this became part of a new British Rail Research Division, based in the purpose-built Railway Technical Centre, which also housed the Department of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering (DM&EE) and later the headquarters of British Rail Engineering Limited. Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
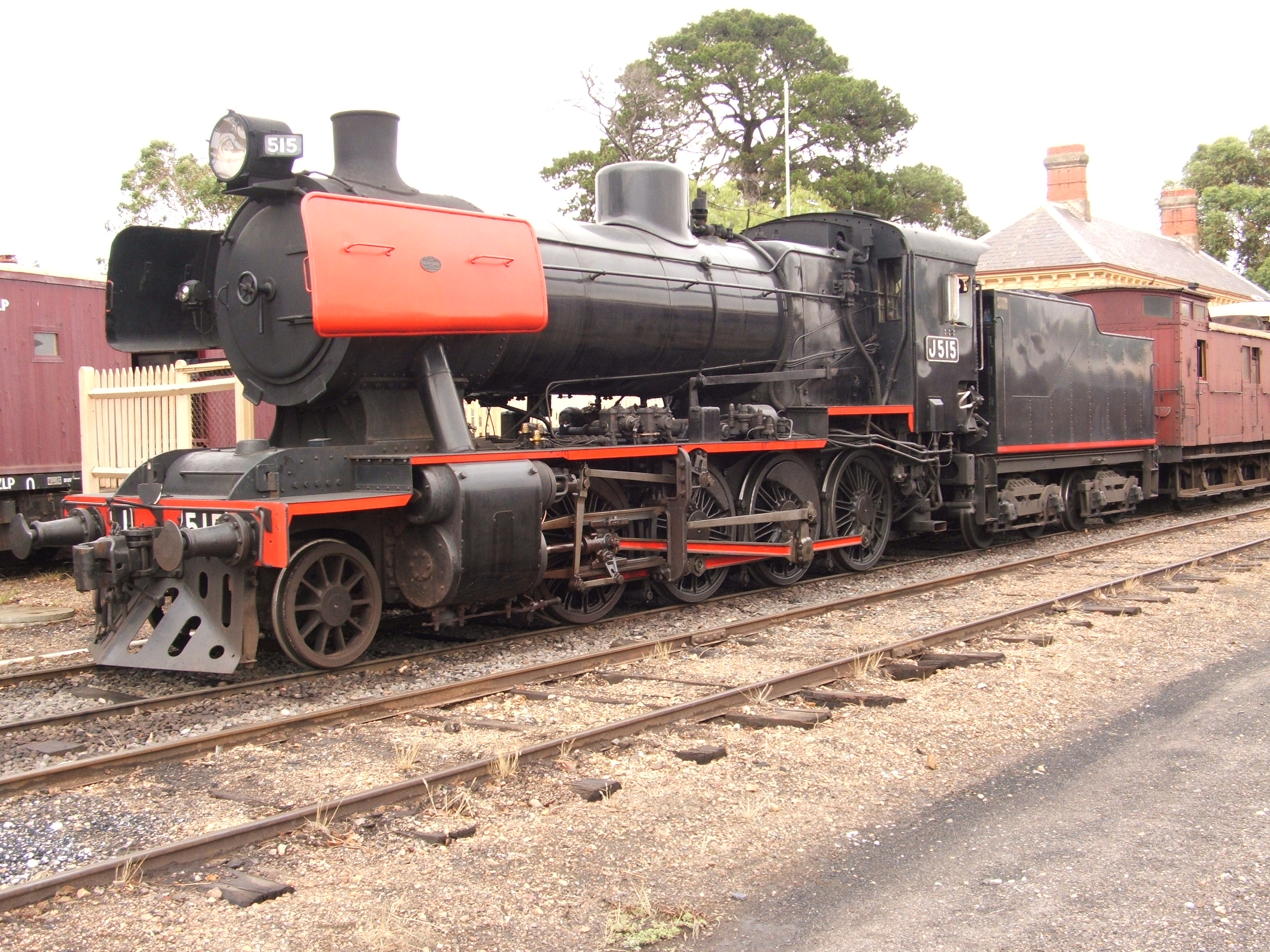
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. At times it was also referred to on some railroads in the United States of America as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
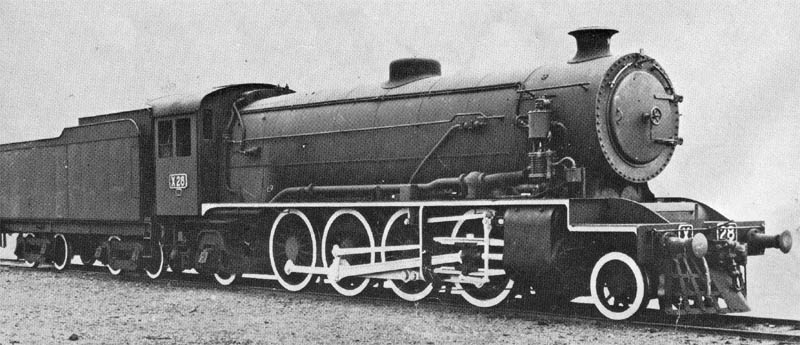
WD Austerity 2-10-0
The War Department (WD) "Austerity" 2-10-0 is a type of heavy freight steam locomotive that was introduced during the Second World War in 1943. Background The Austerity 2-10-0 was based on the Austerity 2-8-0, and was designed to have interchangeable parts by R.A. Riddles. It had the same power output as the 2-8-0 but a lighter axle load, making it suitable for secondary lines. Design It had a parallel boiler and round-topped firebox. While the 2-8-0 had a narrow firebox, the 2-10-0 had a wide firebox placed above the driving wheels. This arrangement was common in the United States (e.g. the USRA 0-8-0) but unusual in Britain, where wide fireboxes were usually used only where there was a trailing bogie, e.g. in 4-4-2 and 4-6-2 types. These were the first 2-10-0 locomotives to work in Great Britain, and the first major class of ten-coupled engines — they had been preceded by two 0-10-0 locomotives; the Great Eastern Railway's Decapod and the Midland Railway's Lickey B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WD Austerity 2-8-0
The War Department (WD) "Austerity" 2-8-0 is a type of heavy freight steam locomotive that was introduced in 1943 for war service. A total of 935 were built, making this one of the most-produced classes of British steam locomotive. They were nicknamed ''Ozzies'' by the railwaymen. Overview The Austerity 2-8-0 was based on the LMS Class 8F, which until that point had been the government's standard design. Various modifications were made to the 8F design by R.A. Riddles in order to prioritise low cost over design life. These included a boiler of simpler construction which was parallel rather than tapered and a round-topped firebox rather than a Belpaire firebox. The firebox was made of steel rather than the rarer and more expensive copper. The North British Locomotive Company (NBL) of Glasgow built 545 (split between their two works at Hyde Park and Queen's Park) and the Vulcan Foundry (VF) of Newton-le-Willows, Lancashire, built 390. North British also built a larger 2-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. In the United States and elsewhere, this wheel arrangement is commonly known as a Consolidation, after the Lehigh and Mahanoy Railroad’s ''Consolidation'', the name of the first 2-8-0.White, John H. Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, p. 65. The notation 2-8-0T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in side-tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. The Consolidation represented a notable advance in locomotive power. After 1875, it became "the most popular type of freight locomotive in the United States and was built in greater quantities than any other si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Stanier Class 8F
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Stanier Class 8F is a class of steam locomotives designed for hauling heavy freight. 852 were built between 1935 and 1946 (not all to LMS order), as a freight version of William Stanier's successful Black Five, and the class saw extensive service overseas during and after the Second World War. Background LMS freight traction suffered from the adoption of the Midland Railway's small engine policy which had left it with trains double-headed by underpowered 0-6-0s supplemented by disappointing Garratts and Fowler 7F 0-8-0s. The 8F design incorporated the two-cylinder arrangement of the Black Fives. They were initially classified 7F, but this was later changed to the more familiar 8F. On the outbreak of the World War II, the design was chosen to become the country's standard freight design, reprising the role the GCR Class 8K had in the First World War. The War Department had 208 8Fs built by Beyer Peacock and North British Loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Electrification System
A railway electrification system supplies electric power to railway trains and trams without an on-board prime mover or local fuel supply. Electric railways use either electric locomotives (hauling passengers or freight in separate cars), electric multiple units (passenger cars with their own motors) or both. Electricity is typically generated in large and relatively efficient generating stations, transmitted to the railway network and distributed to the trains. Some electric railways have their own dedicated generating stations and transmission lines, but most purchase power from an electric utility. The railway usually provides its own distribution lines, switches, and transformers. Power is supplied to moving trains with a (nearly) continuous conductor running along the track that usually takes one of two forms: an overhead line, suspended from poles or towers along the track or from structure or tunnel ceilings, or a third rail mounted at track level and contacted by a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas turbines, are classed as diesel-electric or gas turbine-electric and not as electric locomotives, because the electric generator/motor combination serves only as a power transmission system. Electric locomotives benefit from the high efficiency of electric motors, often above 90% (not including the inefficiency of generating the electricity). Additional efficiency can be gained from regenerative braking, which allows kinetic energy to be recovered during braking to put power back on the line. Newer electric locomotives use AC motor-inverter drive systems that provide for regenerative braking. Electric locomotives are quiet compared to diesel locomotives since there is no engine and exhaust noise and less mechanical noise. The lack of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |