|
BMO SmartFolio
BMO SmartFolio is a digital investment management service offered by Canada’s Bank of Montreal. Broadly referred to as a robo-advisor, the service allows investors to answer a series of questions online about their investment goals, time horizon and risk tolerance, then are recommended a model portfolio made up of index-tracking exchange-traded funds based on the investor’s profile, managed by financial professionals with BMO Global Asset Management and BMO Nesbitt Burns. Launched to the public on January 18, 2016 by the bank's full-service investment firm, BMO Nesbitt Burns, it was the first digital portfolio management service offered by a big five Canadian bank. BMO SmartFolio was developed in-house to appeal to the growing number of investors looking for investment management alternatives to traditional brokerages. As of December 18, 2017, the minimum amount required to open a BMO SmartFolio account is $1,000, reduced from the $5,000 minimum amount set when the service wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Management
Investment management is the professional asset management of various securities, including shareholdings, bonds, and other assets, such as real estate, to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of investors. Investors may be institutions, such as insurance companies, pension funds, corporations, charities, educational establishments, or private investors, either directly via investment contracts or, more commonly, via collective investment schemes like mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, or REITs. The term asset management is often used to refer to the management of investment funds, while the more generic term fund management may refer to all forms of institutional investment, as well as investment management for private investors. Investment managers who specialize in ''advisory'' or ''discretionary'' management on behalf of (normally wealthy) private investors may often refer to their services as money management or portfolio management within the context of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brokerage Firm
A broker is a person or firm who arranges transactions between a buyer and a seller for a commission when the deal is executed. A broker who also acts as a seller or as a buyer becomes a principal party to the deal. Neither role should be confused with that of an agent—one who acts on behalf of a principal party in a deal. Definition A broker is an independent party whose services are used extensively in some industries. A broker's prime responsibility is to bring sellers and buyers together and thus a broker is the third-person facilitator between a buyer and a seller. An example would be a real estate or stock broker who facilitates the sale of a property. Brokers can furnish market research and market data. Brokers may represent either the seller or the buyer but generally not both at the same time. Brokers are expected to have the tools and resources to reach the largest possible base of buyers and sellers. They then screen these potential buyers or sellers for the perfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
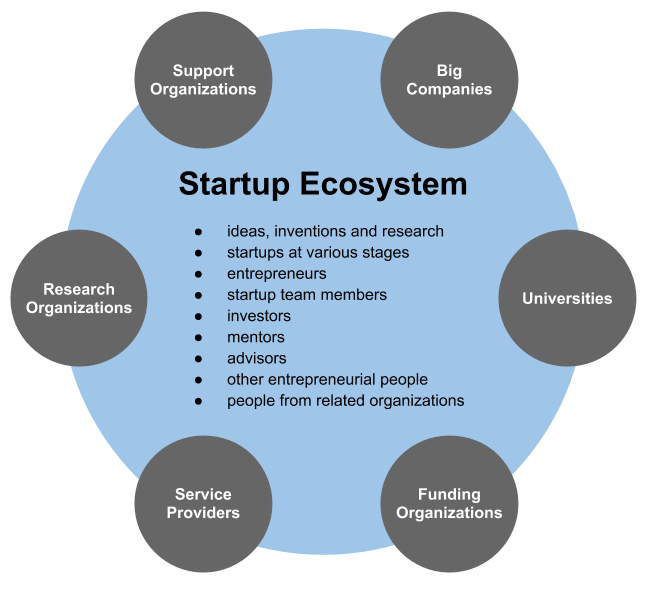
Startup Company
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses that never intend to become registered, startups refer to new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo founder. At the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to be successful and influential.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017 Actions Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will begin market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building a minimum viable product (MVP), i.e. a prototype, to develop and validate their business models. The startup process can take a long period of time (by so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Technology
Fintech, a portmanteau of "financial technology", refers to firms using new technology to compete with traditional financial methods in the delivery of financial services. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, cloud computing, and big data are regarded as the "ABCD" (four key areas) of fintech. The use of smartphones for mobile banking, investing, borrowing services, and cryptocurrency are examples of technologies designed to make financial services more accessible to the general public. Fintech companies consist of both startups and established financial institutions and technology companies trying to replace or enhance the usage of financial services provided by existing financial companies. A subset of fintech companies that focus on the insurance industry are collectively known as insurtech or insuretech companies. Key areas Academics Artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, cloud computing, and big data are considered the four key areas of FinTech. Artificial intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Crisis Of 2007-2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitability assessmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Account
A joint account is a bank account that has been opened by two or more individuals or entities. Joint accounts are commonly opened by close relatives (such as by a married couple) or by business partners in an unincorporated business, but it can be used in other circumstances. Ordinarily, anyone can deposit funds into a joint account, but when opening an account the joint account holders may indicate to the financial institution whether a single account holder may make withdrawals or whether the consent of other account holders is required. A joint account is not the same as adding an authorized signatory or additional cardholder to an account, that is, a person who is authorized by the account holder to effect transactions on the account. Under this arrangement the primary account holder remains fully and solely liable for all transactions on the account. Accounts by corporate entities are not, in themselves, joint accounts. Opening an account When opening a joint bank accou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Education Savings Plan
A registered education savings plan (RESP) in Canada is an investment vehicle available to caregivers to save for their children's post-secondary education. The principal advantages of RESPs are the access they provide to the Canada Education Savings Grant (CESG) and as a method of generating tax-deferred income. Tax benefits An RESP is a tax shelter designed to benefit post-secondary students. With an RESP, contributions (comprising the investment's principal) are, or have already been, taxed at the contributor's tax rate, while the investment growth (and CESG) is taxed on withdrawal at the recipient's tax rate. An RESP recipient is typically a post-secondary student; these individuals generally pay little or no federal income tax, owing to tuition and education tax credits. Thus, with the tax-free principal contribution available for withdrawal, CESG, and nearly-tax-free interest, the student will have a good source of income to fund their post-secondary education. If the benefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax-Free Savings Account
A tax-free savings account (TFSA, french: links=no, Compte d'épargne libre d'impôt, CELI) is an account available in Canada that provides tax benefits for saving. Investment income, including capital gains and dividends, earned in a TFSA is not taxed in most cases, even when withdrawn. Contributions to a TFSA are not deductible for income tax purposes, unlike contributions to a registered retirement savings plan (RRSP). Despite the name, a TFSA does not have to be a cash savings account. Like an RRSP, a TFSA may contain cash and/or other investments such as mutual funds, segregated funds, certain stocks, bonds, or guaranteed investment certificates (GICs). The cash on hand in a TFSA collects interest just like a regular savings account, except that the interest is tax free. History The first tax-free savings account was introduced by Jim Flaherty, then Canadian federal Minister of Finance, in the 2008 federal budget. It came into effect on January 1, 2009. This measure wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Five Banks
Big Five is the name colloquially given to the five largest banks that dominate the banking industry of Canada: Bank of Montreal (BMO), Bank of Nova Scotia (Scotiabank), Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (CIBC), Royal Bank of Canada (RBC), and TD Bank Group (Toronto Dominion-Bank). All of the five Canadian banks maintain their respective headquarters in Toronto's Financial District, primarily along Bay Street. All five banks are classified as Schedule I banks that are domestic banks operating in Canada under government charter. The banks' shares are widely held, with any entity allowed to hold a maximum of twenty percent. According to a ranking produced by Standard & Poor's, in 2017, the Big Five banks of Canada are among the world's 100 largest banks, with TD Bank, RBC, Scotiabank, BMO, and CIBC at 26th, 28th, 45th, 52nd and 63rd place, respectively. Additionally, RBC and TD Bank are on the Financial Stability Board's list of systemically important banks as of 2020. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of Montreal
The Bank of Montreal (BMO; french: Banque de Montréal, link=no) is a Canadian multinational investment bank and financial services company. The bank was founded in Montreal, Quebec, in 1817 as Montreal Bank; while its head office remains in Montreal, the operational headquarters and executive offices have been located in Toronto, Ontario since 1977. One of the Big Five banks in Canada, it is the fourth-largest bank in Canada by market capitalization and assets, and one of the eight largest banks in North America and the top 50 in the world. It is commonly known by its ticker symbol BMO (pronounced ), on both the Toronto Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange. In October 2021, it had CA$634 billion in assets under administration (AUA). The Bank of Montreal swift code is BOFMCAM2 and the institution number is 001. On 23 June 1817, John Richardson and eight merchants signed the Articles of Association to establish the Montreal Bank in a rented house in Montreal, Quebec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |