|
BRST Algorithm
Boender-Rinnooy-Stougie-Timmer algorithm (BRST) is an optimization algorithm suitable for finding global optimum of black box functions. In their paper Boender ''et al.'' describe their method as a stochastic method involving a combination of sampling, clustering and local search, terminating with a range of confidence intervals on the value of the global minimum. The algorithm of Boender ''et al.'' has been modified by Timmer. Timmer considered several clustering methods. Based on experiments a method named "multi level single linkage" was deemed most accurate. Csendes' algorithms {{cite journal , last = Csendes , first = T. , title = Nonlinear parameter estimation by global optimization—Efficiency and reliability , journal = Acta Cybernetica , volume = 8 , issue = 4 , year = 1988 , pages = 361–370 , url = http://www.inf.u-szeged.hu/actacybernetica/edb/vol08n4/Csendes_1988_ActaCybernetica.xml are implementations of the algorithm of oender ''et al.''ref name="boend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Optimum
In mathematical analysis, the maxima and minima (the respective plurals of maximum and minimum) of a function, known collectively as extrema (the plural of extremum), are the largest and smallest value of the function, either within a given range (the ''local'' or ''relative'' extrema), or on the entire domain (the ''global'' or ''absolute'' extrema). Pierre de Fermat was one of the first mathematicians to propose a general technique, adequality, for finding the maxima and minima of functions. As defined in set theory, the maximum and minimum of a set are the greatest and least elements in the set, respectively. Unbounded infinite sets, such as the set of real numbers, have no minimum or maximum. Definition A real-valued function ''f'' defined on a domain ''X'' has a global (or absolute) maximum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. Similarly, the function has a global (or absolute) minimum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. The value of the function a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The term can be used to refer to many inner workings, such as those of a transistor, an engine, an algorithm, the human brain, or an institution or government. To analyse an open system with a typical "black box approach", only the behavior of the stimulus/response will be accounted for, to infer the (unknown) ''box''. The usual representation of this ''black box system'' is a data flow diagram centered in the box. The opposite of a black box is a system where the inner components or logic are available for inspection, which is most commonly referred to as a white box (sometimes also known as a "clear box" or a "glass box"). History The modern meaning of the term "black box" seems to have entered the English language around 1945. In electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain Software
Public-domain software is software that has been placed in the public domain, in other words, software for which there is absolutely no ownership such as copyright, trademark, or patent. Software in the public domain can be modified, distributed, or sold even without any attribution by anyone; this is unlike the common case of software under exclusive copyright, where licenses grant limited usage rights. Under the Berne Convention, which most countries have signed, an author automatically obtains the exclusive copyright to anything they have written, and local law may similarly grant copyright, patent, or trademark rights by default. The Convention also covers programs, and they are therefore automatically subject to copyright. If a program is to be placed in the public domain, the author must explicitly disclaim the copyright and other rights on it in some way, e.g. by a waiver statement. In some jurisdictions, some rights (in particular moral rights) cannot be disclaimed: fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clustering Method
Clustering can refer to the following: In computing: * Computer cluster, the technique of linking many computers together to act like a single computer *Data cluster, an allocation of contiguous storage in databases and file systems * Cluster analysis, the statistical task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group are placed closer together (such as the k-means clustering) *In hash tables, the mapping of keys to nearby slots In economics: *Business cluster, a geographic concentration of interconnected businesses, suppliers, and associated institutions in a particular field In graph theory: *The formation of clusters of linked nodes in a network, measured by the clustering coefficient See also *Cluster (other) may refer to: Science and technology Astronomy * Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft * Asteroid cluster, a small asteroid family * Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
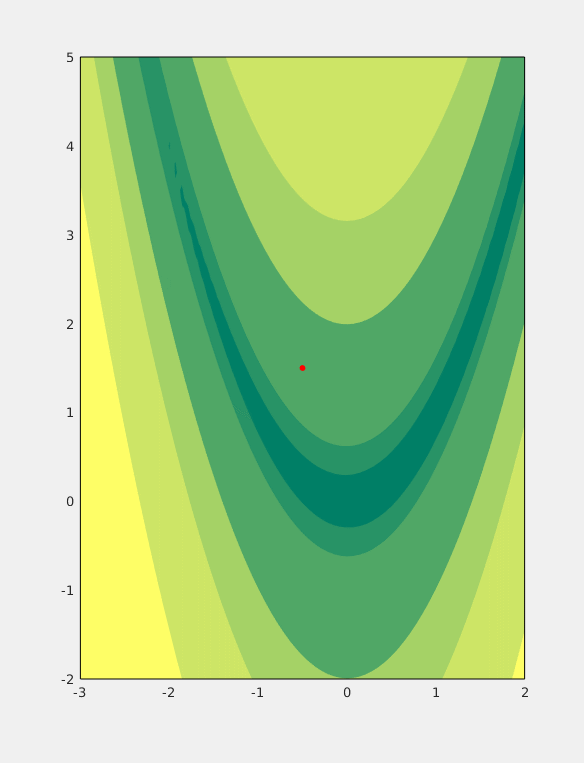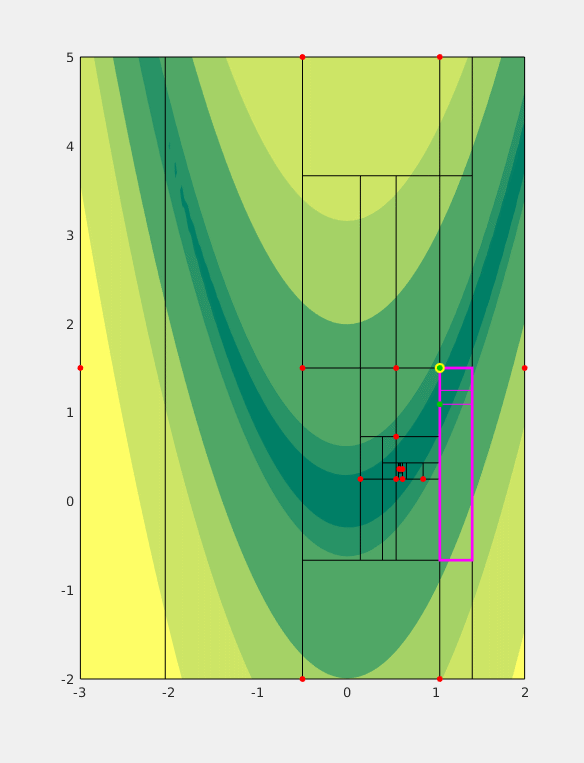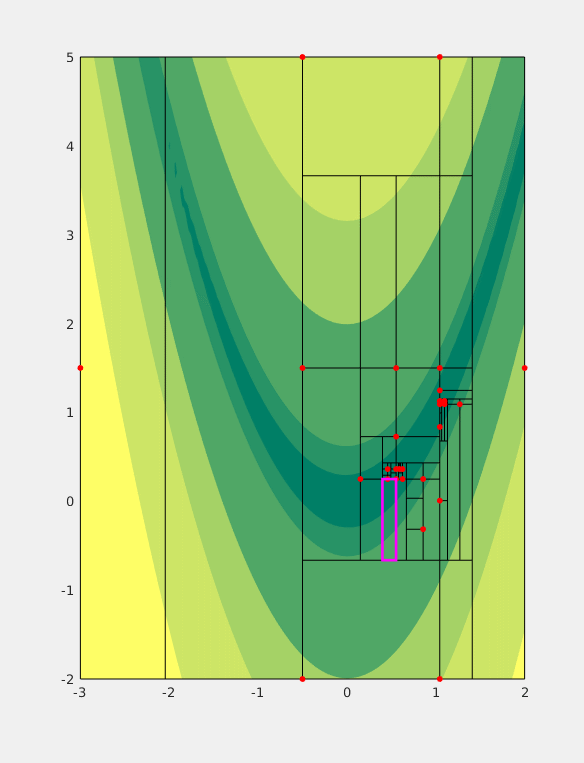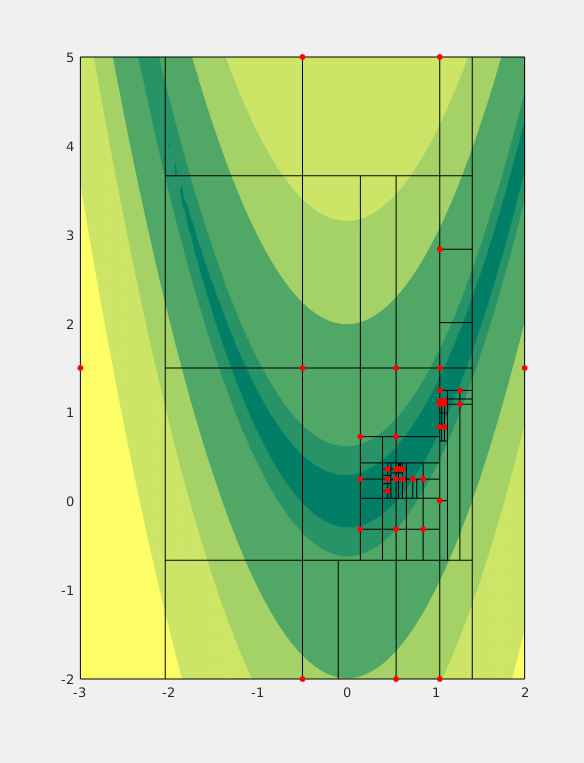
MCS Algorithm
For mathematical optimization, Multilevel Coordinate Search (MCS) is an efficient algorithm for bound constrained global optimization using function values only. To do so, the n-dimensional search space is represented by a set of non-intersecting hypercubes (boxes). The boxes are then iteratively split along an axis plane according to the value of the function at a representative point of the box (and its neighbours) and the box's size. These two splitting criteria combine to form a global search by splitting large boxes and a local search by splitting areas for which the function value is good. Additionally, a local search combining a (multi-dimensional) quadratic interpolant of the function and line searches can be used to augment performance of the algorithm (''MCS with local search''); in this case the ''plain'' MCS is used to provide the starting (initial) points. The information provided by local searches (local minima of the objective function) is then fed back to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |